Session 3-Demand and Supply.ppt
- 1. Managerial Economics Session 3 Demand and Supply Lectured by Prof. Dr. Ferdinand D. Saragih, MA.
- 2. 2 Overview III. Market Equilibrium IV. Price Restrictions V. Comparative Statics II. Market Supply Curve – The Supply Function – Supply Shifters – Producer Surplus I. Market Demand Curve – The Demand Function – Determinants of Demand – Consumer Surplus
- 3. 3 Market Demand Curve Shows the amount of a good that will be purchased at alternative prices. Law of Demand – The demand curve is downward sloping. Quantity D Price
- 4. 4 Determinants of Demand Income Prices of substitutes Prices of complements Advertising Population Consumer expectations
- 5. 5 The Demand Function An equation representing the demand curve Qx d = f(Px , PY , M, H,) – Qx d = quantity demand of good X. – Px = price of good X. – PY = price of a substitute good Y. – M = income. – H = any other variable affecting demand
- 6. 6 Change in Quantity Demanded Price Quantity D0 4 7 10 6 A A to B: Increase in quantity demanded B
- 7. 7 Price Quantity D0 D1 6 7 D0 to D1: Increase in Demand Change in Demand 13
- 8. 8 Consumer Surplus: The value consumers get from a good but do not have to pay for.
- 9. 9 I got a great deal! That company offers a lot of bang for the buck! Gateway 2000 provides good value. Total value greatly exceeds total amount paid. Consumer surplus is large.
- 10. 10 I got a lousy deal! That car dealer drives a hard bargain! I almost decided not to buy it! They tried to squeeze the very last cent from me! Total amount paid is close to total value. Consumer surplus is low.
- 11. 11 Price Quantity D 10 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 Consumer Surplus: The value received but not paid for Consumer Surplus: The Discrete Case
- 12. 12 Consumer Surplus: The Continuous Case Price $ Quantity D 10 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 Value of 4 units Consumer Surplus Total Cost of 4 units
- 13. 13 Market Supply Curve The supply curve shows the amount of a good that will be produced at alternative prices. Law of Supply – The supply curve is upward sloping Price Quantity S0
- 14. 14 Supply Shifters Input prices Technology or government regulations Number of firms Substitutes in production Taxes Producer expectations
- 15. 15 The Supply Function An equation representing the supply curve: Qx S = f(Px , PR ,W, H,) – Qx S = quantity supplied of good X. – Px = price of good X. – PR = price of a related good – W = price of inputs (e.g., wages) – H = other variable affecting supply
- 16. 16 Change in Quantity Supplied Price Quantity S0 20 10 B A 5 10 A to B: Increase in quantity supplied
- 17. 17 Price Quantity S0 S1 8 5 7 S0 to S1: Increase in supply Change in Supply 6
- 18. 18 Producer Surplus The amount producers receive in excess of the amount necessary to induce them to produce the good. Price Quantity S0 Producer Surplus Q* P*
- 19. 19 Market Equilibrium Balancing supply and demand – Qx S = Qx d Steady-state
- 20. 20 Price Quantity S D 5 6 12 Shortage 12 - 6 = 6 6 If price is too low… 7
- 21. 21 Price Quantity S D 9 14 Surplus 14 - 6 = 8 6 8 8 If price is too high… 7
- 22. 22 Price Restrictions Price Ceilings – The maximum legal price that can be charged – Examples: Gasoline prices in the 1970s Housing in New York City Proposed restrictions on ATM fees Price Floors – The minimum legal price that can be charged. – Examples: Minimum wage Agricultural price supports
- 23. 23 Price Quantity S D P* Q* Ceiling Price Q s PF Impact of a Price Ceiling Shortage Q d
- 24. 24 Full Economic Price The dollar amount paid to a firm under a price ceiling, plus the nonpecuniary price. PF = Pc + (PF - PC) PF = full economic price PC = price ceiling PF - PC = nonpecuniary price
- 25. 25 An Example from the 1970s Ceiling price of gasoline - $1 3 hours in line to buy 15 gallons of gasoline – Opportunity cost: $5/hr – Total value of time spent in line: 3 $5 = $15 – Non-pecuniary price per gallon: $15/15=$1 Full economic price of a gallon of gasoline: $1+$1=2
- 26. 26 Impact of a Price Floor Price Quantity S D P* Q* QS Qd Surplus PF
- 27. 27 Comparative Static Analysis How do the equilibrium price and quantity change when a determinant of supply and/or demand change?
- 28. 28 Applications of Demand and Supply Analysis Event: The WSJ reports that the prices of PC components are expected to fall by 5-8 percent over the next six months. Scenario 1: You manage a small firm that manufactures PCs. Scenario 2: You manage a small software company.
- 29. 29 Use Comparative Static Analysis to see the Big Picture! Comparative static analysis shows how the equilibrium price and quantity will change when a determinant of supply or demand changes.
- 30. 30 Scenario 1: Implications for a Small PC Maker Step 1: Look for the “Big Picture” Step 2: Organize an action plan (worry about details)
- 31. 31 Price of PCs Quantity of PC’s S D S* P0 P* Q0 Q* Big Picture: Impact of decline in component prices on PC market
- 32. 32 So, the Big Picture is: – PC prices are likely to fall, and more computers will be sold Use this to organize an action plan – contracts/suppliers? – inventories? – human resources? – marketing? – do I need quantitative estimates? – etc.
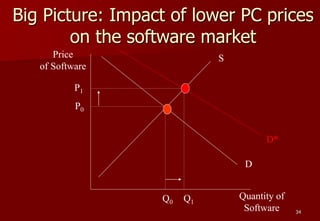
- 33. 33 Scenario 2: Software Maker More complicated chain of reasoning to arrive at the “Big Picture” Step 1: Use analysis like that in Scenario 1 to deduce that lower component prices will lead to – a lower equilibrium price for computers – a greater number of computers sold. Step 2: How will these changes affect the “Big Picture” in the software market?
- 34. 34 Price of Software Quantity of Software S D Q0 D* P1 Q1 Big Picture: Impact of lower PC prices on the software market P0
- 35. 35 The “big picture” for the software maker: – Software prices are likely to rise, and more software will be sold Use this to organize an action plan
- 36. 36 Summary Use supply and demand analysis to – clarify the “big picture” (the general impact of a current event on equilibrium prices and quantities) – organize an action plan (needed changes in production, inventories, raw materials, human resources, marketing plans, etc.)