Design device driver for wireless device using 32 bit microcontroller
- 1. A SEMINAR ON “DESIGN DEVICE DRIVER FOR WIRELESS DEVICE USING 32 BITMICROCONTROLLER” UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF VG
- 3. What is Bluetooth? • • • • • open specification low-cost low-power short-range radio technology Support point to point & point to multipoint connection
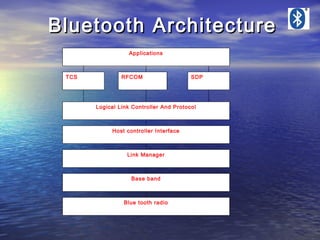
- 4. Bluetooth Architecture Applications TCS RFCOM SDP Logical Link Controller And Protocol Host controller Interface Link Manager Base band Blue tooth radio
- 5. Bluetooth Radio • Provides actual physical connection interface between Bluetooth devices • Uses faster acknowledgement and frequency hops and shorter packets • operating in the 2.4 GHz band
- 6. Base band • Physical layer of the Bluetooth • Packets transmitted in either Synchronous Connection-Oriented (SCO) links or Asynchronous Connectionless (ACL) links • Uses inquiry and paging procedures for different Bluetooth Devices
- 7. Link Manager Protocol(LMP) • Provides link setup between Bluetooth devices • Handles security aspects, such as authentication and encryption • Controls and negotiates base band packet size • Controls the connection states of the Bluetooth unit on a Pico net
- 8. Service Discovery Protocol(SDP) • Gives applications the capability to find out • • which services are provided by or available through a Bluetooth device. Once the services available are found, the SDP gives applications the capability of determining the characteristics of those services. Two or more Bluetooth devices would then be able to establish a connection.
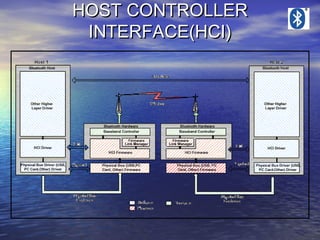
- 10. HOST CONTROLLER INTERFACE • The HCI provides a interface to the base band controller and link manager, • Access to hardware status and control registers.
- 11. HOST CONTROLLER INTERFACE • HCI exists across 3 sections, 1 The Host Firmware 2 HCI Driver (software entity) 3 Host Controller Transport Layer
- 12. L2CAP as a wireless driver • Data engine which takes data from lower base band IC to upper layer of the Bluetooth stack. • Manages the quality of service, mission from the base band to the upper layer. • Decides the channeling across the different profiles for the application i.e. SDP • Ultimately the L2CAP enables the wireless connection establishment with other Bluetooth device.
- 13. LOGICAL LINK CONTROL AND ADAPTATION PROTOCOL • L2CAP FUNCTIONAL OPERATION • L2CAP GENERAL OPERATION • L2CAP STATE MACHINE
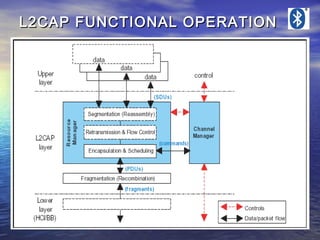
- 14. L2CAP FUNCTIONAL OPERATION • PROTOCOL MULTIPLEXING • SEGMENTATION AND REASSEMBLING • QUALITIY OF SERVICE
- 16. QUALITIY OF SERVICE • The L2CAP connection establishment process allows the exchange of information regarding the quality of service (QoS) expected between two Bluetooth units. • Each L2CAP implementation must monitor the resources used by the protocol and ensure that QoS contracts are honoured.
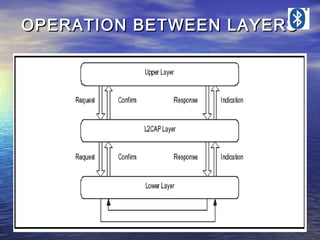
- 17. L2CAP GENERAL OPERATION • CHANNEL IDENTIFIERS • OPERATION BETWEEN DEVICES • OPERATION BETWEEN LAYERS
- 18. CHANNEL IDENTIFIERS • Channel identifiers (CIDs) are local names representing a logical channel end-point on the device. • Implementations are free to manage the CIDs in a manner best suited for that particular implementation. • CID assignment is relative to a particular device and a device can assign CIDs independently from other devices.
- 22. High Level Design L2CAP Signalling Assumptions • Prefix signal between peers at the same layer with the • • • • • • • protocol initials(L2CAP) Prefix signal between higher and lower layers with the lower layer’s initials (L2CA) Suffix requests from a higher layer to a lower layer with “Req” Suffix confirmation of requests sent from a lower layer to an upper layer with “Cnf” If a response from a lower layer is negative , the suffix “Neg” may be used instead of “Cnf”. Suffix indications of events sent from a lower layer to higher layer with “Ind” Suffix responses to indication sent from a higher layer to a lower layer with “Rsp” If a response to an indication requires further processing , “Rsp “ may be replaced with “Pnd”, which is an abbreviation for pending response.
