Antigen.pptx
- 1. Antigen: Antigen is a substance usually protein in nature and sometimes polysachharide , and glycoproteins which when introduced into vertebrate host can induce the specific immune response either by producing specific antibodies or especially sensitized T-cells or both. Types of antigen: 1. Complete antigen or immunogen: Immunogenecity is the inherent ability of a substance to induce the specific immune response resulting in the formation of antibodies.Immunogen are foreign substance which can induce an immune response by themselves. Immunogen are generally high molecular weight substances and proteinous in nature.
- 3. 2. Incomplete antigen or hapten: Hapten or incomplete antigens are those which can't induce an immune response by themselves. Haptens are not immunogenic but are antigenic because they can react with immune lymphocytes or antibodies.Haptens being incabable of inducing immune response by themselves so they are converted into immunogen with the specific molecule known as carrier.Haptens are usually low molecular weight substances and non-proteinous in nature. Hapten-carrier conjugates have native antigenic determinants of the carrier as well as new determinants of the hapten
- 4. All molecules that have the property of immunogenicity also have the property of antigenicity but the reverse is not true. For e.g some small molecules like haptens are antigenic in nature but incapable by themselves of inducing immune response. Carrier molecule: The carrier molecules for hapten may be serum proteins such as albumin,globulin or synthesized polypeptides.Haptens are of two types: •Complex haptens are relatively large molecules and combine with specific antibody forming visible precipitate.e.g Capsular polysacharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae,Cardiolipin etc. •Simple haptens do not form visible precipitate.
- 5. Factors influencing Immunogenicity: The immune system actually recognize particular macromolecules generally either proteins or polysaccharides. Proteins are the most potent immunogens than polysachharides. Immunogenicity is infleunced by following 6 properties of immunogen.They are: •Chemical Composition:Majority of immunogens are protein and glycoprotein in nature.They are the strongest antigens because they have the largest array of potential building blocks(amino acids).Heteropolymers(composed of different amino acids)are usually more immunogenic than homopolymers(composed of single amino acids).
- 6. •Molecular Size: Molecular size plays an important role in immunogenicity of the molecule.Usually the larger molecule is better immunogenic.Molecules having less than 10,000 D mass cant induce immune response and are called poor immunogens.e.g Drugs are poor immunogens. •Genetic constituent of Host:The genetic constitution of an immunized animal also influences the type of immune response as well as the degree of response.For e.g If polysachharide is injected, than no immune response is induced by rabbit. If polysachharide is injected than immune response is induced by Guinea pig
- 7. •Foreignness:The immune system possess the capacity to distinguish between self and non self molecules. Antigen are non-self in nature because our immune system generally produces no immune response against self antigen. The greater the phylogenetic distance between two species, the greater the structural difference between them.For .e.g The antigen Bovine serum albumin is not immunogenic when injected into cow but strongly immunogenic when injected into rabbit.
- 8. •Method/Route of administration and Dose:Dose and route of administration of antigen is also a factor of immunogenicity.Antigen administrated intravenously is carried first to spleen where as antigen administrated subcutaneously movest first to local lymph nodes.Differences in the lymphoid cells may be reflected in subsquent immune response.An insufficient dose will not stimulate an immune response and excessive dose also cant induce immune response but are tolerable.For e.g An 0.5 mg dose of antigen fails to induce an immune response in mice,whereas a thousand fold lower dose of same antigen can induce immune response in Guinea pig.
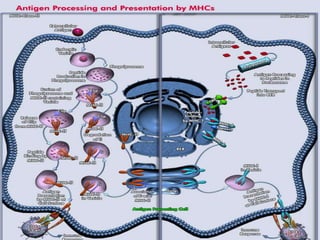
- 9. •Antigen processing and presentation:The development of both humoral and cell mediated immune response requires interaction of T-cells with antigen that has been processed and presented together with MHC molecules. Larger, insoluble macromolecules generally are more immunogenic than small and soluble ones. Macromolecules or Antigens that cannot be degraded and presented with MHC molecules are poor immunogen.Molecules which are polymer of L- amino acids can easily degraded due to the presence of degradative enzymes than D-amino acids.So our body can recognize L-amino acids and acts as high immunogens.
- 10. Antigen determinants(epitopes) Immune cells donot interact with or recognise an entire immunogen molecule,instead lymphocytes recognize discrete sites on the macromolecules called epitopes or antigenic determinants. Epitopes are the sites on or within the antigen with Which antibodies react. Immunogens or macromolecules may contain 1 or more epitope but all epitope are not immunogenic.Epitopes are very small i.e just four or five amino acids or monosachharides residue 3 D structure and steric structure.
