Shock.pdf
- 2. Definition of shock • Shock is a state in which there is inadequate blood flow to the tissues to meet demand. • Shock and hypotension often co-exist, BUT a normal blood pressure DOES NOT exclude the diagnosis of shock • Imbalance between tissue supply and demand →Anaerobic Metabolism →Lactic Acid Production • The acute circulatory failure if prolonged, results in irreversible organ failure. • Mortality is high without early diagnosis and treatment. Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015 Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 3. Clinical features-- Signs common to most forms of shock – Pallor, mottled skin, cold extremities, sweating and thirst. – Rapid and weak pulse often only detected on major arteries (femoral or carotid). – Low blood pressure (BP), narrow pulse pressure, BP sometimes undetectable. – Capillary refill time (CRT) > 3 seconds. – Cyanosis, dyspnoea, tachypnoea are often present in varying degrees depending on the mechanism. – Consciousness usually maintained, but anxiety, confusion, agitation or apathy are common. – Oliguria or anuria. Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 4. Different types of Shock 1. Hypovolaemic 2. Cardiogenic 3. Distributive 4. Obstructive Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 5. Signs specific to the mechanism of shock -- Hypovolaemic shock • The common signs of shock listed above are typical of hypovolaemic shock. • Do not underestimate hypovolaemia. Signs of shock may not become evident until a 50% loss of blood volume in adults. Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 6. Distributive Shock • Caused by maldistribution of blood flow from peripheral vasodilatation and decrease in systemic vascular resistance (SVR) (decreased afterload) • Sepsis • Anaphylaxis • Neurogenic
- 7. Signs specific to the mechanism of shock - Septic shock – High fever or hypothermia (< 36 °C), rigors, confusion – BP may be initially maintained, but rapidly, same pattern as for hypovolaemic shock. Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 8. Signs specific to the mechanism of shock - Anaphylactic shock – Significant and sudden drop in BP – Tachycardia – Frequent cutaneous signs: rash, urticaria, angioedema – Respiratory signs: dyspnoea, bronchospasm Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 9. Signs specific to the mechanism of shock - Cardiogenic shock – Respiratory signs of left ventricular failure (acute pulmonary oedema) are dominant: tachypnoea, crepitations on auscultation. – Signs of right ventricular failure: raised jugular venous pressure, hepatojugular reflux, sometimes alone, more often associated with signs of left ventricular failure. Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 10. Causes of Cardiogenic Shock Hollenberg SM, Kavinsky CJ, ParrilloJE. Cardiogenic shock. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131(1):47-59.
- 11. Trauma Patients Can Present with A Combination of Different Types of Shock Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 12. The aetiological diagnosis is oriented by: – The context: trauma, insect bite, ongoing medical treatment, etc. – The clinical examination: • fever • skin pinch consistent with dehydration • thoracic pain from a myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolus • abdominal pain or rigidity of the abdominal wall from peritonitis, abdominal distension from intestinal obstruction • blood in stools, vomiting blood in intestinal haemorrhage • subcutaneous crepitations, likely anaerobic infection Medical Guidelines Medicins Sans Fronteires on Shock
- 13. Characteristics of different types of shock Type of shock JVP/CVP Cardiac output (CO) Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) Clinically Hypovolemic ↓ ↓ ↑ Cold and shut down Cardiogenic ↑ ↓ ↑ Cold and shut down Distributive ↓ ↓/-/↑ ↓ Warm and dilated Obstructive ↑ ↓ ↑ Cold and shut down Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 14. Lab studies • FBC • RP • LFT • Amylase • Cardiac biomarkers • ABG • Cultures • Lactate Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 15. Imaging • USS • Maximal inferior vena cava diameter was better able to differentiate a central venous pressure <10mmHg from a central venous pressure >10mmHg • Abdominal aortic aneurysm • Echo • Cardiac ejection fraction to determine etiology of shock – depressed in cardiogenic shock • Cardiac tamponade • Aortic dissection • Pulmonary embolism • CXR • Heart size, presence/absence of pulmonary edema/infiltrates/effusion/ pneumothorax • CT scan • Only if USS is inconclusive Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 16. Management of Shock (General) • Definitive treatment for patients in shock depends on the specific etiology; however, this may not be immediately clear on initial presentation • Thus initiation of therapy and patient stabilization may occur simultaneously with evaluation. • The goals in treating patients in shock are restoring adequate organ perfusion and oxygen delivery while considering/treating the possible cause(s) of shock Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 17. Initial Stabilization • Airway • Breathing • Circulation Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 18. Management of Shock (General) • Early recognition and prompt treatment of the underlying cause of shock • Ensure oxygenation and maintain perfusion • Usually aim for: • Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) ≥ 65mmHg .