Design and Implementation of the Security Graph Language
- 1. Design and Implementation of Security Graph Language (SGL) Dr. Asankhaya Sharma Director of Software Engineering CA Veracode
- 2. Motivation ● Software is built using large amounts of third-party code (up to 90%) 2
- 3. Motivation ● Software is built using large amounts of third-party code (up to 90%) For each Java library depended on, 4 others are added For each JS library depended on, 9 others are added 3
- 4. ● Unaudited third-party code is a liability ○ Apache Struts (2018) ■ CVE-2018-11776: RCE via URL ■ CVE-2017-5638: RCE via HTTP headers (Equifax breach) ○ Malicious libraries (eslint-scope, crossenv, 2018) ○ Heartbleed (OpenSSL, 2017) ○ GHOST (glibc, 2015) ○ Apache Commons Collections deserialization RCE (2015) Motivation 4
- 5. ● Manual auditing is infeasible ○ Hundreds of dependencies ○ Constantly changing ● Automated audits ○ Dependency-level ■ Ensure you’re not using a vulnerable version ○ Source-level ■ Ensure you’re not vulnerable, despite using a vulnerable version ■ Ensure you won’t be vulnerable as things change ● Potential vulnerabilities, anti-patterns Motivation 5
- 6. ● Capture the space in some abstract form ● Be able to interrogate it using flexible queries ● Automate and share these queries to rule out classes of issues What we want 6
- 7. SGL ● Graph query language ● Open source security domain ○ Libraries, vulnerabilities, licenses ○ Methods, classes 7
- 8. ● Program analysis ○ Represent code as syntax trees ○ Reify intermediate structures, e.g. call graph, data-flow graph ○ Use transitive closure to derive insights ○ Query dependency graphs, etc. ● Vulnerability description ○ Structured alternative to CVEs SGL: use cases 8
- 9. Related work ● Code analysis + graph databases ○ Yamaguchi, Fabian, et al. "Modeling and discovering vulnerabilities with code property graphs." Security and Privacy (SP), 2014 IEEE Symposium on. IEEE, 2014. ● Graph query languages ○ Gremlin ○ Cypher ● Vulnerability description languages ○ OVAL 9
- 10. ● Declarative Gremlin subset ● Compiled to Gremlin ● Transitive closure ● Optimizations ○ Reachability indices ○ Query planning SGL: implementation 10
- 11. ● Graph traversals ● Represent frontier as a stream ● Composition of (stateful) functions ● Turing-complete ○ Stateful variables ○ Imperative control flow ○ Branching Detour: Gremlin 11
- 13. Detour: Gremlin ● Lots of imperative transformations ● Traversal direction matters ● Difficult to express imperative algorithms, e.g. Tarjan’s SCCs ○ Pure Gremlin is all about one homogenous stream ○ Lambda steps aren’t supported by all back ends ● Dynamically-typed ○ Use of strings as variables: cannot validate, inconsistent use ○ Everything is a traversal; actual traversals, control flow, etc. 13
- 14. Detour: Gremlin ● Security researchers are concerned with the domain, not the details of traversing graphs ● A DSL should exist at a higher level of abstraction ● SGL: ○ Is declarative ○ Provides useful primitives, e.g. an efficient SCC implementation ○ Is typed 14
- 15. “Does this version of Apache Commons Collections contain a method named readObject?” SGL: language features library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method method(name: ‘readObject’) 15
- 16. SGL: language features library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method method(name: ‘readObject’) commons-collections 3.2.2 readObject ... ... ... has_method depends_on calls calls path 16
- 17. method(name: ‘readObject’) method_in_library library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) SGL: equivalence (sort of) library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method method(name: ‘readObject’) ≈ 17
- 18. “What methods does this version of Apache Commons Collections contain?” SGL: results library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method 18
- 19. SGL: results library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method commons-collections 3.2.2 ... ... has_method depends_on calls calls ... ...has_method ... 19
- 20. method(name: ‘readObject’) method(name: ‘readExternal’) method(name: ‘readResolve’) SGL: results library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) has_method 20
