Data structure and algorithm
- 1. NADAR SARASWATHI COLLEGE OF ARTS&SCIENCE,THENI DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE&INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY V.VANMATHY I-MSC(CS)
- 2. DATA STRUCTURE ALGORITHMS 0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound&FIFO branch and bound TOPIC:
- 3. 0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound Given N items with weight W[0…..n-1],values V[0…..n-1] and a knapsack with capacity C select the items such that: 1. The sum of weight taken into the knapsack I less than or equal to c. 2. The sum of values of the items in the knapsack I maximum among all the possible combinations
- 4. 0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound Input: N=4,C=15,V[]={10,10,12,18},W[]={2,4,6,9} Output: Items taken into the knapsack are 1101 Maximum profit is 38 Explanation: 1 in the output indicates that the item is included in the knapsack while 0 indicates that the item I excluded.
- 5. 0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound Since the maximum possible cost all owed is 15, the ways to select items are: (1101)->cost=2+4+9=15,profit=10+10+18=38 (0011)->cost=6+9=15,profit=12+18=30 (1110)->cost=2+4+6=12,profit=32 Hence,maximum profit possible wit hin a cost of 15 is 38.
- 6. 0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound Input: N=4,C=21,V[]={18,20,14,18},w[]={6,3,5,9} Output: Items taken into the knapsack are 1101 Maximum profit is 56 Explanation: Cost=6+3+9=18 Profit=18+20+18=56
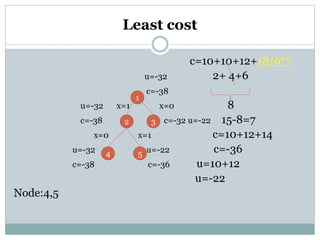
- 7. Least cost Upper= node:1 profit: 10 10 12 18 M=15 weight:2 4 6 9 c=-38u=-32 c=10+10+12+18/9*3 u=10+10+12 2 + 4 + 6 u=-32 upper value find the value remove 12 the value 18/9*3 find the answer 15-12=3 u=-32 c=10+10+12+2*3 c=-38 1 c
- 8. Least cost 18/9*5 remove value c=10+10+12+18/9*5 find the value u answer 2+ 4+6 u=-32 x=1 c=-38 10 u=-32 x=0 15-10=5 c=-38 c=-32 u=-22 c=10+12+10 c=-32 u=10+12 node: 2,3 u=-22 1 2 3
- 9. Least cost c=10+10+12+18/9*7 u=-32 2+ 4+6 c=-38 u=-32 x=1 x=0 8 c=-38 c=-32 u=-22 15-8=7 x=0 x=1 c=10+12+14 u=-32 u=-22 c=-36 c=-38 c=-36 u=10+12 u=-22 Node:4,5 1 2 3 4 5
- 10. Least cost c=10+10+12+18 u=-32 2+ 4+6 +9 x=1 c=-38 u=-32 x=0 c=-38 c=-32 u=-22 x=1 x=0 c=10+10+18 u=-32 u=-22 c=-38 c=-38 c=-36 u=10+10+18 x=1 x=0 u=-38 Node:7 u=-38 c=-38 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 k
- 11. Least cost u=-32 lower bound>upper bound x=1 x=0 c=-38 -20>-38 u=-32 u=-22 kill value node 9 c=-38 c=-32 x=1 x=0 u=-32 u=-22 x=1 x=0c=-38 c=-36 c=10+10 u=-32 u=-38 2+4 c=-38 c=-38 c=20 x=1 x=0 u=-38 node: 9 c=-38 k c=-20 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 k X={1,1,0,1} 10+10+0+18=38 2+4+0+9=15
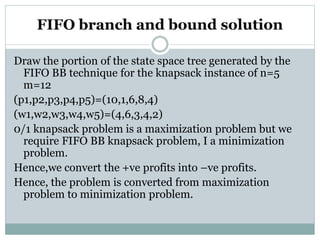
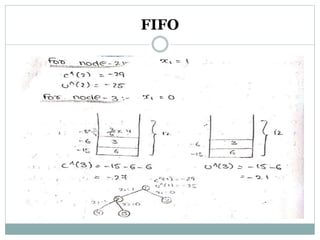
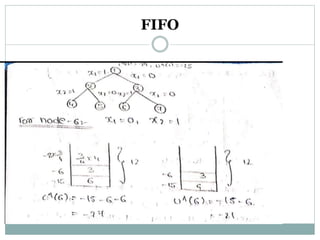
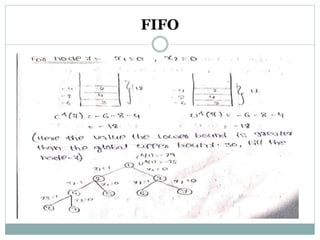
- 12. FIFO branch and bound solution Draw the portion of the state space tree generated by the FIFO BB technique for the knapsack instance of n=5 m=12 (p1,p2,p3,p4,p5)=(10,1,6,8,4) (w1,w2,w3,w4,w5)=(4,6,3,4,2) 0/1 knapsack problem is a maximization problem but we require FIFO BB knapsack problem, I a minimization problem. Hence,we convert the +ve profits into –ve profits. Hence, the problem is converted from maximization problem to minimization problem.
- 13. FIFO EXAMPLE
- 14. FIFO
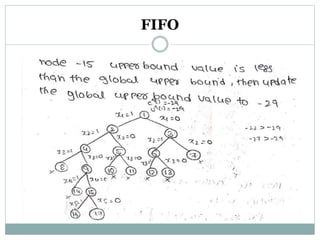
- 15. FIFO
- 16. FIFO
- 17. FIFO
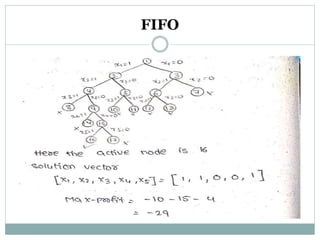
- 18. FIFO
- 19. FIFO
- 20. FIFO
- 21. FIFO
- 22. FIFO
- 23. FIFO
- 24. FIFO
- 25. FIFO


![0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound
Given N items with weight W[0…..n-1],values
V[0…..n-1] and a knapsack with capacity C select the
items such that:
1. The sum of weight taken into the knapsack I less
than or equal to c.
2. The sum of values of the items in the knapsack I
maximum among all the possible combinations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanudatastructurealgorithumppt-220121133249/85/Data-structure-and-algorithm-3-320.jpg)
![0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound
Input: N=4,C=15,V[]={10,10,12,18},W[]={2,4,6,9}
Output:
Items taken into the knapsack are
1101
Maximum profit is 38
Explanation:
1 in the output indicates that the item is included in
the knapsack while 0 indicates that the item I
excluded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanudatastructurealgorithumppt-220121133249/85/Data-structure-and-algorithm-4-320.jpg)

![0/1 knapsack least cost branch and bound
Input: N=4,C=21,V[]={18,20,14,18},w[]={6,3,5,9}
Output:
Items taken into the knapsack are
1101
Maximum profit is 56
Explanation:
Cost=6+3+9=18
Profit=18+20+18=56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanudatastructurealgorithumppt-220121133249/85/Data-structure-and-algorithm-6-320.jpg)