String and string buffer
- 1. Chapter 11 String & StringBuffer http://www.java2all.com
- 2. String Handling http://www.java2all.com
- 3. String Handling : In Java, a string is defined as a sequence of characters. But, unlike many other languages that implement strings as character arrays, java implements strings as objects of type String. Java handles String by two classes StringBuffer and String. The String and StringBuffer classes are defined in java.lang. Thus, they are available to all programs automatically. http://www.java2all.com
- 4. 1. String Concatenation (+) EX : Output : import java.util.*; class str3 S1 = Java { public static void main(String args[]) S2 = 2all { Concatenation Operator = Java2all String s1 = new String ("Java"); String s2 = "2all"; S3 = Java2all String s3 = s1+s2; S4 = ABCD System.out.println("S1 = " + s1); System.out.println("S2 = " + s2); System.out.println("Concatenation Operator = " + s1+s2); System.out.println("S3 = " + s3); byte num [] = {65,66,67,68}; String s4 = new String(num); System.out.println("S4 = " + s4); } http://www.java2all.com
- 5. 2. Character Extraction : The String class provides ways in which characters can be extracted from a String object. Method Description charAt() function is used to extract a single character char charAt(int indexnum) from a String. indexnum is the index number of the character that we want to extract. Used to extract more than one character at a time, void getChars(int sourceStart, int sourceStart specifies beginning of the string, and sourceEnd, char target[], int sourceEnd specifies end of the string. The array that will targetStart) receive the characters is specified by target. The index within target at which the substring will be copied. This is an alternative to getChars( ) that stores the characters in an array of bytes. It uses the default Byte[ ] getBytes( ) character-to-byte conversions provided by the platform. Char[ ] toCharArray( ) Same as getChars http://www.java2all.com
- 6. 3. String Comparison : The String class provides several methods that compare strings or substrings within strings. equals( ) – used to compare two strings General form: Boolean equals(Object str) Here, str is a String object. It returns true if the strings contain the same character otherwise it returns false . http://www.java2all.com
- 7. The comparison is case-sensitive. equalsIgnoreCase( ) – Same as equals but this ignores case. General form: Boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str) Here, str is the String object. It returns true if the strings contain the same character otherwise it returns false. http://www.java2all.com
- 8. This is case in – sensitive. regionMatches( ) This method compares a specific region inside a string with another specific region in another string. There is an overloaded form that allows you to ignore case in such comparisons. General form: Boolean regionMatches(int startIndex, String str2, int str2StartIndes, int numChars) http://www.java2all.com
- 9. Boolean regionMatches(Boolean ignoreCase, int startIndex, String str2, int str2StartIndex, int numChars) startsWith( ) and endsWith() The startsWith( ) method determines whether a given String begins with a specified string. endsWith( ) determines whether the String ends with a specified string. General Form Boolean startsWith(String str) Boolean endsWith(String str) equals( ) Versus = = http://www.java2all.com
- 10. Equals( ) method and the = = operator perform two different operations. The equals ( ) method compares the characters inside a String object. The = = operator compares two object references to see whether they refer to the same instance. compareTo( ) It is not enough to know that two strings just for equal or not. For sorting applications, we need to know which is less than, equal to, or greater than the other string. http://www.java2all.com
- 11. The String method compareTo( ) serves this purpose. General Form: int compareTo(String str) http://www.java2all.com
- 12. 4 Modifying a string : If we want to modify a String, we must either copy it into a StringBufer or we can use following String methods: http://www.java2all.com
- 13. Method Description String substring(int n) Gives substring starting from nth character. Gives substring starting from nth char up to String substring(int n, int m) mth S1.concat(s2) Concatenates s1 and s2 The replace() method replaces all occurrences String replace(char original, of one character in the invoking string with char replacement) another character. Remove white space at the beginning and end String trim( ) of the string. http://www.java2all.com
