Challenge@RuleML2015 Modeling Object-Relational Geolocation Knowledge in PSOA RuleML
- 1. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work PSOA RuleML Integration of Relational and Object-Centered Geospatial Data The 9th International Web Rule Symposium RuleML 2015 Challenge August 2-5, 2015 Gen Zou Faculty of Computer Science, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton, Canada 1 / 22
- 2. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 2 / 22
- 3. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 3 / 22
- 4. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Backround Geospatial data are increasingly available on the Web, e.g. Geonames and LinkedGeoData Many real-world applications are built on top of data sets that contain geospatial information Integration of application data with external geospatial data becomes a popular topic 4 / 22
- 5. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Backround Data can be modeled in different paradigms Relational Widely used for relational DBs and KBs, representing information in classical logic Object-centered Each object is represented by a unique Object IDentifier (OID) typed by a class and described by an unordered collection of slots, each being a pair of a name and a filler Integration needs cross-paradigm transformation, which can be expressed in the object-relational rule language PSOA RuleML 5 / 22
- 6. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work PSOA RuleML Integrates relational and object-oriented modeling Generalizes RIF-BLD, F-logic and POSL Uses positional-slotted object-applicative (psoa) terms General case: o # f([t1,1 ... t1,n1 ] ... [tm,1 ... tm,nm ] p1->v1 ... pk->vk) Special cases: o # f(t1 ... tn p1->v1 ... pk->vk) o # f(t1 ... tn) o # f( p1->v1 ... pk->vk) o # f 6 / 22
- 7. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 7 / 22
- 8. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Data Sets Two relational data sets and one object-centered data set, expressed in PSOA RuleML Relational data set of house rental information ex:HouseRentalInfo(1 "35 Routliffe Lane" "Toronto" "ON" "CA" 3 2500 "False"^^xs:boolean) ex:HouseRentalInfo(2 "42 Frey Crescent" "Toronto" "ON" "CA" 2 900 "True"^^xs:boolean) Columns: ref number, street, city, province, country, number of bedrooms, price, furnished 8 / 22
- 9. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Data Sets Relational data set containing addresses and their GPS coordinates gc:Geocode(43.778267 -79.426723 "35 Routliffe Lane" "Toronto" "ON" "CA") gc:Geocode(43.74242 -79.291529 "42 Frey Crescent" "Toronto" "ON" "CA") Columns: latitude, longitude, street, city, province, country Object-centered data set consisting of geospatial features (Using Geonames vocabulary) Sample fact: <http://sws.geonames.org/501324/>#gn:Feature( gn:name->"Canadian Tire" gn:featureCode->gn:S.RET geo:lat->43.7 geo:long->-79.1) 9 / 22
- 10. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 10 / 22
- 11. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Hierarchy of Geospatial Entities gr:SubwayStation##gr:GeoEntity gr:Restaurant##gr:GeoEntity gr:Store##gr:GeoEntity gr:House##gr:GeoEntity gr:HouseForRent##gr:House gr:GeoEntity class denotes all geospatial entities that can be located Every gr:GeoEntity-typed object has a slot gr:coord for the precise coordinates of its centroid 11 / 22
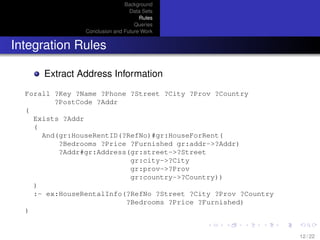
- 12. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Integration Rules Extract Address Information Forall ?Key ?Name ?Phone ?Street ?City ?Prov ?Country ?PostCode ?Addr ( Exists ?Addr ( And(gr:HouseRentID(?RefNo)#gr:HouseForRent( ?Bedrooms ?Price ?Furnished gr:addr->?Addr) ?Addr#gr:Address(gr:street->?Street gr:city->?City gr:prov->?Prov gr:country->?Country)) ) :- ex:HouseRentalInfo(?RefNo ?Street ?City ?Prov ?Country ?Bedrooms ?Price ?Furnished) ) 12 / 22
- 13. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Integration Rules Enrich each GeoEntity with its coordinates, by retrieving the coordinates from the gc:Geocode relation using its address Forall ?O ?Ad ?Lat ?Long ?Street ?City ?Prov ?Country ( ?O#gr:GeoEntity(gr:coord->gr:Point(?Lat ?Long)) :- And(?O#gr:GeoEntity(gr:addr->?Ad) ?Ad#gr:Address(gr:street->?Street gr:city->?City gr:prov->?Prov gr:country->?Country) gc:Geocode(?Lat ?Long ?Street ?City ?Prov ?Country)) ) 13 / 22
