3320 cyclic codes.ppt
- 1. 1 S.72-3320 Advanced Digital Communication (4 cr) Cyclic Codes
- 2. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 2 Targets today Taxonomy of coding How cyclic codes are defined? Systematic and nonsystematic codes Why cyclic codes are used? How their performance is defined? How practical encoding and decoding circuits are realized? How to construct cyclic codes?
- 3. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 3 Cryptography (Ciphering) Source Coding Compression Coding Line Coding Error Control Coding Error Correction Coding Error Detection Coding - Secrecy/ Security - Encryption (DES) - Redundancy removal: - Destructive (jpeg, mpeg) - Non-destructive (zip) - Makes bits equal probable - Strives to utilize channel capacity by adding extra bits - for baseband communications - RX synchronization - Spectral shaping for BW requirements - error detection - used in ARQ as in TCP/IP - feedback channel - retransmissions - quality paid by delay = FEC - no feedback channel - quality paid by redundant bits Taxonomy of Coding FEC: Forward Error Correction ARQ: Automatic Repeat Request DES: Data Encryption Standard
- 4. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 4 Background Coding is used for – error detection and/or error correction (channel coding) – ciphering (security) and compression (source coding) In coding extra bits are added or removed in data transmission Channel coding can be realized by two approaches – FEC (forward error coding) block coding, often realized by cyclic coding convolutional coding – ARQ (automatic repeat request) stop-and-wait go-back-N selective repeat … etc. Note: ARQ applies FEC for error detection
- 5. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 5 Block and convolutional coding Block coding: mapping of source bits of length k into (binary) channel input sequences n (>k) - realized by cyclic codes! Binary coding produces 2k code words of length n. Extra bits in the code words are used for error detection/correction (1) block, and (2) convolutional codes: – (n,k) block codes: Encoder output of n bits depends only on the k input bits – (n,k,L) convolutional codes: each source bit influences n(L+1) encoder output bits – n(L+1) is the constraint length – L is the memory depth Essential difference of block and conv. coding is in simplicity of design of encoding and decoding circuits (n,k) encoder k bits n bits k input bits n output bits n(L+1) output bits input bit
- 6. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 6 Why cyclic codes? For practical applications rather large n and k must be used. This is because in order to correct up to t errors it should be that Hence for , large n and k must be used (next slide) Cyclic codes are – linear: sum of any two code words is a code word – cyclic: any cyclic shift of a code word produces another code word Advantages: Encoding, decoding and syndrome computation easy by shift registers 1 2 1 ... 1 2 n k n t i n i n n n t number of syndromes (or check-bit error patterns) number of error patters in encoded word 2 1 1 1 log note: (1 ) C C t i n i R q n k n R n / 1 C R k n (n,k) block coder k-bits n-bits
- 7. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 7 Example Consider a relatively high SNR channel such that only 1 or 2 bit errors are likely to happen. Consider the ration Take a constant code rate of Rc=k/n=0.8 and consider e with some values of larger n and k : This demonstrates that long codes are more advantages when a high code rate and high error correction capability is required (10,8) 0.35, (32,24) 0.89, (50,40) 0.97 e e e (n,k) block coder k-bits n-bits Number of 2-bit error patterns Number of check-bits / C R k n 2 1 2 1 1 log ( , ) log 1 2 t c i n R i n n k n k n n e =
- 8. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 8 Some block codes that can be realized by cyclic codes (n,1) Repetition codes. High coding gain (minimum distance always n- 1), but very low rate: 1/n (n,k) Hamming codes. Minimum distance always 3. Thus can detect 2 errors and correct one error. n=2m-1, k = n - m, Maximum-length codes. For every integer there exists a maximum length code (n,k) with n = 2k - 1,dmin = 2k-1. BCH-codes. For every integer there exist a code with n = 2m-1, and where t is the error correction capability (n,k) Reed-Solomon (RS) codes. Works with k symbols that consists of m bits that are encoded to yield code words of n symbols. For these codes and Nowadays BCH and RS are very popular due to large dmin, large number of codes, and easy generation Code selection criteria: number of codes, correlation properties, code gain, code rate, error correction/detection properties 3 k 3 m k n mt min 2 1 d t 2 1,number of check symbols 2 m n n k t min 2 1 d t 1: Task: find out from literature what is meant by dual codes! 3 m
- 9. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 9 Defining cyclic codes: code polynomial and generator polynomial An (n,k) linear code X is called a cyclic code when every cyclic shift of a code X, as for instance X’, is also a code, e.g. Each (n,k) cyclic code has the associated code vector with the n-bit code polynomial Note that the (n,k) code vector has the polynomial of degree of n-1 or less. Mapping between code vector and code polynomial is one-to-one, e.g. they specify each other uniquely Manipulation of the associated polynomial is done in a Galois field (for instance GF(2)) having elements {0,1}, where operations are performed mod-2. Thus results are always {0,1} -> binary logic circuits applicable For each cyclic code, there exists only one generator polynomial whose degree equals the number of check bits q=n-k in the encoded word 1 2 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n n n p x p x p x p x X 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n x x x x X 2 3 0 1 ' ( ) n n n x x x x X 1 2 2 3 0 1 '( ) n n n n n p x p x p x p x X