- 14. 5 valueOf() : The valueOf() method converts data from internal format into a human-readable form. It has several forms: String valueOf(double num) String valueOf(long num) String valueOf(Object ob) String valueOf(char chars[ ] ) String valueOf(char chars[], int startIndex, int numChars) http://www.java2all.com
- 15. Method & Example Method Call Description S2=s1.toLowerCase; Converts the string s1 to lowercase S2=s1.toUpperCase; Converts the string s1 to uppercase S2=s1.replace(‘x’,’y’) Replace all appearances of x with y. Remove white spaces at the beginning and of the S2=s1.trim() string s1 S1.equals(s2) Returns true if s1 and s2 are equal S1.equalsIgnoreCase(s Returns true if s1=s2, ignoring the case of characters 2) S1.length() Gives the length of s1 http://www.java2all.com
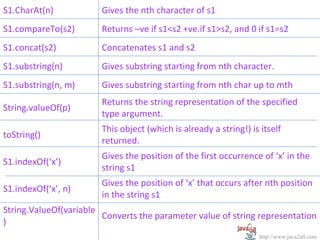
- 16. S1.CharAt(n) Gives the nth character of s1 S1.compareTo(s2) Returns –ve if s1<s2 +ve.if s1>s2, and 0 if s1=s2 S1.concat(s2) Concatenates s1 and s2 S1.substring(n) Gives substring starting from nth character. S1.substring(n, m) Gives substring starting from nth char up to mth Returns the string representation of the specified String.valueOf(p) type argument. This object (which is already a string!) is itself toString() returned. Gives the position of the first occurrence of ‘x’ in the S1.indexOf(‘x’) string s1 Gives the position of ‘x’ that occurs after nth position S1.indexOf(‘x’, n) in the string s1 String.ValueOf(variable Converts the parameter value of string representation ) http://www.java2all.com
- 17. import java.util.*; class str1 { public static void main(String args[]) { String s1 = "Bhagirath"; System.out.println("S1 = " + s1); int length = s1.length(); System.out.println("S1 lenth = " + length); System.out.println("S1 lowercase = " + s1.toLowerCase()); System.out.println("S1 uppercase = " + s1.toUpperCase()); System.out.println("S1 replace a with z = " + s1.replace('a','z')); System.out.println("S1 indexOf('e')= " + s1.indexOf('e')); System.out.println("S1 lastindexof('e') = " + s1.lastIndexOf('e')); String s2 = "ViewSonic"; System.out.println("S2 = " + s2); System.out.println("S1 and S2 trim = " + s1.trim() + s2.trim()); System.out.println("S1 and S2 equals = " + s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println("S1 and S2 equals ignoring case = " + s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); System.out.println("S1 and S2 compareTo = " + s1.compareTo(s2)); System.out.println("S1 and S2 concate = " + s1.concat(s2)); System.out.println("S1 substring(n) = " + s1.substring(5)); System.out.println("S1 substring(n,m) = " + s1.substring(5,8)); System.out.println("S1 toString() = " + s1.toString()); int i = 100; System.out.println("S1.valueOf(variable) = " + (s1.valueOf(i)).length()); // converts the parameter to string http://www.java2all.com
- 18. System.out.println("Start with " + s1.startsWith("P")); System.out.println("Start with " + s1.endsWith("y")); } } http://www.java2all.com
- 19. Output : S1 = Bhagirath S1 lenth = 9 S1 lowercase = bhagirath S1 uppercase = BHAGIRATH S1 replace a with z = Bhzgirzth S1 indexOf('e')= -1 S1 lastindexof('e') = -1 S2 = ViewSonic S1 and S2 trim = BhagirathViewSonic S1 and S2 equals = false S1 and S2 equals ignoring case = false S1 and S2 compareTo = -20 S1 and S2 concate = BhagirathViewSonic S1 substring(n) = rath S1 substring(n,m) = rat S1 toString() = Bhagirath S1.valueOf(variable) = 3 Start with false Start with false http://www.java2all.com
- 20. import java.util.*; class str4 { public static void main(String args[]) { String s = "This is a dAmo of the getChars method."; int start = 10; int end = 14; char buf[] = new char[10]; //System.out.println("Character at 10 = " + s.charAt(10)); s.getChars(start, end, buf,0); Output : System.out.println(buf); s.getChars(start, end, buf,5); jav System.out.println(buf); jav jav byte bt [] = new byte[10]; 32 s.getBytes(start, end, bt,0); System.out.println(bt[0]); 74 System.out.println(bt[1]); System.out.println(bt[2]); 97 System.out.println(bt[3]); 118 char buf1[] = s.toCharArray(); Welcome to Java2all System.out.println(buf1); } } http://www.java2all.com
