ETT 05203 Lecture 5 IP addressing.ppt
- 2. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes IPv4 has been in use since the start of the Internet, and is widely deployed across the Internet, and home networks In the lecture you will learn IPv4 address structure IPV4 Address classes Special and reserved IP addresses Broadcast basics
- 3. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes IPv4 uses 32 bits for addressing The 32 bits are split into 4 bytes and each byte is separated by a dot(.) So it is of this form: a.b.c.d Where the value of a,b,c or d is between 0-255 decimal A typical IP address appears like this: 192.168.0.1 Networks and Nodes An IP address has two components: - A network component, and a node component.
- 4. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes As an Analogy if you think of the house address: it is of the form: House Number + Street name e.g 12 King Street. For computer networks the network number is equivalent to the street name and the house number is the Node Address The earlier implementation of IPv4 used address classes to divide the address space into network and node components This arrangement was very wasteful of IP addresses and was discontinued, but the terms Class A, B and C networks are still used
- 5. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes IPv4 Address Classes The address classes divide the address space into addresses that support: Large numbers of nodes – Intended for a large organization – Class A addresses Medium number of nodes- Class B addresses Small number of nodes- Intended for a small organization – Class C addresses IP addresses reserved for Multicast- Class D addresses IP addresses reserved for experimental purposes only ( R&D or Study) - Class E addresses
- 6. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes For Example Class A addresses would be used by large organizations (e.g. IBM) which had lots of computers (nodes) and so would require a large number of node addresses. Because there would only be a small number of large organizations then there would only be a small number of class A networks A class A address uses 8 bits for the network Address and 24 bits for node addresses. We can write this as: Net.Node.Node.Node Therefore there can only be 256 (28) Class A networks but each network can have 16,777,216 (224) nodes.
- 7. Class B network addresses were for medium sized organizations and used 2 bytes (16 bits) for the Network and 2 bytes for node addresses. We can write this as: Net.Net.Node.Node Class C network addresses were for small organizations and used 3 bytes for the Network and 1 byte for node addresses. Net.Net.Net.Node The table on the next slide shows the summary of the distribution between Network and Node IPs
- 8. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes
- 9. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes How to Distinguish IP Address Classes We need a way of distinguishing a class A address from a Class B ,C,D or E address The method used was to use the location on the first 0 bit in the most significant bits of the first byte. Class A If the first bit is 0 then we have a class A Address The other 7 bits can be either 0 or 1 (shown as X) This means that a class A network address is always in the range 0 to 127 – all zeros 00000000, and all ones – 01111111 except first 0
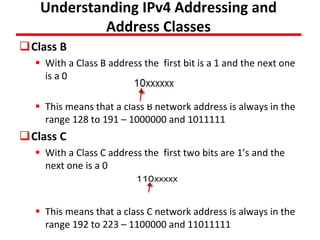
- 10. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Class B With a Class B address the first bit is a 1 and the next one is a 0 This means that a class B network address is always in the range 128 to 191 – 1000000 and 1011111 Class C With a Class C address the first two bits are 1’s and the next one is a 0 This means that a class C network address is always in the range 192 to 223 – 1100000 and 11011111
- 11. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Class D Class D addresses have their first three bits set to “1” and their fourth bit set to “0” This means that a class C network address is always in the range 223 to 239 – 1110000 and 11101111 Class D addresses are used for multicasting applications Multicasting means to transmit a single message to a select group of recipients. A simple example of multicasting is sending an e-mail message to a mailing list Teleconferencing and videoconferencing also use multicasting
- 12. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Note that multicasting refers to sending a message to a select group whereas broadcasting refers to sending a message to everyone connected to a network In multicasting data is not destined for a particular host, that is why there is no need to extract host address from the IP address, and Class D does not have any subnet mask. Class E Class E networks are defined by having the first four network address bits as 1 That encompasses addresses from 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 – 11110000 to 11111111 This IP Class is reserved for experimental purposes only (R&D or Study)
- 13. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Like Class D, this class too is not equipped with any subnet mask. This type of addressing is known as classful addressing and resulted in very wasteful IP address allocation. It was replaced by a newer method called Classless Inter- Domain Routing (CIDR)
- 14. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Public, Private and Special Addresses All IPv4 IP addresses can be divided into three major groups Global, or public, or external 0r 'WAN addresses' — those that are used in the Internet Private, or local, or internal addresses or ‘LAN addresses’ — those that are used in the local network (LAN) Special addresses – these are set aside for specific uses
- 15. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Public IP addresses It is a public global address that is used on the Internet It is assigned to every computer that connects to the Internet where each IP is unique A public IP address can be either static or dynamic A static public IP address does not change and is used primarily for hosting webpages or services on the Internet A dynamic public IP address is chosen from a pool of available addresses and changes each time one connects to the Internet (this is provided by the ISP) Most Internet users will only have a dynamic IP assigned to their computer which goes off when the computer is disconnected from the Internet. Thus when it is re-connected it gets a new IP
