sheet resistivity
- 1. RESISTIVITY Roll. No. 17MSE006 , 17MSE011 , 17MSE012 , 17MSE017 MTech Student, SSE PDPU
- 2. OUTLINE • To understand the concept of resistivity • Resistivity measurement technique • Sheet resistance • Measurement Errors and precautions • Wafer Mapping • Contactless resistivity measurement technique • Strength and weaknesses of Various measurement techniques • Conclusion
- 3. TO UNDERSTAND THE CONCEPT OF RESISTIVITY • Measure of the resisting power of a specified material to the flow of an electric current. • Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter ρ (rho). • The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-meter (Ω⋅m) • Resistivity ρ=R(A/L) Material Resistivity, ρ (Ω·m) Superconductors 0 Metals 10−8 Semiconductors Variable Electrolytes Variable Insulators 1016 Super insulators ∞
- 4. Resistivity Measurement Technique Two point probe method Four point probe method
- 5. 1.TWO POINT PROBE METHOD Basically a two point contact Each contact serves as a current and as a voltage probe Appear to be easier but the interpretation of the measured data is difficult due to various resistance inclusion Rw V Rw Rc Rc RDUT DUT RT = V/I= 2RW + 2RC + RDUT
- 6. 2.FOUR POINT PROBE METHOD Originally proposed by wenner to measure the resistivity of the earth Later, Adopted for semiconductor wafer as well and widely used in wafer manufacturing industries V Rw Rc Rc RDUT DUT
- 7. WHY FOUR POINT PROBE? • To attain the standardization of Probe technique with utmost accuracy • Current path is same as that of the two probe method • But, Voltage is measured with two additional contact • Input impedance of voltmeter around 1012 ohms or higher so current not large amount pass in voltmeter. • the voltage drops across RW and RC are negligibly small and can be neglected and the measured voltage is essentially the voltage drop across the DUT
- 8. • The four point probe method, as indicated in Figure, has four equally spaced in-line probes with probe tip diameters small compared to the probe spacing, S. Depletion region act as an insulator Keep current flow in the emitter V N P t S S S Current source and measurement
- 9. • Current is most commonly passed between the outer two probes, and the voltage difference is measured between the two inner probes. Resistivity in a four-point probe measurement is given by 𝜌 = 2𝜋𝑠𝐹 𝑉 𝐼 • Where s is the distance between two probe F represents the correction factor • F = F1 F2 F3 • F1 corrects for sample thickness, • F2 for lateral sample dimensions, • F3 for placement of the probes relative to the sample edges.
- 10. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE: Source.: F.M.Smits, "Measurement of Sheet Resistivities with the Four-Point Probe", The Bell System Technical Journal 37, 711-718 Reference: RESISTIVITY OF A SEMICONDUCTOR BY THE FOUR-PROBE METHOD (Dr Jeethendra Kumar P K) Let a Sample n-type Germanium Semiconductor Dimensions : (L) 2mm x (d) 5.4mm x (t) 0.5mm Probe Spacing (S) : 2mm Resistivity for equally spaced probes is given by 𝜌 = 2𝜋𝑠𝐹 𝑉 𝐼 Calculating ratios “t/S” and “d/S” t/S = 0.25 ; d/S = 2.7 𝜌 = 4.53𝑡 × 𝐹 × 𝑉 𝐼 It is observed by experimentation that the sample with thickness-gap ratio t/S≤0.5, the geometric factor 2πS is given by 2πS = 𝜋 𝑙𝑛2 × 𝑡 =4.53t Hence for a finite width and non-negligible thickness is given by: 𝐹 = 𝑓1 𝑓2 Where 𝑓1 & 𝑓2 are determined from the graph 𝑓1 = 1 ; 𝑓2 = 0.59 𝜌 = 1.33 × 10−3 × 𝑉 𝐼
- 11. The sample is placed under the four probes such that the probes are parallel to the longer side (length) of the sample. Reference: RESISTIVITY OF A SEMICONDUCTOR BY THE FOUR-PROBE METHOD (Dr Jeethendra Kumar P K) The current is set to 0.1mA by adjusting set-current knob. The voltage developed across the inner probes is noted Current (mA) Sample-1 mV V/I 0.1 5.4 54.0 0.2 10.5 52.5 0.3 16.0 53.3 0.4 21.1 52.7 0.5 26.5 53.0 0.6 31.7 52.8 0.7 37.0 52.8 0.8 42.3 53.3 0.9 48.0 53.0 1.0 53.0 53.0 1.1 58.3 53.0 1.2 63.5 52.9 1.3 69.0 53.0 1.4 74.4 53.1 1.5 79.8 53.2 Average V/I 53.0 𝜌 = 1.33 × 10−3 × 53 = 0.0708 𝛺 − 𝑚 = 7.08 𝛺 − 𝑐𝑚
- 12. SHEET RESISTANCE • Measure of the resistivity averaged over the surface • Sheet resistance is a measure of resistance of thin films that are nominally uniform in thickness. • The utility of sheet resistance as opposed to resistance or resistivity is that it is directly measured using a four-point probe measurement or indirectly by using a non- contact eddy current based testing device. • Sheet resistance can be used to compare the electrical properties of devices that are significantly different in size. 𝑅 = 𝑅 𝑠ℎ 𝐿 𝑊 ohms 𝑅 = 𝜌 𝐿 𝐴 = 𝜌 𝐿 𝑊𝑡 = 𝜌 𝑡 𝐿 𝑊 Ohms
- 13. CONTD. • Since 𝐿 𝑊 has no units, 𝜌 𝑡 should have units of ohms. But 𝜌 𝑡 is not the sample resistance. • To distinguish between R and 𝜌 𝑡 , Often in practice, surface resistivity is given in units of Ω 𝑆𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 • Sheet resistance is applicable as long as the measurement is related to a square.