- 21. import java.util.*; class str5 { public static void main(String args[]) { String s1 = "Rome was not built in a not day"; System.out.println("S1 = " + s1); /*System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf('o')); System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not")); System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf('o',5)); System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not", 15)); System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf('o')); System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf("not")); System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf('o',15)); System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf("not", 15)); */ String s2 = "Rome was not built in a Not day"; System.out.println("S2 = " + s2); //System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not")); //System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.lastIndexOf("not")); System.out.println("Region Matches = "); boolean b1 = s1.regionMatches(false,9,s2,24,3); System.out.println("b1 = " + b1); } } http://www.java2all.com
- 22. Output : S1 = Rome was not built in a not day S2 = Rome was not built in a Not day Region Matches = b1 = false http://www.java2all.com
- 23. import java.util.*; class str6 { public static void main(String args[]) { String s1 = "Hello"; String s2 = new String(s1); System.out.println(s1 + " equals " + s2 + " -> " + s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1 + " == " + s2 + " -> " + (s1 == s2)); } } Output : Hello equals Hello -> true Hello == Hello -> false http://www.java2all.com
- 24. StringBuffer Class http://www.java2all.com
- 25. StringBuffer class : StringBuffer is a peer class of String. String creates strings of fixed length, while StringBuffer creates strings of flexible length that can be modified in terms of both length and content. So Strings that need modification are handled by StringBuffer class. We can insert characters and substrings in the middle of a string, or append another string to the end. http://www.java2all.com
- 26. StringBufer defines these Constructor: StringBuffer() StringBuffer(int size) StringBuffer(String str) http://www.java2all.com
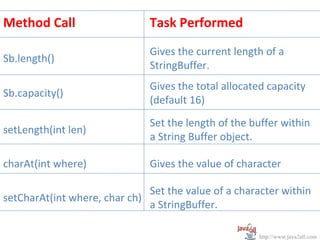
- 27. Method Call Task Performed Gives the current length of a Sb.length() StringBuffer. Gives the total allocated capacity Sb.capacity() (default 16) Set the length of the buffer within setLength(int len) a String Buffer object. charAt(int where) Gives the value of character Set the value of a character within setCharAt(int where, char ch) a StringBuffer. http://www.java2all.com
- 28. Appends the string s2 to s1 at S1.append(s2) the end Inserts the string s2 at the S1.insert(n,s2) position n of the string s1 S1.reverse() Reverse the string of s1 Delete the nth character of S1.deleteCharAt(nth) string s1 Delete characters from start to S1.delete(StartIndex, endIndex) end. http://www.java2all.com
- 29. import java.util.*; class strbuf1 Output : { public static void main(String args[]) { StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer(); s1 = StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("Bhagirath"); s2 = Bhagirath StringBuffer s3 = new StringBuffer(s2); StringBuffer s4 = new StringBuffer(100); s3 = Bhagirath System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); System.out.println("s2 = " + s2); s1.length = 0 System.out.println("s3 = " + s3); s2.length = 9 System.out.println("s1.length = " + s1.length()); s3.length = 9 System.out.println("s2.length = " + s2.length()); System.out.println("s3.length = " + s3.length()); s4.length = 0 System.out.println("s4.length = " + s4.length()); s1.capacity = 16 System.out.println("s1.capacity = " + s1.capacity()); System.out.println("s2.capacity = " + s2.capacity()); s2.capacity = 25 System.out.println("s3.capacity = " + s3.capacity()); s3.capacity = 25 System.out.println("s4.capacity = " + s4.capacity()); s4.capacity = 100 } } http://www.java2all.com
- 30. import java.util.*; class strbuf2 { public static void main(String args[]) { StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("Java2all"); StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("Hello"); System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); //System.out.println("s1.charAt(5) = " + s1.charAt(5)); //s1.setCharAt(5,'z'); //System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); //System.out.println("Inserting String = " + s1.insert(5,s2)); //System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); //System.out.println("Appending String = " + s1.append(s2)); //System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); //System.out.println("Reversing String = " + s1.reverse()); //System.out.println("Deleting 5th character = " + s1.deleteCharAt(5)); System.out.println("Deleting 5 to 8 character = " + s1.delete(5,8)); } } Output : s1 = Java2all Deleting 5 to 8 character = Java2 http://www.java2all.com