- 16. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Public IP addresses will be issued by an Internet Service Provider They ranges from 1 to 191 in the first octet, with the exception of the private address range established below Private IP addresses An IP address is considered private if the IP number falls within one of the IP address ranges reserved for private networks such as a Local Area Network (LAN) The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of the IP address space for private networks (local networks) Class A: 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 Class B: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 Class C: 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
- 17. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes Private IP addresses are used for numbering the computers in a private network This includes home, school and business LANs in airports and hotels which makes it possible for the computers in the network to communicate with each other Devices with private IP addresses cannot connect directly to the Internet If the private network is connected to the Internet (through an Internet connection via ISP) then each computer will have a private IP as well as a public IP It’s important for technicians to understand that IT personnel can choose to use any of the private address ranges for their LAN devices
- 18. Understanding IPv4 Addressing and Address Classes It is not at all uncommon for a technician to be confronted with a client’s network where the local addresses are in the range of 10.0.0.(1-254), and the subnet mask used is 255.255.255.0 This is an example of using Class A private addresses with a Class C subnet, which makes this a Class C network It is the subnet mask that defines which “class” a LAN network’s addressing is using
- 19. Subnetting What is Subnetting? Sub-netting allows you to create smaller network (sub networks; subnets) inside a large network by borrowing bits from the Host ID portion of the address We can use those borrowed bits to create additional networks, resulting in smaller-sized networks Suppose I want to build a network that will support up to 30 devices in different segments. Without sub-netting, I will need four (4) Class C networks to support this design. For example: Network #1: 192.168.1.0 Network #2: 192.168.2.0 Network #3: 192.168.3.0 Network #4: 192.168.4.0
- 20. Sub-netting Each of these networks will support 254 IP addresses leading to a wastage of (254 * 4) – (30 * 4) IP addresses i.e. 896 IP addresses! If you look at the design requirement of 30 hosts per network, you will discover that I only need 5 bits in the host ID portion of a Class C network to satisfy my requirement This means I still have 3 bits unused that I can use those three bits to create smaller networks For this example, let’s take the 192.168.1.0 network
- 21. Subnetting By borrowing 3 bits, I can create 8 subnets: 192.168.1.0 192.168.1.32 192.168.1.64 192.168.1.96 192.168.1.128 192.168.1.160 192.168.1.192 192.168.1.224
- 22. Subnetting These subnet addresses probably look weird to you – they look like normal IP addresses. However, looking at them in their binary form makes things clearer:
- 23. Subnetting With subnetting, not only have we used only one Class C network, we have created 8 subnets from that network, each one supporting up to 30 hosts! We can use 4 of these subnets for our network and reserve the remaining 4 subnets for future expansion This results in great waste reduction – from 896 wasted IP addresses to 120 reserved IP addresses Subnet Masks With what we have done, we have created a problem for computers and other networking devices: how are they supposed to differentiate between a subnet 192.168.1.32 and an IP address 192.168.1.32? This is where subnet masks (also called network masks) come in.
- 24. Subnetting A subnet mask is the representation of the network portion of an address. It is also made up of 32 bits with all the bits that represent the network portion being marked as 1s and the other parts marked as 0s For example, the subnet masks of the IP address classes are: Class A: 255.0.0.0 Class B: 255.255.0.0 Class C: 255.255.255.0 Therefore, a Class C network of 192.168.1.0 can be represented as: 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0.
- 25. Subnetting Note: It can also be represented using prefix length (CIDR) notation where only the 1s that make up the network portion are counted and represented with a slash e.g. 192.168.1.0/24. With subnetting, the borrowed bits from the host ID are counted as part of the network bits. So if we revisit our example above again, the 192.168.1.32 subnet can be represented as 192.168.1.32 255.255.255.224 (or 192.168.1.32/27) By comparing the “turned on” bits (i.e. 1s) in the subnet mask to an IP address, a network device can determine what network a particular IP address belongs to
- 26. Subnetting For example, the 172.17.250.145 IP address with a subnet mask of 255.255.248.0 belongs to the 172.17.248.0 255.255.248.0 subnet
- 27. Subnetting A Note about CIDR So far, we have talked about subnetting in terms of IPv4 address classes. This was just to help with understanding – most networks today are classless. In a bid to slow down the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses and also reduce the size of the Internet routing table, the IETF introduced Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) in 1993 which basically did away with classes So with CIDR, we just have a network represented by a network address and a prefix length e.g. 192.45.96.0/22. Note: In the CIDR example I used above (192.45.96.0/22), this address block will be seen as Class C in a classful network.