- 14. Minority Majority (carrier injection) Probe spacing CurrentSample Size High Resistivity Materials FACTORS AFFECTING THE MEASUREMENT ACCURACY Measurement Errors and Precautions
- 15. SAMPLE SIZE • correction factor F depends on the thickness of the material • If the wafer or the layer to be measured is appreciably thinner than the probe spacing, the calculated resistivity varies directly with thickness. • It is therefore very important to determine the thickness accurately for resistivity determination.
- 16. MINORITY - MAJORITY CARRIER INJECTION • Metal-semiconductor contacts do inject minority carriers, but their injection efficiency is low. • However, under high current conditions it may not be negligible. • Minority carrier injection causes conductivity modulation because increased minority carrier density leads to increased majority carrier density (to maintain charge neutrality) and subsequent enhanced conductivity. • To reduce minority carrier injection, the surface should have a high recombination rate for minority carriers. This is best achieved by using lapped surfaces.
- 17. PROBE SPACING • A mechanical four-point probe exhibits small random probe spacing variations. • Such variations give erroneous values of resistivity or sheet resistance, especially when evaluating uniformly doped wafers. • In such cases it is very important to know whether any non-uniformities are due to the wafer, due to process variations, or due to measurement errors.
- 18. CURRENT • The current can affect the measured resistivity in two ways: 1. by an apparent resistivity increase produced by wafer heating 2. by an apparent resistivity decrease due to minority and/or majority carrier injection. 10−2 10−1 100 101 102 103 10−2 10−1 100 101 102 103 104 Current (mA) Resistivity(Ω-cm) SheetResistance(Ω- Square)
- 19. HIGH RESISTIVITY MATERIALS • Materials of very high resistivity are more difficult to measure by four-point probe method. • Moderately doped wafers can become highly resistive at low temperatures and are similarly difficult to measure.
- 20. WAFER MAPPING • originated in the 1970s • originally developed to characterize ion implantation uniformity • During wafer mapping the sheet resistance or some other parameter proportional to ion implant dose is measured at many locations across a sample. The data are then converted to two-dimensional or three- dimensional contour maps • Contour maps are a more powerful display of process uniformity than displaying the same data in tabular form. A well-designed contour map gives instant information about ion implant uniformity, flow patterns during diffusion, epitaxial reactor non-uniformities, etc.
- 21. THE MOST COMMON SHEET RESISTANCE WAFER MAPPING TECHNIQUES ARE: Wafer mapping techniques Double implant technique Modulated photoreflectance Optical densitometry
- 22. DOUBLE IMPLANT TECHNIQUE A p-type (n-type) impurity is implanted into an n-type (p-type) substrate at a dose 1 and energy E1. desired low-dose impurity is implanted at dose 2 and energy E2, with E2 < E1. E2 should be less than E1 to prevent penetration through the first implant layer. The sheet resistance Rsh2 after the second implant is measured and compared to Rsh1 without annealing the second implant. The second sheet resistance measurement relies on the implant damage of the second implant being proportional to the implant dose.
- 23. Four-point probe sheet resistance Four- point prob contour map (A) Boron, 1015 𝑐𝑚−2 , 40 keV, Rsh (average) = 98.5 ohms/square (B) (B) Arsenic, 1015 𝑐𝑚−2 , 80 keV, Rsh (average) = 98.5 ohms/square 1% intervals, 200 mm diameter Si wafer A B
- 24. MODULATED PHOTO REFLECTANCE In the modulated photo reflectance ,an Ar+ ion laser beam, incident on the semiconductor sample, is modulated at a frequency of 0.1 to 10 MHz, creating transient thermal waves near the surface that propagate at different speeds in damaged and crystalline regions. Hence, signals from regions with various damages differ, leading to a measure of crystal damage. The thermal wave diffusion length at a 1 MHz modulation frequency is 2 to 3 μm. The small temperature variations cause small volume changes of the wafer near the surface and the surface expands slightly. These changes include both thermoelastic and optical effects, and they are detected with a second laser—the probe beam—by measuring the reflectivity change
- 25. • The technique is contactless and non-destructive and has been used to measure implant doses from 10^11 to 10^15 cm^3 • Its chief strength lies in the ability to detect low-dose implants contactless and to display the information as contour maps. Damaged layer Therma l signal Pump laser Sample Detector Prob laser Modulated photoreflectance contour map (A) Boron, 6.5*1012 𝑐𝑚−2 , 70 keV, 648 TW units (B) Boron, 5*1012 𝑐𝑚−2 , 30 keV, 600 TW units 0.5% intervals, 200 mm diameter Si wafer A B
- 26. OPTICAL DENSITOMETRY A transparent substrate, typically glass, is coated with a thin film consisting of a polymer carrier and an implant sensitive radiochromic dye. During implant, the dye molecule undergoes heterolytic cleavage, resulting in positive ions with a peak light absorption at a wavelength of 600 nm. When this polymer-coated glass wafer is ion implanted, the film darkens. The amount of darkening depends on the implant energy, dose, and species.
