Computer programming 2 Lesson 15
- 1. Computer Programming 2 Lesson 15 – Java – Methods Prepared by: Analyn G. Regaton
- 2. What is a method? In mathematics, we might have studied about functions. For example, f(x) = x2 is a function that returns a squared value of x. If x = 2, then f(2) = 4 If x = 3, f(3) = 9 and so on. Similarly, in computer programming, a function is a block of code that performs a specific task. In object-oriented programming, the method is a jargon used for function. Methods are bound to a class and they define the behavior of a class.
- 3. Types of Java methods Standard Library Methods User-defined Methods Standard Library Methods The standard library methods are built-in methods in Java that are readily available for use. These standard libraries come along with the Java Class Library (JCL) in a Java archive (*.jar) file with JVM and JRE. For example, print() is a method of java.io.PrintSteam. The print("...") method prints the string inside quotation marks. sqrt() is a method of Math class. It returns the square root of a number. Here's a working example: public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // using the sqrt() method System.out.print("Square root of 4 is: " + Math.sqrt(4)); } } Output: Square root of 4 is: 2.0
- 4. Types of Java methods Standard Library Methods User-defined Methods User-defined Method We can also create methods of our own choice to perform some task. Such methods are called user-defined methods. How to create a user-defined method? Here is how we can create a method in Java: public static void myMethod() { System.out.println("My Function called"); } Here, we have created a method named myMethod(). We can see that we have used the public, static and void before the method name. public - access modifier. It means the method can be accessed from anywhere. static - It means that the method can be accessed without any objects. void - It means that the method does not return any value. We will learn more about this later in this tutorial. This is a simple example of how we can create a method. However, the complete syntax of a method definition in Java is: modifier static returnType nameOfMethod (parameters) { // method body }
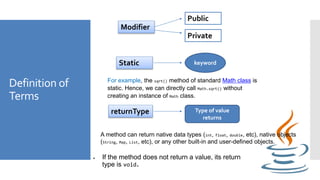
- 5. Definition of Terms Modifier Public Private Static keyword For example, the sqrt() method of standard Math class is static. Hence, we can directly call Math.sqrt() without creating an instance of Math class. returnType Type of value returns If the method does not return a value, its return type is void. A method can return native data types (int, float, double, etc), native objects (String, Map, List, etc), or any other built-in and user-defined objects.
- 6. Definition of Terms nameOf Method identifier Particular method Static keyword For example calculateArea(), display(), and so on parameters( arguments) Values passed to a method Method body Statements enclosed { }
- 7. Figure 1
- 8. How to call java method? Here's how myMethod(); This statement calls myMethod() method that was declared earlier. Working of the method call in Java •While executing the program code, it encounters myFunction(); in the code. •The execution then branches to the myFunction() method and executes code inside the body of the method. •After the execution of the method body, the program returns to the original state and executes the next statement after the method call.
- 9. Example program Let's see how we can use methods in a Java program. class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("About to encounter a method."); // method call myMethod(); System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!"); } // method definition private static void myMethod(){ System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()!"); } } Output: About to encounter a method. Printing from inside myMethod(). Method was executed successfully!
- 10. Another example class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // create object of the Output class Output obj = new Output(); System.out.println("About to encounter a method."); // calling myMethod() of Output class obj.myMethod(); System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!"); } } class Output { // public: this method can be called from outside the class public void myMethod() { System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()."); } } Output: About to encounter a method. Printing from inside myMethod(). Method was executed successfully! Since the method is not static, it is called using the object obj of the class. obj.myMethod();
- 11. Method Arguments and Return Value Let's take an example of a method returning a value. class SquareMain { public static void main(String[] args) { int result; // call the method and store returned value result = square(); System.out.println("Squared value of 10 is: " + result); } public static int square() { // return statement return 10 * 10; } } Output: Squared value of 10 is: 100
- 12. Example: Method Accepting Arguments and Returning Value public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int result, n; n = 3; result = square(n); System.out.println("Square of 3 is: " + result); n = 4; result = square(n); System.out.println("Square of 4 is: " + result); } // method static int square(int i) { return i * i; } } Output: Squared value of 3 is: 9 Squared value of 4 is: 16
- 13. We can also pass more than one argument to the Java method by using commas. For example, public class Main { // method definition public static int getIntegerSum (int i, int j) { return i + j; } // method definition public static int multiplyInteger (int x, int y) { return x * y; } public static void main(String[] args) { // calling methods System.out.println("10 + 20 = " + getIntegerSum(10, 20)); System.out.println("20 x 40 = " + multiplyInteger(20, 40)); } } Output: 10 + 20 = 30 20 x 40 = 800
- 14. What are the advantages of using methods? 1. The main advantage is code reusability. public class Main { // method defined private static int getSquare(int x){ return x * x; } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { // method call int result = getSquare(i); System.out.println("Square of " + i + " is: " + result); } } } Output: Square of 1 is: 1 Square of 2 is: 4 Square of 3 is: 9 Square of 4 is: 16 Square of 5 is: 25 2. Methods make code more readable and easier to debug.