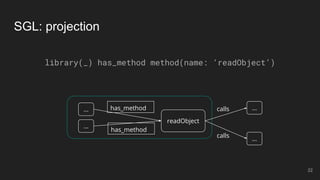
- 21. “What libraries contain the method readObject?” SGL: projection library(_) has_method method(name: ‘readObject’) 21
- 22. SGL: projection library(_) has_method method(name: ‘readObject’) 22 readObject ... ... has_method calls calls ... ... has_method
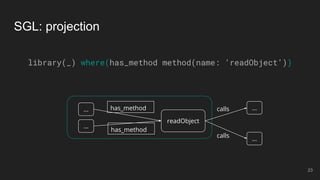
- 23. SGL: projection library(_) where(has_method method(name: ‘readObject’)) readObject ... ... has_method calls calls ... ... has_method 23
- 24. SGL: equivalence library(_) where(has_method method(name: ‘readObject’)) = method(name: ‘readObject’) method_in_library 24
- 25. “What are the direct dependencies of Apache Commons Collections?” SGL: transitive closure library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) depends_on 25
- 26. SGL: transitive closure “What are all the dependencies of Apache Commons Collections?” library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) depends_on* 26
- 27. SGL: aggregations “What are 5 dependencies of Apache Commons Collections?” library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) depends_on* limit(5) aggregation 27
- 28. “How many dependencies of Apache Commons Collections are there?” SGL: aggregations library(coord1: ‘commons-collections’, version: ‘3.2.2’) depends_on* count aggregation 28
- 29. let depends_on_method = depends_on has_method in spring depends_on_method SGL: bindings, abstraction let spring = library( 'java', 'org.springframework', 'spring-webmvc', '4.3.8.RELEASE' ) in spring depends_on* 29
- 30. Compilation let spring = library( 'java', 'org.springframework', 'spring-webmvc', '4.3.8.RELEASE' ) in spring depends_on* g.V() .hasLabel('library') .has('language', 'java') .has('group', 'org.springframework') .has('artifact', 'spring-webmvc') .has('version', '4.3.8.RELEASE') .emit().repeat(out('depends_on').dedup()) 30
- 31. Demo ● Vulnerable methods ● Struts ○ CVE-2018-11776, Apache Struts ○ A malicious URL leads to an RCE via OGNL execution ○ Source: ActionProxy#getMethod ○ Sink: OgnlUtil#compileAndExecute 31
- 32. ● Homomorphism-based bag semantics… ○ The result of evaluating a query Q against a graph G consists of all possible homomorphisms from Q to G ○ In other words, bindings of query variables are completely unconstrained, vs limited so two variables can’t be bound to the same thing* ○ Results are bags, not sets ○ Practically, like Gremlin, SPARQL, relational databases, and unlike Cypher ● … without joins (officially) * Refer to Angles et. al, 2017. "Foundations of Modern Query Languages for Graph Databases." ACM Comput. Surv. 50, 5, Article 68 (September 2017) Semantics 32
- 33. Semantics ● Not Turing-complete ○ Programs always terminate ● No side effects ○ Every expression is referentially transparent ● Easier to rewrite and analyze 33
- 34. ● We consider a type as the product of a label (e.g. library, method) and associated properties library(…) :: Library method(…) :: Method Type system 34
- 35. Type system library(…) depends_on* :: Library library(…) has_method :: Method library(…) count :: Integer library(…) where(…) :: Library 35
- 36. ● Reduction to relational algebra ○ (Inner) join: edge traversal ○ Project: where ○ Select: vertex predicates ○ Treat transitive closure as an extensional relation ● Reorder selections ● Index usage ● Join ordering Optimizations 36
- 37. ● Reorder selections ○ Gremlin does this (along with other optimizations) ○ Perform more specific selections first dedup library(coord1: ‘org.springframework’) → library(coord1: ‘org.springframework’) dedup Optimizations 37
- 38. ● Index usage ○ Gremlin takes advantage of traditional indices, e.g. for locating vertices in a graph ○ We extend this with reachability indices where possible library(…) depends_on* has_method method(…) ○ Simplest scheme: store the transitive closure in a bit matrix ■ With index: O(n2 ) space, O(1) time ■ Without: no space, O(nd ) time + potentially large constant factor ○ More sophisticated indexing schemes exist Optimizations 38