- 31. import java.util.*; public class strbuf3 { Output : public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("Hello world!"); s = Hello world! s.length() = 12 System.out.println("s = " + s); System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.length()); s.length() = 28 System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.capacity()); // Change the length of buffer to 5 characters: Hello s.setLength(5); s.length() = 5 System.out.println(s); s.length() = 28 System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.length()); System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.capacity()); } } http://www.java2all.com




![1. String Concatenation (+)
EX : Output :
import java.util.*;
class str3 S1 = Java
{
public static void main(String args[])
S2 = 2all
{ Concatenation Operator = Java2all
String s1 = new String ("Java");
String s2 = "2all";
S3 = Java2all
String s3 = s1+s2; S4 = ABCD
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1);
System.out.println("S2 = " + s2);
System.out.println("Concatenation Operator = " + s1+s2);
System.out.println("S3 = " + s3);
byte num [] = {65,66,67,68};
String s4 = new String(num);
System.out.println("S4 = " + s4);
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-4-320.jpg)
![2. Character Extraction :
The String class provides ways in which
characters can be extracted from a String object.
Method Description
charAt() function is used to extract a single character
char charAt(int indexnum) from a String. indexnum is the index number of the
character that we want to extract.
Used to extract more than one character at a time,
void getChars(int sourceStart, int sourceStart specifies beginning of the string, and
sourceEnd, char target[], int sourceEnd specifies end of the string. The array that will
targetStart) receive the characters is specified by target. The index
within target at which the substring will be copied.
This is an alternative to getChars( ) that stores the
characters in an array of bytes. It uses the default
Byte[ ] getBytes( )
character-to-byte conversions provided by the
platform.
Char[ ] toCharArray( ) Same as getChars
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-5-320.jpg)








![5 valueOf() :
The valueOf() method converts data from
internal format into a human-readable form. It has
several forms:
String valueOf(double num)
String valueOf(long num)
String valueOf(Object ob)
String valueOf(char chars[ ] )
String valueOf(char chars[], int startIndex, int
numChars)
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-14-320.jpg)

![import java.util.*;
class str1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s1 = "Bhagirath";
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1);
int length = s1.length();
System.out.println("S1 lenth = " + length);
System.out.println("S1 lowercase = " + s1.toLowerCase());
System.out.println("S1 uppercase = " + s1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println("S1 replace a with z = " + s1.replace('a','z'));
System.out.println("S1 indexOf('e')= " + s1.indexOf('e'));
System.out.println("S1 lastindexof('e') = " + s1.lastIndexOf('e'));
String s2 = "ViewSonic";
System.out.println("S2 = " + s2);
System.out.println("S1 and S2 trim = " + s1.trim() + s2.trim());
System.out.println("S1 and S2 equals = " + s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println("S1 and S2 equals ignoring case = " + s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
System.out.println("S1 and S2 compareTo = " + s1.compareTo(s2));
System.out.println("S1 and S2 concate = " + s1.concat(s2));
System.out.println("S1 substring(n) = " + s1.substring(5));
System.out.println("S1 substring(n,m) = " + s1.substring(5,8));
System.out.println("S1 toString() = " + s1.toString());
int i = 100;
System.out.println("S1.valueOf(variable) = " + (s1.valueOf(i)).length()); // converts the parameter
to string
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-17-320.jpg)


![import java.util.*;
class str4
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s = "This is a dAmo of the getChars method.";
int start = 10;
int end = 14;
char buf[] = new char[10];
//System.out.println("Character at 10 = " + s.charAt(10));
s.getChars(start, end, buf,0); Output :
System.out.println(buf);
s.getChars(start, end, buf,5);
jav
System.out.println(buf); jav jav
byte bt [] = new byte[10]; 32
s.getBytes(start, end, bt,0);
