I2C programming with C and Arduino
- 1. How to use I2C with AVR Sunday, April 28, 13
- 2. I2C abstract(1) AVR1 AVR2 SCL SDA Vdd I2C is one of communication systems for Microcomputer. I2C uses 2 lines, SCL(clock), SDA(data). Sunday, April 28, 13
- 3. I2C abstract(2) AVR1 AVR2 SCL SDA SCL(clock) is used to send clock for synchronization. SDA(data) is used for sending data. 1 bit data is transferred every clock. 1 0 1 0 Sunday, April 28, 13
- 4. I2C abstract(3) Master You can connect more than 2 boards. One board must be Master and the others are Slave. Each slave has own address. Master can send data to each slave using the address. Slave1 Slave2 Slave3 Slave4 SDA address1 address2 address3 address4 SCL Sunday, April 28, 13
- 5. I2C abstract(4) Master For example, if Master wants to send data to Slave2, Master sends address2 to SDA line.All Slaves receives the address. Only Slave2 replies. Slave1 Slave2 Slave3 Slave4 SDA address1 address2 address3 address4 SCL address2 reply The data is mine! I must send replay. The data is not mine. I will ignore it. The data is not mine. I will ignore it. The data is not mine. I will ignore it. Sunday, April 28, 13
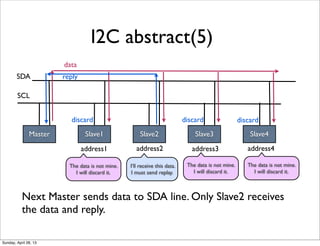
- 6. I2C abstract(5) Master Next Master sends data to SDA line. Only Slave2 receives the data and reply. Slave1 Slave2 Slave3 Slave4 SDA address1 address2 address3 address4 SCL data reply I’ll receive this data. I must send replay. The data is not mine. I will discard it. The data is not mine. I will discard it. The data is not mine. I will discard it. discard discard discard Sunday, April 28, 13
- 7. Program I2C with AVR In this instance, you use arduino uno. Arduino uno has Atmega168. I am going to explain how to program Atmega168 with C, without Arduino library. Sunday, April 28, 13
- 8. Connection SDA pin and SCL pin are fixed. On Arduino Uno, analog4 = SDA, analog 5 = SCL. Connect A4 and A5 of each Arduino. Vcc Sunday, April 28, 13
- 9. C programming on Arduino IDE Arduino language is based on C. You can use all construction of C. When you write C on Arduino IDE, you have to replace “main and while” with “setup() and loop()”. Initialize process must be inside setup() and loop process must be inside loop(). #include<avr.io.h> void main(int){ //initialize process while(1){ //loop process } } #include<avr.io.h> void setup(){ //initialize process } void loop(){ //loop process } Normal C C on Arduino IDE Sunday, April 28, 13
- 10. I2C registers(Atmega168 version) If you want to use I2C function on Microcomputer, you have to use registers for I2C. (Sometimes different microcomputers have different registers, you have to see data sheet.) These are I2C resisters(NOT all). TWAR is TWI(Slave) Address Register. Slave address is set in this register. TWBR is TWI Bit Rate Register. This is to decide SCL clock. TWCR is TWI Control Register.You can control I2C with this register. TWDR is TWI Data Register.The data to be transferred or received is set in this register. TWSR is TWI Status Register. The status of I2C communication is set in this register. TWA6 TWA5 TWA4 TWA3 TWA2 TWA1 TWA0 TWGCETWAR TWBR7 TWBR6 TWBR5 TWBR4 TWBR3 TWBR2 TWBR1 TWBR0 TWINT TWEA TWSTA TWSTO TWWC TWEN - TWIE TWD7 TWD6 TWD5 TWD4 TWD3 TWD2 TWD1 TWD0 TWS7 TWS6 TWS5 TWS4 TWS3 - TWPS1 TWPS0 TWBR TWCR TWDR TWSR Sunday, April 28, 13
- 11. The simplest I2C sequence This is the simplest sequence of I2C. If you want to send data more than 1 byte.You have to repeat (4)(5). Master Slave (1)Start (2)Slave Adress (3)Ack (4)Data (5)Ack (6)Stop Sunday, April 28, 13