- 10. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 10 Example: Generating of (7,4) cyclic code, by generator polynomial G(p)=p3 +p+1 3 2 3 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 6 5 3 (1101) 1 (1011) 1 ( 1 ) ( 1 ) 1 p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p M G X MG 4 3 p p 3 2 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 (1111111) p p p p p p p p p <- message <- encoded word <- generator The same result obtained by Maple:
- 11. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 11 Rotation of cyclic code yields another cyclic code Theorem: A single cyclic shift of X is obtained by multiplication of pX where after division by the factor pn+1 yields a cyclic code at the remainder: and by induction, any cyclic shift i is obtained by Example: Important point of implementation is is that the division by pn+1 can be realized by a tapped shift register. '( ) ( )mod( 1) n p p p p X X ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )mod( 1) i i n p p p p X X not a three-bit code (1010), divide by the common factor 3 3 ( ) 1 011 1 1 1 p p p p p X 3 ( ) p p p p X 2 101 ( ) 1 p p X 3 3 3 1 1 1 1 p p p p p n-1 bit rotated code word Shift left by 1 bit:
- 12. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 12 Prove that Note first that then, by using (1) and (2) Repeating the same division with higher degrees of p yields then '( ) ( )mod( 1) n p p p p X X 1 2 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n n n p p x p x p x p x p X 1 1 2 1 2 1 0 1 1 1 2 2 1 0 1 1 ) '( ) n n n n n n n n n n n n x p x p x p x p x p x p x x p x p x p x p X 1 2 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n n n p x p x p x p x X (1) (2) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )mod( 1) i i n p p p p X X
- 13. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 13 Cyclic codes and the common factor pn+1 Theorem: Cyclic code polynomial X can be generated by multiplying the message polynomial M of degree k-1 by the generator polynomial G of degree q=n-k where G is an q-th order factor of pn + 1. Proof: assume message polynomial: and the n-1 degree code is or in terms of G Consider then a shifted code version… 1 2 1 0 1 2 ( ) k k k k p m p m p m p x M 1 2 1 0 1 2 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) k k k k p p m p p m p p m p p x X MG G G G G 1 2 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n n n p x p x p x p x X
- 14. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 14 Now, if and assume G is a factor of pn+1 (not M), then X’(p) must be a multiple of G that we actually already proved: Therefore, X’ can be expressed by M1G for some other data vector M1 and X’ is must be a code polynomial. Continuing this way for p(i)X(p), i = 2,3… we can see that X’’, X’’’ etc are all code polynomial generated by the multiplication MG of the respective, different message polynomials Therefore, the (n,k) linear code X, generated by MG is indeed cyclic when G is selected to be a factor of pn+1 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 0 1 2 1 0 1 ( ) ( 1) ( ) ( 1) '( ) n n n n n n n n n n n p p x p x p x p x p x p x p x p x p x x p p p X X MG ( ) p p p X MG '( ) mod( 1) n X p p p MG G is a factor of pn+1 term has the factor pn+1 must be a multiple of G
- 15. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 15 Cyclic Codes & Common Factor 2 21 7 4 21, 3 7 21 1 , 7 1 3 3 2 3 2 3 3 1 x y p x y x y x y M 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 0 1 2 1 0 1 ( ) ( 1) ( ) ( 1) '( ) n n n n n n n n n n n p p x p x p x p x p x p x p x p x p x x p p p 1 M G X X MG
- 16. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 16 Factoring cyclic code generator polynomial Any factor of pn+1 with the degree of q=n-k generates an (n,k) cyclic code Example: Consider the polynomial p7+1. This can be factored as Both the factors p3+p+1 or p3,+p2+1 can be used to generate an unique cyclic code. For a message polynomial p2 +1 the following encoded word is generated: and the respective code vector (of degree n-1 or smaller) is Hence, in this example 7 3 3 2 1 ( 1)( 1)( 1) p p p p p p 2 3 5 2 ( 1)( 1) 1 p p p p p p (n,k) cyclic encoder k-bits n-bits 0101 0100111 0100111 3 7 4 q n k n k
- 17. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 17 Example of Calculus of GF(2) in Maple
- 18. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 18 Encoder applies shift registers for multiplication of data by the generator polynomial Figure shows a shift register to realize multiplication by p3 +p+1 In practice, multiplication can be realized by two equivalent topologies: unit delay element XOR-circuit Data in Encoded bits x0 x1 xn-1 Note that the tap order is opposite in these topologies Fibonacci-form Galois-form Delay element
- 19. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 19 Example: Multiplication of data by a shift register out 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 generator polynomial determines connection of taps word to be encoded Encoded word 3 4 2 ( 1)( 1) p p p p p p 3 p p 4 3 2 1 1 11101 p p p x0 x1 x3 1 2 1 2 1 0 ( ) n n n n p x p x p x p x X
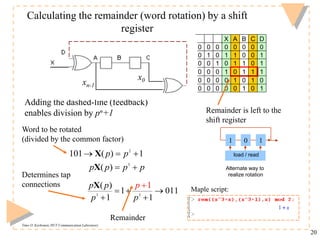
- 20. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 20 Determines tap connections Word to be rotated (divided by the common factor) Adding the dashed-line (feedback) enables division by pn+1 Remainder Calculating the remainder (word rotation) by a shift register X A B C D 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 3 101 ( ) 1 ( ) p p p p p p X X 3 3 ( ) 1 011 1 1 1 p p p p p X Remainder is left to the shift register 1 0 1 load / read Alternate way to realize rotation x0 xn-1 Maple script:
- 21. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 21 Examples of cyclic code generator polynomials The generator polynomial for an (n,k) cyclic code is defined by and G(p) is a factor of pn+1, as noted earlier. Any factor of pn+1 that has the degree q (the number of check bits) may serve as the generator polynomial. We noticed earlier that a cyclic code is generated by the multiplication where M(p) is the k-bit message to be encoded Only few of the possible generating polynomials yield high quality codes (in terms of their minimum Hamming distance) 1 1 1 ( ) 1, q q q p p p g pg q n k G ( ) ( ) ( ) p p p X M G Some cyclic codes: 3 ( ) 0 1 p p p G
- 22. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 22 Systematic cyclic codes Define the length q=n-k check vector C and the length-k message vector M by Thus the systematic n:th degree codeword polynomial is 1 1 1 0 ( ) k k p m p m p m M 1 1 1 0 ( ) q q p c p c p c C 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n k k k q q q p p m p m p m c p c p c p p p X M C How to determine the check-bits?? Question: Why these denote the message bits still the message bits are M(p) ??? check bits message bits (n,k) cyclic encoder k-bits n-bits
- 23. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 23 Determining check-bits Note that the check-vector polynomial is the remainder left over after dividing ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) q p p p p p p X M G M C ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n k p p p p p p M C M G G ( )/ ( ) n k p p p M G ( ) p C Example: (7,4) Cyclic code: ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) n k p p p p C M G 1010 -> 1010001 3 2 3 7 4 6 4 ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) p p p p p p p p p p G M M 3 2 3 3 6 4 3 2 3 2 6 4 ( ) ( ) ( )/ ( ) 1 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 ( ) ( ) ( 1)( 1) 1 n k n k p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p C Q M G M C Q G Definition of systematic cyclic code 7 7 5 1 1 5 5
- 24. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 24 Division of the generated code by the generator polynomial leaves no reminder 3 2 3 2 6 4 6 5 3 5 4 3 5 4 2 3 2 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p 3 2 3 3 6 4 3 2 3 2 6 4 ( ) ( ) ( )/ ( ) 1 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 ( ) ( ) ( 1)( 1) 1 n k n k p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p p C Q M G M C Q G 3 2 3 7 4 6 4 ( ) 1 ( ) ( ) p p p p p p p p p p G M M This can be used for error detection/correction as we inspect later
- 25. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 25 Circuit for encoding systematic cyclic codes We noticed earlier that cyclic codes can be generated by using shift registers whose feedback coefficients are determined directly by the generating polynomial For cyclic codes the generator polynomial is of the form In the circuit, first the message flows to the shift register, and feedback switch is set to ‘1’, where after check-bit-switch is turned on, and the feedback switch to ‘0’, enabling the check bits to be outputted 1 0 1 2 1 2 1 ( ) 1 q q q q q p p p g p g pg G
- 26. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 26 Decoding cyclic codes Every valid, received code word R(p) must be a multiple of G(p), otherwise an error has occurred. (Assume that the probability of noise to convert code words to other code words is very small.) Therefore dividing the R(p)/G(p) and considering the remainder as a syndrome can reveal if an error has happed and sometimes also to reveal in which bit (depending on code strength) Division is accomplished by a shift registers The error syndrome of q=n-k bits is therefore This can be expressed also in terms of the error E(p) and the code word X(p) while noting that the received word is in terms of error ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) p p p S R G ( ) ( ) ( ) p p p R X E ( ) mod ( ) ( ) / ( ) ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) p p p p p p p S X E G S E G hence
- 27. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 27 Decoding cyclic codes: syndrome table 16.20 ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) s x e x g x Using denotation of this example:
- 28. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 28 ( ) g x ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) s x r x g x Table 16.6 Decoding cyclic codes: error correction
- 29. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 29 Decoding circuit for (7,4) code syndrome computation To start with, the switch is at “0” position Then shift register is stepped until all the received code bits have entered the register This results is a 3-bit syndrome (n - k = 3 ): that is then left to the register Then the switch is turned to the position “1” that drives the syndrome out of the register Note the tap order for Galois-form shift register 3 ( ) 1 p p p G 1 0 received code syndrome x0 x1 xn-1 ( ) mod ( )/ ( ) p p p S R G
- 30. Timo O. Korhonen, HUT Communication Laboratory 30 Lessons learned You can construct cyclic codes starting from a given factored pn+1 polynomial by doing simple calculations in GF(2) You can estimate strength of designed codes You understand how to apply shift registers with cyclic codes You can design encoder circuits for your cyclic codes You understand how syndrome decoding works with cyclic codes and you can construct the respect decoder circuit