- 39. ● Join ordering (i.e. query planning) ○ Given n relations, n! possible orderings ○ Essential problems: query equivalence, cost Optimizations library(_) where(has_method method(name: ‘readObject’)) method(name: ‘readObject’) method_in_library 39
- 40. ● Join ordering ○ Enumerate equivalent queries ■ Convert queries into domain graph ■ Compute all possible orderings ■ Certain orderings are invalid, e.g. not Optimizations readObject has_method... ... has_method method1 has_method library1 40
- 41. ● Join ordering ○ Query cost ■ Observation: certain orderings are known to be more efficient ■ e.g. many-to-one relations ■ Notion of redundancy: vertices traversed which don’t contribute to result Optimizations readObject has_method ... ... has_method readObject ... ... has_method vs 41
- 42. ● Join ordering ○ Query cost ■ Redundancy for many-to-one relations ■ For the others, statistics from a large dataset ● Product of cardinalities Optimizations Edge Avg out-deg Avg in-deg depends_on 4.0 4.1 has_file 43.5 1.0 has_method 1508.2 8.9 calls 27.2 30.6 embeds 54.9 22.0 defines 14.4 1.8 has_library_hash 1.0 2.6 has_method_hash 4.9 18.6 has_library 16.4 1.9 has_vulnerable_method 1.8 2.1 has_version_range 2.9 1.2 has_class 217.0 11.1 extends 1.0 1.0 42
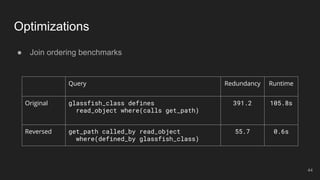
- 43. ● Join ordering benchmarks Optimizations let glassfish_class = class(regex 'org.glassfish.*') in let read_object = method(method_name:'readObject') in let get_path = method( class_name:'java/io/File', method_name:'getPath') in glassfish_class defines read_object where(calls get_path) 43
- 44. ● Join ordering benchmarks Optimizations Query Redundancy Runtime Original glassfish_class defines read_object where(calls get_path) 391.2 105.8s Reversed get_path called_by read_object where(defined_by glassfish_class) 55.7 0.6s 44
- 45. Dataset ● Public data from Maven Central ● 79M vertices, 582M edges, 76GB ● Call graphs computed with CHA/RTA ● Bytecode hashing 45
- 46. ● Program analysis ● Vulnerability description ○ Structured alternative to CVEs SGL: use cases 46
- 47. ● CVEs ○ Useful canonical identifiers for vulnerabilities ○ Not machine-readable ■ Vulnerable components must be identified manually (and inconsistently) ■ False positives on real-world systems ■ Difficult to deduplicate Describing vulnerabilities 47
- 48. Describing vulnerabilities ● Idea: represent vulnerabilities as SGL queries ○ Structured and can be processed by tools ○ Flexibility, e.g. dynamic updates ○ Trivially check by executing ○ Relate to existing data, libraries and vulns ● Deduplication ○ Relies on query equivalence; difficult for arbitrary queries ○ Idea: define a subset that can be checked for equivalence 48
- 49. ● Constant queries that can be compared, i.e. a data structure ● Normalized form ○ Bindings ○ Vertex predicates ○ No edge steps ○ Must begin at vulnerability ○ Expand syntactic sugar ○ Sort Normal forms vulnerability(cwe: 1) has_version_range union( version_range(from: '1.0', to: '1.1')) union( has_library union( library('java', 'web', 'core', '1.0'), library('java', 'web', 'core', '1.1')), has_vulnerable_method union( method('com/example/Controller', 'config', '()'))) 49
- 50. Reification ● We’d also like to use vulnerabilities in queries ○ “Find all vulnerable libraries” ● Reify vulnerabilities as vertices ● Distinguish by storing normalized query in a property 50
- 51. Considerations ● Dynamically-updating vulnerabilities ○ e.g. when a new library version is released ○ Can be convenient, but would require manual review anyway ● Finding similar vulnerabilities ○ Search for vulnerabilities associated with a library ○ Generalize query by removing predicates 51
- 52. ● Expressiveness ○ Datalog without user-defined rules ■ Computation? ○ Arbitrary “diamond” joins library(…) ?a depends_on library(…) ?b, ?a has_method method(…) method_in_library ?b Future work 52
- 53. ● More domains ○ Dataflow graphs Future work 53
- 54. Try it out ● www.sourceclear.com ● Sign up for a free trial ● Activate an agent ● SRCCLR_ENABLE_SGL=true srcclr scan --url https://github.com/srcclr/example-java-maven --sgl 54
- 55. Thank you! 55 ● Questions? ● More info - sgl.org ● Contact ○ Twitter - @asankhaya