…. formula MAP = SBP + 2(DBP) 3 • Urine output ≥ 0.5ml/kg/hr Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 19. Treatment – Monitoring • Cardiovascular monitoring • Cardiac monitoring, BP cuffs automated Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 20. Treatment -- Fluid resuscitation • Only approximately 50% of hypotensive patients are volume responsive • Passive leg raise can rapidly, noninvasively and easily as a reversible tool to assess volume responsiveness • Leg is raised from horizontal to vertical position and then assess volume responsiveness • Crystalloid is usually used for the initial treatment of undifferentiated shock Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 21. Management -- Vasopressor • Once patient is euvolemic but there is still ineffective oxygen delivery, vasoactive medications are likely required • Vasopressor medications used to support mean arterial pressure by increasing systemic vascular resistance and/or cardiac output • Noradrenaline is a strong alpha agonist with some beta 1 activity and is a recommended initial choice for most categories of shock • Metaanalysis of 11 trials showed there is a statistically significant increased risk of death associated with dopamine. Thus should not be used as a first line pressor agent Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 22. Treating Shock – Vasopressors Activity at Receptors Agent α1 α2 𝛽1 𝛽2 Dopaminergic Dobutamine + + ++++ ++ 0 Adrenaline ++++ ++++ ++++ +++ 0 Noradrenaline +++ +++ +++ +/++ 0
- 23. Restoring Blood Pressure • Mean arterial pressure is the preferred blood pressure to target during resuscitation • The recommended initial goal is 65 mm Hg. A higher goal of 80 to 85 mm Hg may help patients with chronic hypertension, while a lower target may be better tolerated in patients with reduced systolic function, older patients, and patients with end-stage liver disease • After blood pressure falls below a critical threshold, tissue perfusion decreases linearly. That critical threshold can vary between organ systems and individuals, and the target can later be personalized based on global and regional perfusion as assessed with urine output, mental status, or lactate clearance • Decisions to titrate vasopressors to achieve mean arterial pressure goals should be balanced against potential adverse effects, including arrhythmias, cardiovascular events, and ischemia Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 24. Restoring Blood Pressure • Norepinephrine is the first line vasopressor agent • A second vasopressor is routinely added when norepinephrine doses exceed 40 or 50 μg/min • Epinephrine or vasopressin as second line vasopressor agent Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 25. Hypovolaemic shock - Due to inadequate circulating fluid volume Causes: - divided to haemorrhagic or non-haemorrhagic (major burns; gastrointestinal losses: vomiting, fistulas; urinary losses: diabetes, diabetes insipidus; evaporative losses with fever, abdominal surgery) Management: - fluid resuscitation - haemorrhagic cause: transfusion of red cells and blood products. - review source of bleeding and stop bleeding promptly - use of hemostatic agent Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 26. Cardiogenic shock - due to cardiac pump failure resulting from myocardial or valvular failure Causes: - commonest: acute coronary syndrome - other causes: arrhythmia, myocardial contusions post-trauma; myocarditis; acute valvular dysfunction; cardiomyopathy - echo is very useful in reviewing the cause and monitor the progress Management: - Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): reperfusion by fibrinolytics or Per Cutaneous Intervention (angiogram ± angioplasty ± stenting) - control arrhythmia: pharmacological, electrical: pacing/ cardioversion - optimise preload by fluid: a trial of small bolus of fluid with close observation of CVP/BP trend - inotropic support: augment myocardial contractility. Increasing diastolic blood pressure to increase coronary perfusion pressure and flow - afterload: vasodilator will cause further hypotension, use with caution in normotensive patients - mechanical device: Intraaortic Ballon Pump (IABP), Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 27. Distributive shock Due to peripheral vascular dilatation causes a fall in peripheral resistance. The cardiac output is often increased but the perfusion of vital organs is comprised because the body loses its ability to distribute blood properly (vasoplegia) Causes: - septic shock; anaphylaxis; neurogenic shock Management: - Fluid resus - Septic shock: prompt antibiotics, source control - Inotropic support: start when BP is refractory to fluid. Usually noradrenaline for septic shock - Anaphylaxis: SC/ IV/ IM adrenaline Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 28. Anaphylactic Shock • Mainstay of treatment is rapid administration of adrenaline • Adrenaline should be administered immediately if anaphylaxis is suspected. • Adrenaline should be given intramuscularly if intravenous access is not available; treatment should not be delayed by attempting to place an intravenous line. • The standard intramuscular dose of adrenaline is 0.3 mg to 0.5 mg in a 1:1000 dilution, and dosing may be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes as clinically indicated. Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 29. 2016 Sepsis-3 committee – Sepsis Definition • Sepsis—A life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated host response to infection, resulting in organ dysfunction • Septic shock—Circulatory, cellular, and metabolic abnormalities in septic patients, presenting as fluid-refractory hypotension requiring vasopressor therapy with associated tissue hypoperfusion (lactate > 2 mmol/L Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Defi nitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016; 315(8):801–810. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0287