- 14. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Integration Rules Extract information from the object-centered data set Forall ?O ?Name ?Lat ?Long ( ?O#gr:GeoEntity(gr:name->?Name gr:coord->gr:Point(?Lat ?Long)) :- ?O#gn:Feature(gn:name->?Name geo:lat->?Lat geo:long->?Long) ) 14 / 22
- 15. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Integration Rules Map feature codes in the object-centered data set Forall ?O ( ?O#gr:SubwayStation :- ?O#gn:Feature(gn:featureCode->gn:S.MTRO) ) Forall ?O ( ?O#gr:Restaurant :- ?O#gn:Feature(gn:featureCode->gn:S.REST) ) Forall ?O ( ?O#gr:Store :- ?O#gn:Feature(gn:featureCode->gn:S.RET) ) 15 / 22
- 16. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Rules Inferencing Geospatial Relationships Derive a GeoEntity ?O is in an ?Area by composing the slot gr:coord and the gr:RCCProperPartOf relation Forall ?O ?Ad ?Pt ?Area ( ?O#gr:GeoEntity(gr:in->?Area) :- And( ?O#gr:GeoEntity(gr:coord->?Pt) gr:RCCProperPartOf(?Pt ?Area) ) ) 16 / 22
- 17. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Rules Inferencing Geospatial Relationships Derive gr:RCCProperPartOf between a point and a box, defined by its minimum latitude, minimum longitude, maximum latitude, and maximum longitude, through arithmetic computation Forall ?Lat ?Long ?LatMin ?LongMin ?LatMax ?LongMax ( gr:RCCProperPartOf(gr:Point(?Lat ?Long) gr:Box(?LatMin ?LongMin ?LatMax ?LongMax)) :- And ( External(pred:numeric-greater-than-or-equal(?Lat ?LatMin)) External(pred:numeric-greater-than-or-equal(?Long ?LongMin)) External(pred:numeric-less-than-or-equal(?Lat ?LatMax)) External(pred:numeric-less-than-or-equal(?Long ?LongMax)) ) ) 17 / 22
- 18. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Rules Inferencing Geospatial Relationships Derive the distance (measured in km) of ?O1 and ?O2 to be less or equal than ?Distance, used an external function gr:distanceLessEqual Forall ?Lat1 ?Long1 ?Lat2 ?Long2 ?Distance ?Name ?G ?F ( gr:inDistance(?O1 ?O2 ?Distance) :- And( ?O1#gr:GeoEntity(gr:coord->gr:Point(?Lat1 ?Long1)) ?O2#gr:GeoEntity(gr:coord->gr:Point(?Lat2 ?Long2)) External( gr:distanceLessEqual(?Lat1 ?Long1 ?Lat2 ?Long2 ?Distance))) ) 18 / 22
- 19. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 19 / 22
- 20. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Queries Look for certain type of geospatial entities in a region and their addresses And(?H#gr:HouseForRent(gr:in->gr:Box(43 -80 44 -79) gr:addr->?Addr) ?Addr#gr:Address(gr:street->?Street)) Look for all geospatial entities near a specific entity All stores within 5km of the house with reference number 2: And(?S#gr:Store(gr:name->?Name) gr:inDistance(gr:HouseRentID(2) ?S 5)) All houses within 2km of the subway station named "Spadina" And(?S#gr:SubwayStation(gn:name->"Spadina") ?H#gr:HouseForRent gr:inDistance(?H ?S 2)) 20 / 22
- 21. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Outline 1 Background 2 Data Sets 3 Rules 4 Queries 5 Conclusion and Future Work 21 / 22
- 22. Background Data Sets Rules Queries Conclusion and Future Work Conclusion and Future Work Demonstrate the usefulness of PSOA rules for the integration of geospatial data modeled in different paradigms A similar approach can be applied to enrich other data sets containing address information Future work Expand KB with required ground facts imported from a relational and/or graph database Evaluate reasoning performance on expanded KB 22 / 22






![Background
Data Sets
Rules
Queries
Conclusion and Future Work
PSOA RuleML
Integrates relational and object-oriented modeling
Generalizes RIF-BLD, F-logic and POSL
Uses positional-slotted object-applicative (psoa) terms
General case:
o # f([t1,1 ... t1,n1 ] ... [tm,1 ... tm,nm ] p1->v1 ... pk->vk)
Special cases:
o # f(t1 ... tn p1->v1 ... pk->vk)
o # f(t1 ... tn)
o # f( p1->v1 ... pk->vk)
o # f
6 / 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/challengeruleml2015modelingobject-relationalgeolocationknowledgeinpsoaruleml-150806082717-lva1-app6892/85/Challenge-RuleML2015-Modeling-Object-Relational-Geolocation-Knowledge-in-PSOA-RuleML-6-320.jpg)