- 23. Establishing a Connection Once An ACL connection is established across the lower layers, L2CAP packets can be sent across it. The first message sent is an L2CAP_ConnectReq. In addition to the usual Opcode, identifier, and Length fields, the message carries the following parameters • A Protocol Service Multiplexer (PSM) valve specifying the protocol using this connection • A source Channel ID(CID) the Channel CID allocated to the connection by initiating device
- 24. L2CAP THE STATE MACHINE • CLOSED • WAIT_CONNECT • WAIT_CONNECT_RSP • CONFIG • OPEN • WAIT_DISCONNECT
- 25. Configuration states and transitions
- 26. States and transitions for L2CAP
- 27. RESULT • Protocol/channel multiplexing Input: Test logger function TestLog_L2CAP_Prot_HCI () is used to provide the input like. Number of channels : 2 Channel ID: 1 Protocol RFCOM1 with Input string “Data from channel 1” Channel ID: 2 Protocol TCP with Input string “Data from channel 2” Channel ID: 3 Protocol RFCOM2 with Input string “Data from channel 3” • Output in the textlogger.txt Function used for output “TestLog_L2CAP_Prot_SDP ()” RFCOM1 mapped to Channel 1 “Data from channel1” TCP mapped to Channel 2 “Data from channel2” RFCOM2 not mapped to a channel “exceeded channel capacity”
- 28. • Segmentation and reassembly, Fragmentation and Recombination Input: Test logger function TestLog_L2CAP_Seg_HCI () is used to provide the input like. Length of Data: 120454 Bytes Packet size: 16 Bytes Input file: clouds.jpeg Output in the textlogger.txt Function used for output TestLog_L2CAP_Seg_SDP() Data is sent in 1044 packets with delimiter as 16 bytes per packet Segment Size: 32 Fragmentation unit: 32 Data Loss: NILL
- 29. • Quality of Service Input: Test logger function TestLog_L2CAP_QoS_HCI()is used to provide the input like. Length of Data: 120464 Bytes Packet size: 16 Bytes Input file: earth.jpeg Output in the textlogger.txt Function used for output TestLog_L2CAP_QoS_SDP() The variable length data 120464 bytes are received successfully
- 30. REFERENCE • [1] Bluetooth wireless Technology specifications, version 1.1. www.pal_wireless.com • [2] • [3] Palm’s Bluetooth Wireless Technology Page • • • • • http://www.palmos.com/dev/tech/bluetooth/ [4] Palm’s Bluetooth Whitepaper http://www.palmos.com/dev/tech/bluetooth/palm_bluetooth_whitepaper.pd [5] http://www.lynuxworks.com/writing device driver for on lynux OS [6] http://www.oreilly.com/catalog/linuxdrive2/chapter/book [7] C Programming language BRIAN W. KERNIGAHAN DENNIS M.RITCHIE [8] MauriceJ.Bach, “The Design of the UNIX operating system”, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited ND.
- 31. THANK YOU ALL
Editor's Notes
- #4: The Bluetooth specification is open - publicly available and royalty free. The cost factor has been a stumbling block for this technology but prices to mass produce it are improving. Signals transmit up to 10 meters but can transmit up to 100 meters with higher powered BT devices such as a network access point. Low power radios are well suited for small mobile devices. Ad-hoc communication allows for the formation of piconets on the fly. Voice is an important distinction between BT and other wireless technologies like 802.11x Anywhere – This is a WORLD standard – every country supports BT in the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band except ???

























![REFERENCE
• [1] Bluetooth wireless Technology specifications, version 1.1.
www.pal_wireless.com
• [2]
• [3] Palm’s Bluetooth Wireless Technology Page
•
•
•
•
•
http://www.palmos.com/dev/tech/bluetooth/
[4] Palm’s Bluetooth Whitepaper
http://www.palmos.com/dev/tech/bluetooth/palm_bluetooth_whitepaper.pd
[5] http://www.lynuxworks.com/writing device driver for on lynux
OS
[6] http://www.oreilly.com/catalog/linuxdrive2/chapter/book
[7] C Programming language BRIAN W. KERNIGAHAN DENNIS
M.RITCHIE
[8] MauriceJ.Bach, “The Design of the UNIX operating system”,
Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited ND.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designdevicedriverforwirelessdeviceusing32bit-microcontroller-140121233503-phpapp02/85/Design-device-driver-for-wireless-device-using-32-bit-microcontroller-30-320.jpg)