- 30. Septic Shock • Starting with broad-spectrum antimicrobials, particularly in the setting of hypotension, and then rapidly de-escalating to an antimicrobial with the narrowest spectrum based on local sensitivity patterns. • If the clinical course suggests the illness is not actually due to infection, the antibiotics should be stopped immediately • Antibiotics de-escalation should be discussed daily. A 7- to 10-day course or even shorter may be appropriate for most infections, although a longer course may be needed if source control cannot be achieved, in immunocompromised hosts, and in S aureusbacteremia, endocarditis, or fungal infections Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
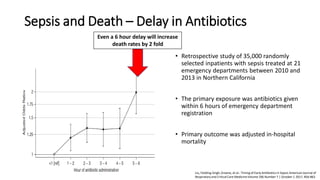
- 31. Sepsis and Death – Delay in Antibiotics • Retrospective study of 35,000 randomly selected inpatients with sepsis treated at 21 emergency departments between 2010 and 2013 in Northern California • The primary exposure was antibiotics given within 6 hours of emergency department registration • Primary outcome was adjusted in-hospital mortality Even a 6 hour delay will increase death rates by 2 fold Liu, Fielding-Singh, Greene, et al.: Timing of Early Antibiotics in Sepsis American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care MedicineVolume 196 Number 7 | October 1 2017, 856-863
- 32. Septic Shock – Fluid Resuscitation • Rescue: During the initial minutes to hours, fluid boluses (a 1- to 2-L fluid bolus of crystalloid/balanced crystalloid solution) are required to reverse hypoperfusion and shock • Optimization: During the second phase, the benefits of giving additional fluid to improve cardiac output and tissue perfusion should be weighed against potential harms • Stabilization: During the third phase, usually 24 to 48 hours after the onset of septic shock, an attempt should be made to achieve a net-neutral or a slightly negative fluid balance • De-escalation: The fourth phase, marked by shock resolution and organ recovery, should trigger aggressive fluid removal strategies Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 33. Septic Shock – Fluid resuscitation • Within the first 3 hours patients have a lactate level checked, blood cultures drawn prior to antibiotics, broad-spectrum antibiotics given, and 30mL/kg of crystalloid/balanced crystalloid given for hypotension or lactate ≥ 4 mmol/L. • Within 6 hours, vasopressors should be started for hypotension that does not respond to fluid resuscitation to maintain a mean arterial pressure ≥ 65 mm Hg. • Measuring the lactate level is an objective way to assess response to resuscitation, better than other clinical markers, and it continues to be an integral part of sepsis definitions and the Surviving Sepsis Campaign care bundle Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The Emergency Department. Emergency Medicine Practice2014, 16:3 Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 34. Septic Shock – Source Control • Source control can range from removal of infected intravascular devices to a chest tube for empyema to percutaneous or surgical intervention in cases of cholecystitis and pyelonephritis Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 35. Septic Shock – Role of corticosteroids • In septic shock, they have a vasopressor-sparing role and reduce the duration of shock, ventilator use, and ICU stay • However, the evidence is not conclusive that giving corticosteroids for sepsis improves clinical outcomes or survival • They can be added as adjunctive therapy for patients requiring higher doses of vasopressors • If corticosteroids are used in septic shock, current guidelines recommend hydrocortisone 200 mg per day intravenously as a continuous drip or 50 mg bolus in 4 divided doses for at least 3 days Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 36. Septic Shock – Biomarkers • C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate have been used in the past, but with limited success • Procalcitonin has emerged as a method to help detect bacterial infections early and to guide de-escalation or discontinuation of antibiotics. • Galactomannan and beta-D-glucan can be used to detect infections with fungi, specially Aspergillus. Beta-d-glucan is more sensitive for invasive Aspergillus, while galactomannan is more specific Siddharth Dugar et al Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based managementCLEVELAND CLINIC JOURNAL OF MEDICINE VOLUME 87 • NUMBER 1 JANUARY 2020
- 37. Obstructive shock Due to obstruction of great vessels or heart that impedes the blood flow Causes: - cardiac tamponade; tension pneumothorax; pulmonary or air embolism Mangement: - Prompt relief of obstruction: e.g. pericardiocentesis for tamponade, chest drain for tension pneumothorax - Fluid and inotrope are for temporary support Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, the Chinese Universityof Hong Kong July 2015
- 38. Pitfalls Jeremy Richards et al. Diagnosis And Management Of Shock In The EmergencyDepartment. EmergencyMedicine Practice 2014, 16:3
- 39. Thankyou