Network layer Part 5
- 1. 4 Tutun Juhana Telecommunication Engineering Network Layer (Part 5) School of Electrical Engineering & Informatics Institut Teknologi Bandung Computer Networks
- 3. Address Mapping • Static Mapping – Static mapping means creating a table that associates a logical address with a physical address This table is stored in each machine on the network – This has some limitations because physical addresses may change static mapping table must be updated periodically This overhead could affect network performance. • Dynamic Mapping – In dynamic mapping, each time a machine knows the logical address of another machine, it can use a protocol to find the physical address • Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) : logical address physical address • Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP): physical address logical address It is replaced by BOOTP dan DHCP 3
- 5. 5
- 6. 6
- 8. Encapsulation Indicating the data carried is an ARP packet 8
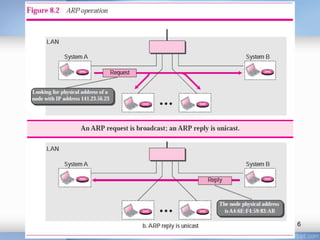
- 9. Operation • Steps Involved 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The sender knows the IP address of the target IP asks ARP to create an ARP request message, filling in the sender physical address, the sender IP address, and the target IP address. The target physical address field is filled with 0s. The message is passed to the data link layer where it is encapsulated in a frame using the physical address of the sender as the source address and the physical broadcast address as the destination address. Every host or router receives the frame. Because the frame contains a broadcast destination address, all stations remove the message and pass it to ARP. All machines except the one targeted drop the packet. The target machine recognizes the IP address. The target machine replies with an ARP reply message that contains its physical address. The message is unicast. The sender receives the reply message. It now knows the physical address of the target machine. The IP datagram, which carries data for the target machine, is now encapsulated in a frame and is unicast to the destination. 9
- 10. 10
- 11. 11
- 12. 12
- 13. Proxy ARP • A technique to create a subnetting effect. • A proxy ARP is an ARP that acts on behalf of a set of hosts • Whenever a router running a proxy ARP receives an ARP request looking for the IP address of one of these hosts, the router sends an ARP reply announcing its own hardware (physical) address • After the router receives the actual IP packet, it sends the packet to the appropriate host or router 13
- 14. 14