![Types of Java
methods
Standard Library
Methods
User-defined Methods
Standard Library Methods
The standard library methods are built-in methods in Java
that are readily available for use. These standard libraries
come along with the Java Class Library (JCL) in a Java
archive (*.jar) file with JVM and JRE.
For example,
print() is a method of java.io.PrintSteam.
The print("...") method prints the string inside
quotation marks.
sqrt() is a method of Math class. It returns the square
root of a number.
Here's a working example:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// using the sqrt() method
System.out.print("Square root of 4 is: " + Math.sqrt(4));
}
}
Output:
Square root of 4 is: 2.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-3-320.jpg)




![Example
program
Let's see how we can use methods in a Java program.
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("About to encounter a method.");
// method call
myMethod();
System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!");
}
// method definition
private static void myMethod(){
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()!");
}
}
Output:
About to encounter a method.
Printing from inside myMethod().
Method was executed successfully!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-9-320.jpg)
![Another
example
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create object of the Output class
Output obj = new Output();
System.out.println("About to encounter a method.");
// calling myMethod() of Output class
obj.myMethod();
System.out.println("Method was executed successfully!");
}
}
class Output {
// public: this method can be called from outside the class
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod().");
}
}
Output:
About to encounter a method.
Printing from inside myMethod().
Method was executed successfully!
Since the method is not static, it is called using the object obj of the class.
obj.myMethod();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-10-320.jpg)
![Method
Arguments
and Return
Value
Let's take an example of a method returning a
value.
class SquareMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result;
// call the method and store returned value
result = square();
System.out.println("Squared value of 10 is: " +
result);
}
public static int square() {
// return statement
return 10 * 10;
}
}
Output:
Squared value of 10 is: 100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-11-320.jpg)
![Example:
Method
Accepting
Arguments
and Returning
Value
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result, n;
n = 3;
result = square(n);
System.out.println("Square of 3 is: " +
result);
n = 4;
result = square(n);
System.out.println("Square of 4 is: " +
result);
}
// method
static int square(int i) {
return i * i;
}
}
Output:
Squared value of 3 is: 9
Squared value of 4 is: 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-12-320.jpg)
![We can also
pass more
than one
argument to
the Java
method by
using
commas.
For example,
public class Main {
// method definition
public static int getIntegerSum (int i, int j) {
return i + j;
}
// method definition
public static int multiplyInteger (int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling methods
System.out.println("10 + 20 = " + getIntegerSum(10, 20));
System.out.println("20 x 40 = " + multiplyInteger(20, 40));
}
}
Output:
10 + 20 = 30
20 x 40 = 800](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-13-320.jpg)
![What are the
advantages of
using
methods?
1. The main advantage is code reusability.
public class Main {
// method defined
private static int getSquare(int x){
return x * x;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// method call
int result = getSquare(i);
System.out.println("Square of " + i + " is: " + result);
}
}
}
Output:
Square of 1 is: 1
Square of 2 is: 4
Square of 3 is: 9
Square of 4 is: 16
Square of 5 is: 25
2. Methods make code more readable and easier to debug.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerprogramming2-chapter13-201030083528/85/Computer-programming-2-Lesson-15-14-320.jpg)