- 27. COMPARISON OF VARIOUS MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES Category Four Point Probe Double Implant Spreading Resistance Modulated Photoreflectan e Optical Densitometry Type Electrical Electrical Electrical Optical Optical Measurement Sheet Resistance Crystal Damage Spreading Resistance Crystal Damage Polymer Damage Resolution(µm) 3000 3000 5 1 3000 Species Active Active Active , Inactive Inactive Inactive Dose Range(𝑐𝑚−2 ) 1012 - 1015 1011 - 1014 1011 - 1015 1011 - 1015 1011 - 1013 Results Direct Calibration Calibration Calibration Calibration Relaxation Minor Serious Minor Serious Serious Requires Anneal Initial Implant Anneal _______ Measure before and after Mapping Techniques for Ion Implantation Uniformity Measurements
- 28. CONTACTLESS RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE Contactless resistivity measurement technique electrical the sample is placed into a microwave circuit and get the transmission or reflection characteristics of a waveguide or cavity, the sample is capacitively coupled to the measuring apparatus the sample is inductively coupled to the apparatus Non-electrical
- 29. ONE SUCH CONTACTLESS TECHNIQUE IS EDDY CURRENT TECHNIQUE • The eddy current measurement technique is based on the parallel resonant tank circuit. • The quality factor of such a circuit is reduced when a conducting material is brought close to the coil due to the power absorbed by the conducting material.
- 30. • In the ultrasound method sound waves are reflected from the upper and lower wafer surfaces located between the two probes . • The phase shift of the reflected sound caused by the impedance variation of the air gap is detected by the sonic receiver. • The phase shift is proportional to the distance from each probe to each surface. With known probe spacing, the wafer thickness can be determined.
- 31. STRENGTH AND WEAKNESSES OF VARIOUS RESISTIVITY MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE
- 32. FOUR-POINT PROBE TECHNIQUE Strength Weakness absolute measurement without recourse to calibrated standards surface damage wafer mapping makes it powerful monitoring tool samples a relatively large volume of the wafer, prevents high resolution measurements
- 33. CONTACTLESS TECHNIQUES Strength Weakness non-contacting nature prevents destruction of material inability to determine the sheet resistance of thin diffused or ion- implanted layers availability of commercial equipment Need of highly doped layer on an insulating substrate to detect such resistance by making sheet resistance of the layer to be on the order of a hundred times lower than the sheet resistance of the substrate
- 34. OPTICAL TECHNIQUES Strength Weakness Ability to measure the implants non- destructively, with small spot size Measurements are qualitative with quantitative doping requires calibrated standards Rapid technique compared to others Possible laser drift Displaying the information in the form of contour plots Al backing plate must be affixed to protect optical sensors
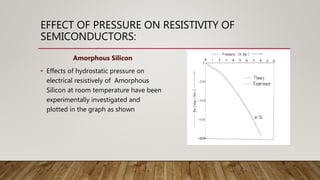
- 35. EFFECT OF PRESSURE ON RESISTIVITY OF SEMICONDUCTORS: Amorphous Silicon • Effects of hydrostatic pressure on electrical resistively of Amorphous Silicon at room temperature have been experimentally investigated and plotted in the graph as shown
- 36. Selenium • Selenium is other group material with a direct band gap in type conduction. It is used in selenium rectifiers. • The effects of pressure on the optical edge of selenium have been studied by Balchan and Drickamer GermaniumSelenium
- 37. RESISTIVITY OF VARIOUS MATERIALS Material Resistivity at 23º C Ohms - meter Material Resistivity at 23º C Ohms - meter Silver 1.59 𝑥10−8 Nichrome 1.50 𝑥10−6 Copper 1.68 𝑥10−8 Coal 3.5 𝑥10−5 Gold 2.20 𝑥10−8 Germanium 4.6 𝑥10−1 Aluminum 2.65 𝑥10−8 Silicon 6.4 𝑥102 Tungsten 5.6 𝑥10−8 Human Skin 5 𝑥105 Iron 9.71 𝑥10−8 Glass 101 𝑡𝑜 1014 Steel 7.2 𝑥10−7 Rubber 1013 Platinum 1.1 𝑥10−7 Sulfur 1015 Lead 2.2 𝑥10−7 Quartz 7.5 𝑥1017
- 38. • Reference: 1. Semiconductor Material And Device Characterization By Dieter K. Schroder 2. Electrical resistivity/ resistance of some semiconductors by Rajendra Kumar and Tanveer Ahmad Wani