System.out.println(bt[0]); 74
System.out.println(bt[1]);
System.out.println(bt[2]);
97
System.out.println(bt[3]); 118
char buf1[] = s.toCharArray(); Welcome to Java2all
System.out.println(buf1);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-20-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
class str5
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s1 = "Rome was not built in a not day";
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1);
/*System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf('o'));
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not"));
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf('o',5));
System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not", 15));
System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf('o'));
System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf("not"));
System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf('o',15));
System.out.println("S1 lastIndexOf= " + s1.lastIndexOf("not", 15)); */
String s2 = "Rome was not built in a Not day";
System.out.println("S2 = " + s2);
//System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.indexOf("not"));
//System.out.println("S1 = " + s1.lastIndexOf("not"));
System.out.println("Region Matches = ");
boolean b1 = s1.regionMatches(false,9,s2,24,3);
System.out.println("b1 = " + b1);
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-21-320.jpg)

![import java.util.*;
class str6
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = new String(s1);
System.out.println(s1 + " equals " + s2 + " -> " + s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1 + " == " + s2 + " -> " + (s1 == s2));
}
}
Output :
Hello equals Hello -> true
Hello == Hello -> false
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-23-320.jpg)




![import java.util.*;
class strbuf1 Output :
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer();
s1 =
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("Bhagirath"); s2 = Bhagirath
StringBuffer s3 = new StringBuffer(s2);
StringBuffer s4 = new StringBuffer(100); s3 = Bhagirath
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 = " + s2); s1.length = 0
System.out.println("s3 = " + s3); s2.length = 9
System.out.println("s1.length = " + s1.length()); s3.length = 9
System.out.println("s2.length = " + s2.length());
System.out.println("s3.length = " + s3.length()); s4.length = 0
System.out.println("s4.length = " + s4.length());
s1.capacity = 16
System.out.println("s1.capacity = " + s1.capacity());
System.out.println("s2.capacity = " + s2.capacity());
s2.capacity = 25
System.out.println("s3.capacity = " + s3.capacity()); s3.capacity = 25
System.out.println("s4.capacity = " + s4.capacity());
s4.capacity = 100
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-29-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
class strbuf2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("Java2all");
StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer("Hello");
System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
//System.out.println("s1.charAt(5) = " + s1.charAt(5));
//s1.setCharAt(5,'z');
//System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
//System.out.println("Inserting String = " + s1.insert(5,s2));
//System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
//System.out.println("Appending String = " + s1.append(s2));
//System.out.println("s1 = " + s1);
//System.out.println("Reversing String = " + s1.reverse());
//System.out.println("Deleting 5th character = " + s1.deleteCharAt(5));
System.out.println("Deleting 5 to 8 character = " + s1.delete(5,8));
}
}
Output :
s1 = Java2all
Deleting 5 to 8 character =
Java2 http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-30-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
public class strbuf3
{ Output :
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("Hello world!");
s = Hello world!
s.length() = 12
System.out.println("s = " + s);
System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.length()); s.length() = 28
System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.capacity());
// Change the length of buffer to 5 characters: Hello
s.setLength(5); s.length() = 5
System.out.println(s); s.length() = 28
System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.length());
System.out.println("s.length() = " + s.capacity());
}
}
http://www.java2all.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stringstringbufferchepter11-120701054017-phpapp02/85/String-and-string-buffer-31-320.jpg)