- 11. Epitopes determine the specificity of the antigen molecule and induce the antibody response. Antibodies are specific for epitopes. There are two types of epitopes. They are: 1.B cell epitope 2.T cell epitope B cell epitope: Antigenic determinants recognized and bound by the B-cell receptor is the B cell epitope.. Epitopes recognized by the B-cell receptor are located on the surface of the antigen. B cells recognize soluble antigen that is free in solution,so B cell epitope should match paratope of Antibody.
- 13. T cell epitope:T cell receptors never bind free antigens or epitopes. It can bind epitope that are bound to MHC molecule. Epitopes recognized by the T-cell receptor are often located in the inner, unexposed side of the antigen, and become accessible to the T-cell receptors after proteolytic processing of the antigen. T cell epitopes must be processed inside the cell so as to bind to the MHC molecules. Hence T cell bound to that epitope which are presented by antigen presenting cells(APCs).
- 15. Origin of Antigen: Antigens can be classified in order of their origins. •Exogenous antigen: Exogenous antigens are those which are entered into the body from outside e.g by inhalation,ingestion or injection. By endocytosis or phagocytosis, exogenous antigens are taken into the antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and processed into fragments. APCs then present the fragments to T helper cells (CD4+) by the use of class II MHC molecules on their surface. •Endogenous antigen: Endogenous antigens are generated within our cells as a result of normal cell metabolism or because of viral or intracellular bacterial infection. The fragments are then presented on the cell surface in the complex with MHC class I molecules. If activated cytotoxic CD8+ T cells recognize them, the T cells begin to secrete various toxins that cause the lysis or apoptosisof the infected cell.
- 16. •Auto antigen: An autoantigen is antigen which is protein and are recognized as non self antigen by the immune system of patients suffering from specific auto immune diseases.The diseases condition where the immune system attacks its own body parts is called auto immune system.
- 17. Sources of antigen: •Particulate: Cells e.g tumor cells, RBC, Leukocytes Microorganisms e.g bacteria,viruses. •Soluble antigens Proteins Polysachharides Nucleic acids Exotoxins and Super antigens.
- 18. Types of Antigen: 1. T-dependent antigens:T dependent antigens are those which produces antibodies with the help of T-cells. In T- dependent antigen T-cells produces cytokines which gives the message to the B-cell for the production of antibody.The produced antibody is monoclonal in nature. 2. T- independent antigen:T-independent antigens are those which can directly stimulate the B-cells to produce antibody without the requirement of T-cell help.e.g Lipopolysachharides.Due to polymeric structure of LPS,B cell don’t require help of T-cell for the production of Antibody. The produced antibody is polyclonal in nature.
- 20. 3. Super antigen: Super antigens activate a large number of T-cells which harms the body.In some cases exposure to super antigens can be fatal.e.g Styphylococcal toxic shock toxin,Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin etc.Normally when ag is encountered in body only 0.5% T cells are activated but when super antigens are encountered 25% T cells are activated. Symptoms when super antigen is encountered are: • High T cell activation • Production of massive cytokines. • Systemic effect like vasculation leakage • Hypotension,fever,chill and shock and death. Superantigens bind non specifically to the ß sub unit of T-cell receptor and at the lateral site of MHC II molecule.
- 21. 4. Cross-reactivity antigen (Heterophile antigen): Certain antigens of similar nature present in different tissues of more than one species are called heterophile antigens or Substances that stimulate the production of antibodies capable of reacting with tissue of a wide variety of un related animals or plants are called cross reacting antigen. • Forssman antigen: • Rickettsial antigen(Weil-felix reaction) • Epstein Barr virus: • Cardiolipin antigen:
- 22. • T cells recognize linear peptides not whole proteins. • T cells only recognize epitopes when they are complexed to MHC molecules. • Therefore protein antigens must be processed and presented by other cells to be recognized by T cells. • This process is referred to as antigen processing and presentation. – Note: the association of antigenic peptides /MHC is a saturable, low-affinity interaction with a slow off/on rate. • In general CD8+ T cells recognize endogenous antigens and CD4+ T cells recognize exogenous antigens. • MHC molecules bind multiple peptides, however each T cell only recognizes one peptide. Antigen Recognition by T Cells
- 25. Antigen recognition and presentation by B cell.