- 12. How to use TWBR and TWSR First, you have to decide the communication speed(SCL) with TWBR and TWSR. SCL = CPU clock/(16+2(TWBR)xPrescaler) TWBR7 TWBR6 TWBR5 TWBR4 TWBR3 TWBR2 TWBR1 TWBR0 TWS7 TWS6 TWS5 TWS4 TWS3 - TWPS1 TWPS0 TWBR TWSR Prescaler parameter (ex) TWBR =0b00000001=1 TWBR =0b00000011=3 TWBR =0b11111111 = 255 (ex) CPU clock = 1Mhz TWBR=255 Prescaler=1 SCL = 1000000/(16+2(255)x1)=2kHz (ex) TWBR =(0<<TWPS1)|(0<<TWPS0) : prescaler is 1 TWBR =(0<<TWPS1)|(1<<TWPS0) : prescaler is 4 TWBR =(1<<TWPS1)|(1<<TWPS0) : prescaler is 64 Sunday, April 28, 13
- 13. How to use TWCR You can control I2C message with TWCR. TWINT TWEA TWSTA TWSTO TWWC TWEN - TWIETWCR Send start condition TWINT TWEA TWSTA TWSTO TWWC TWEN - TWIETWCR Clear TWINT flag after sending message TWINT TWEA TWSTA TWSTO TWWC TWEN - TWIETWCR Send stop condition TWCR = (1<<TWINT)|(1<<TWSTA)|(1<<TWEN); //Start condition while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} //After TWCR, always you have to check whether TWINT is updated TWCR = 0b10000100; //flag clear while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} TWCR = 0b10010100; //finish translation while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} Source code sample Sunday, April 28, 13
- 14. How to use TWSR You can check status of I2C sequence from TWSR. TWS7 TWS6 TWS5 TWS4 TWS3 - TWPS1 TWPS0 TWSR Source code sample //check condition if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x08){ TWDR = 0b00000010; //set slave address TWCR = 0b10000100; //flag clear while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} _delay_ms(1); if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x18){ TWDR = 0b10101010; //write data(1byte) TWCR = 0b10000100; //send data while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); _delay_ms(1); } } Sunday, April 28, 13
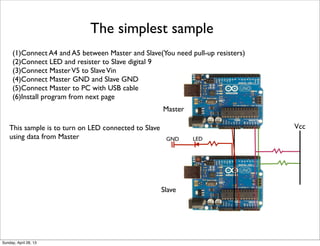
- 15. The simplest sample (1)Connect A4 and A5 between Master and Slave(You need pull-up resisters) (2)Connect LED and resister to Slave digital 9 (3)Connect MasterV5 to SlaveVin (4)Connect Master GND and Slave GND (5)Connect Master to PC with USB cable (6)Install program from next page Vcc Master Slave LEDGND This sample is to turn on LED connected to Slave using data from Master Sunday, April 28, 13
- 16. Sample code(master) #include <avr/io.h> #include <util/delay.h> void setup(){ TWSR = (0<<TWPS1)|(0<<TWPS0); //Prescaler TWBR = 0xFF; //TWBR=255 } void loop(){ TWCR = (1<<TWINT)|(1<<TWSTA)|(1<<TWEN); //Start condition while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} //wait for flag update _delay_ms(1); if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x08){ //check condition TWDR = 0b00000010; //send slave address TWCR = 0b10000100; //flag clear while(!(TWCR & 1<<TWINT)) {} _delay_ms(1); if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x18){ //check condition TWDR = 0b10101010; //write data(1byte) TWCR = 0b10000100; //send data while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); _delay_ms(1); } } TWCR = 0b10010100; //finish translation _delay_ms(2); } Sunday, April 28, 13
- 17. Sample code(slave) #include <avr/io.h> #include <util/delay.h> void setup(){ DDRB = 0xFF; //all PINB is output mode PORTB = 0x00; //all PINB is Low TWAR = 0b00000010; //salve address setting } void loop(){ TWCR = 0b11000100; //start as slave(wait for address) if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x60){ //check status while(1){ TWCR = 0b11000100; //wait for data while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0x80){ //check status char data = TWDR; //receive data PORTB = data; //insert data to PORTB } if((TWSR & 0xF8) == 0xA0){ //check stop status _delay_ms(10); break; } } } } Sunday, April 28, 13