Using Graph Databases For Insights Into Connected Data.
- 1. Using Graph Databases For Insights Into Connected Data Gagan Agrawal Xebia India 1
- 2. SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT DONE RIGHT Netherlands | USA | India | France | UK
- 3. Agenda High level view of Graph Space Comparison with RDBMS and other NoSQL stores Data Modeling Cypher : Graph Query Language Graph Database Internals Graphs In Real World Xebia India 3
- 4. What is a Graph? Xebia India 4
- 6. What is a Graph? A collection of vertices and edges. Set of nodes and the relationships that connect them. Graph Represents Entities as NODES The way those entities relate to the world as RELATIONSHIP Allows to model all kind of scenarios System of road Medical history Supply chain management Data Center Xebia India 6
- 9. High Level view of Graph Space Graph Databases - Technologies used primarily for transactional online graph persistence – OLTP. Graph Compute Engines - Tecnologies used primarily for offline graph analytics - OLAP. Xebia India 9
- 10. Graph Databases Online database management system with Create, Read, Update, Delete methods that expose a graph data model. Built for use with transactional (OLTP) systems. Used for richly connected data. Querying is performed through traversals. Can perform millions of traversal steps per second. Traversal step resembles a join in a RDBMS Xebia India 10
- 11. Graph Database Properties The Underlying Storage : Native / Non-Native The Processing Engine : Native / Non-Native Xebia India 11
- 12. Graph DB – The Underlying Storage Native Graph Storage – Optimized and designed for storing and managing graphs. Non-Native Graph Storage – Serialize the graph data into a relational database, an object oriented database, or some other general purpose data store. Xebia India 12
- 14. Graph DB – The processing Engine Index free adjacency – Connected Nodes physically point to each other in the database Xebia India 14
- 18. Power of Graph Databases Performance Flexibility Agility Xebia India 18
- 19. Comparison Relational Databases NoSQL Databases Graph Databases Xebia India 19
- 20. Relational Databases Lack Relationships Initially designed to codify paper forms and tabular structures. Deal poorly with relationships. The rise in connectedness translates into increased joins. Lower performance. Difficult to cater for changing business needs. Xebia India 20
- 23. NoSQL Databases also lack Relationships NOSQL Databases e.g key-value, document or column oriented store sets of disconnected values/documents/columns. Makes it difficult to use them for connected data and graphs. One of the solution is to embed an aggregate's identifier inside the field belonging to another aggregate. Effectively introducing foreign keys Requires joining aggregates at the application level. Xebia India 23
- 24. NoSQL DB Relationships between aggregates aren't first class citizens in the data model. Foreign aggregate "links" are not reflexive. Need to use some external compute infrastructure e.g Hadoop for such processing. Do not maintain consistency of connected data. Do not support index-free adjacency. Xebia India 24
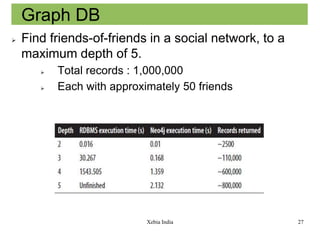
- 27. Graph DB Find friends-of-friends in a social network, to a maximum depth of 5. Total records : 1,000,000 Each with approximately 50 friends Xebia India 27
- 29. Data Modeling with Graph Xebia India 29
- 30. Data Modeling “Whiteboard” friendly The typical whiteboard view of a problem is a GRAPH. Sketch in our creative and analytical modes, maps closely to the data model inside the database. Xebia India 30
- 32. Cypher : Graph Query Language Pattern-Matching Query Language Humane language Expressive Declarative : Say what you want, now how Borrows from well know query languages Aggregation, Ordering, Limit Update the Graph Xebia India 32
- 33. Cypher Cypher Representation : (c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a), (c)-[:KNOWS]->(a) (c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a)<-[:KNOWS]-(c) Xebia India 33
- 34. Cypher START c=node:user(name='Michael') MATCH (c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a), (c)[:KNOWS]->(a) RETURN a, b Xebia India 34
- 35. Other Cypher Clauses WHERE CREATE and CREATE UNIQUE Create nodes and relationships DELETE Provides criteria for filtering pattern matching results. Removes nodes, relationships and properties SET Sets property values Xebia India 35
- 36. Other Cypher Clauses FOREACH UNION Performs an updating action for graph element in a list. Merge results from two or more queries. WITH Chains subsequent query parts and forward results from one to the next. Similar to piping commands in UNIX. Xebia India 36
- 37. Comparison of Relational and Graph Modeling Xebia India 37
- 43. Graph Database Internals Xebia India 43
- 44. Non Functional Characteristics Transactions Fully ACID Recoverability Availability Scalability Xebia India 44
- 45. Scalability Capacity (Graph Size) Latency (Response Time) Read and Write Throughput Xebia India 45
- 46. Capacity 1.9 Release of Neo4j can support single graphs having 10s of billions of nodes, relationships and properties. The Neo4j team has publicly expressed the intention to support 100B+ nodes/relationships/properties in a single graph. Xebia India 46
- 47. Latency RDBMS – more data in tables/indexes result in longer join operations. Graph DB doesn't suffer the same latency problem. Index is used to find starting node. Traversal uses a combination of pointer chasing and pattern matching to search the data. Performance does not depend on total size of the dataset. Depends only on the data being queried. Xebia India 47
- 48. Throughput Constant performance irrespective of graph size. Xebia India 48
- 49. Graphs in the Real World Xebia India 49
- 50. Common Use Cases Social Recommendations Geo Logistics Networks : for package routing, finding shortest Path Financial Transaction Graphs : for fraud detection Master Data Management Bioinformatics : Era7 to relate complex web of information that includes genes, proteins and enzymes Authorization and Access Control : Adobe Creative Cloud, Telenor Xebia India 50
- 54. BigData & Real Time Analytics Services Visualization (Tableau) Analytics Framework (Mahout) Integration (Sqoop, Flume , Storm) Hadoop Powered Solutions (Pig, Hive, Oozie, Hbase Impala) (Solr, Elastic Search) Core Hadoop (HDFS, MapReduce,Zookeeper, Cloudera Trainings - Cloudera Data Analyst / Developer / Admin Training Products - Divolte - Wearable Sensors Solutions - Big data warehousing - Scalable big data etl - High volume web analytics
- 55. Contact us @ Websites www.xebia.in www.xebia.com www.xebia.fr Xebia India infoindia@xebia.com Thought Leadership Htto://xebee.xebia.in http://blog.xebia.com http://podcast.xebia.com
Editor's Notes
- #55: Services should include hadoop consulting rather





























![Cypher
Cypher Representation :
(c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a), (c)-[:KNOWS]->(a)
(c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a)<-[:KNOWS]-(c)
Xebia India
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphdb-nasscom-140115045900-phpapp01/85/Using-Graph-Databases-For-Insights-Into-Connected-Data-33-320.jpg)
![Cypher
START c=node:user(name='Michael')
MATCH (c)-[:KNOWS]->(b)-[:KNOWS]->(a), (c)[:KNOWS]->(a)
RETURN a, b
Xebia India
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphdb-nasscom-140115045900-phpapp01/85/Using-Graph-Databases-For-Insights-Into-Connected-Data-34-320.jpg)