- 28. Subnetting Why do we need subnetting? Now that we have seen what subnetting is, let us consider some of the reasons we create subnets: Reduce wastage As we have already seen, subnetting (and CIDR on a larger scale) helps us conserve both public and private IP addresses Improve Network Performance The larger a network is, the busier (more congested) it is. With subnetting we create small network thereby increasing their performance (easy to manage)
- 29. Subnetting Isolation With smaller networks, you are able to isolate effectively as faults inside one subnet will not necessarily spread into other subnets This is also important during security incidents so that even if one subnet is affected, the entire network is not brought down Easier administration Subnetting, when done properly, can make network administration more effective. For example, a multinational organization can design their network in such a way that each region is assigned an IP address block from a larger address block and subnetting is used within regions to further divide the blocks among networks
- 30. Subnetting Minimum subnet size to accommodate a number of hosts You need to be able to design networks in such a way that there will be enough IP addresses for the devices that will be used on the network Of course, you can always go for a large address block (e.g. /8) but like we already established, using smaller- sized subnets is more efficient As such, you must be able to determine the minimum subnet size that will support a number of hosts on that subnet. To do this, all you need is to determine the number of host bits to support the number of hosts and this means counting in the order of 2
- 31. Subnetting You should also remember to account for the two (2) unusable IP addresses in a block which are used for the network address and broadcast address The table below (next slide) shows the number of usable IP addresses for /31 to /22 (i.e. 1 to 10 host bits) To conserve IP addresses, /31 subnets can be used in cases where there is no need for a network or broadcast address (e.g. point-to-point links) In effect, you can have 2 IP addresses in a /31 subnet if you use the network and broadcast addresses as host IP addresses
- 32. Subnetting Host bits per network No. of Host Bits Equivalent prefix length Subnet Mask Number of usable IP addresses 1 /31 255.255.255.254 21 -2 = 0* 2 /30 255.255.255.252 22 -2 = 2 3 /29 255.255.255.248 23 -2 = 6 4 /28 255.255.255.240 24 -2 = 14 5 /27 255.255.255.224 25 -2 = 30 6 /26 255.255.255.192 26 -2 = 62 7 /25 255.255.255.128 27 -2 = 126 8 /24 255.255.255.0 28 -2 = 254 9 /23 255.255.254.0 29 -2 = 510 10 /22 255.255.252.0 210 -2 = 1022
- 33. Subnetting You can do the same calculation for other prefix lengths. Using this table, we can determine that we need a minimum subnet size of /27 to support 25 hosts of /29 to support 4 hosts of /25 to support 120 hosts, and so on Number of Subnets in an Address Block Given an address block (network/prefix length), you can determine the number of subnets that can be gotten from that address block as long as you know the subnet size requirements. The formula for this is:
- 34. For Example: Calculate the number of /28 subnets from /24 reference address block List of Subnets in an Address block In the previous example, we determined the number of subnets that can be gotten from a particular address block. Now, we need to determine what those subnets actually are.
- 35. Sub-netting To do this, we need to know the following things: The octet in which a subnet exists 1st octet: /1 to /8 2nd octet: /9 to /16 3rd octet: /17 to /24 4th octet: /25 to /32 The maximum number of bits in the boundary (octet) in which the subnet belongs 1st octet: 8 2nd octet: 16 3rd octet: 24 4th octet: 32
- 36. Sub-netting The block size of the subnet For example, a /28 subnet exists in the 4th octet. The maximum number of bits in that octet is 32. Therefore, the block size is: Here’s another example. A /18 subnet exists in the 3rd octet. The maximum number of bits in that octet is 24. Therefore, the block size is: Example:1 What are the /27 subnets that exist in the 174.53.4.0/24 address block?
- 37. Sub-netting Solution: Number of subnets: 227-24 = 23 =8 The /27 subnet exists in the 4th octet. The maximum number of bits in that octet is 32. Therefore, the block size is: 232-27 = 25 =32 Knowing this, we can now list the subnets by starting at first network of the given block and incrementing by the block size in the 4th octet: o 174.53.4.0/27 o 174.53.4.32/27 o 174.53.4.64/27 o 174.53.4.96/27 o 174.53.4.128/27 o 174.53.4.160/27 o 174.53.4.192/27 o 174.53.4.224/27
- 38. Sub-netting Example:2 List the /23 subnets that exist in the 141.67.128.0/21 address block. Solution: Number of subnets: 223-21 = 22 =4 the /23 subnet exists in the 3rd octet. The maximum number of bits in that octet is 24. Therefore, the block size is: 224-23 = 21 =2 Knowing this, we can now list the subnets by starting at first network of the given block and incrementing by the block size in the 3rd octet: 141.67.128.0/23 141.67.130.0/23 141.67.132.0/23 141.67.134.0/23
- 39. Sub-netting Example:3 List the /13 subnets that exist in the 131.80.0.0/12 address block. Solution: Number of subnets: 213-12 = 21 =2 the /12 subnet exists in the 2nd octet. The maximum number of bits in that octet is 16. Therefore, the block size is: 216-13 = 23 = 8 The /13 subnets from the 131.80.0.0/12 block are: 131.80.0.0/13 131.88.0.0/13
- 40. Sub-netting Example:4 What is the valid address range of the 192.168.58.0/28 subnet? Solution The block size is 16 (232-28 = 24 = 16) Therefore, the next subnet will be 192.168.58.16/28 (increment the fourth octet by block size) As such, the valid address range is: Start address: 192.168.58.0 + 1 = 192.168.58.1 End address: 192.168.58.16 – 2 = 192.168.58.14 Broadcast address: 192.168.58.16 – 1 = 192.168.58.15
- 41. Sub-netting
- 42. Sub-netting
- 43. Sub-netting
- 44. Sub-netting