Introduction to programming concepts
- 1. Prepared By: Mr. Richard R. Basilio BSECE
- 2. Introduction to Programming Concepts Hardware Concepts Software Concept Software Development Life Cycle Logic Formulation Programming Cycle Algorithm Pseudocodes Flowchart Flowchart Symbol
- 3. By Wikipedia definition: A computer is a programmable machine that receives input, stores and manipulates data, and provides output in a useful format. The two principal characteristics of a computer are: It responds to a specific set of instructions in a well- defined manner. It can execute a prerecorded list of instructions (a program).
- 4. Modern computers are electronic and digital. The actual machinery -- wires, transistors, and circuits -- is called hardware; the instructions and data are called software.
- 5. Personal Computer (PC): A small, single-user computer based on a microprocessor. In addition to the microprocessor, a personal computer has a keyboard for entering data, a monitor for displaying information, and a storage device for saving data.
- 6. Workstation : A powerful, single-user computer. A workstation is like a personal computer, but it has a more powerful microprocessor and a higher-quality monitor. Minicomputer : A multi-user computer capable of supporting from 10 to hundreds of users simultaneously.
- 7. Mainframe : A powerful multi-user computer capable of supporting many hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously. Supercomputer : An extremely fast computer that can perform hundreds of millions of instructions per second.
- 8. Computers are made of the following basic components: Case with hardware inside: ▪ Power Supply - The power supply comes with the case, but this component is mentioned separately since there are various types of power supplies. ▪ Motherboard - This is where the core components of your computer reside which are listed below. Also the support cards for video, sound, networking and more are mounted into this board.
- 9. ▪ Microprocessor - This is the brain of your computer. It performs commands and instructions and controls the operation of the computer. ▪ Memory - The RAM in your system is mounted on the motherboard. This is memory that must be powered on to retain its contents. ▪ Drive controllers - The drive controllers control the interface of your system to your hard drives. The controllers let your hard drives work by controlling their operation.
- 10. Hard disk drive(s) - This is where your files are permanently stored on your computer. Also, normally, your operating system is installed here. CD-ROM drive(s) - This is normally a read only drive where files are permanently stored. There are now read/write CD-ROM drives that use special software to allow users to read from and write to these drives.
- 11. Floppy drive(s) - A floppy is a small disk storage device that today typically has about 1.4 Megabytes of memory capacity. Monitor - This device which operates like a TV set lets the user see how the computer is responding to their commands.
- 12. Keyboard - This is where the user enters text commands into the computer. Mouse - A point and click interface for entering commands which works well in graphical environments.
- 13. By Wikipedia definition: Hardware is a general term for the physical artifacts of a technology. It may also mean the physical components of a computer system, in the form of computer hardware. It is the tangible part of a computer system.
- 14. Usually the computing systems are complex devices, dealing with a vast array of information categories. The computing systems store, present, and help us modify: Text Audio Images and Data Video
- 15. The information can be represented in one or two ways: analog or digital. Analog data – is a continuous representation, analogous to the actual information it represents. Digital data - is a discrete representation, breaking the information up into separate (discrete) elements. Computers cannot work with analog information directly, so there is a need to digitize the analog information. This is done by breaking the analog information into pieces and representing those pieces using binary digits.
- 16. Digital signals are easier to transmit and offer less room for errors to occur than to analog signal. This leads to accurate data transmission that in turn leads to faster transmission rates and better productivity.
- 17. The type of data that uses in computer system is in digital form which is deals with binary representation. Binary are also far more reliable when they have to represent one out of two possible values. The electronic signals are easier to maintain if they carry only binary data.
- 18. One bit can be either 0 or 1. Therefore, one bit can represent only two outputs. To represent more than two outputs, we need multiple bits. Two bits can represent four outputs because there are four combinations of 0 and 1 that can be made from two bits: 00, 01, 10,11.
- 19. If you have an understanding of the number systems, you will understand the following topics in computer science: You will understand how to calculate network addresses You will understand how to read memory address locations in core dumps You will understand the color definitions in web and application programming You will understand many other concept
- 20. There are different types of number system that used by computer systems. Number System Bases Symbol Binary 2 0-1 Decimal 10 0-9 Octal 8 0-7 Hexadecimal 16 0-9, A-F
- 22. There are may ways on how the computer can represent a character and symbol. Some common types of codes are: ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange) UNICODE
- 23. Acronym: American Standard Code for Information Interchange. is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text.
- 24. Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code (EBCDIC) is an 8-bit character encoding (code page) used on IBM mainframe operating system. EBCDIC was devised in 1963 and 1964 by IBM and was announced with the release of the IBM System/360 line of mainframe computers.
- 25. Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The origins of Unicode date back to 1987, when Joe Becker from Xerox and Lee Collins and Mark Davis from Apple started investigating the practicalities of creating a universal character set
- 26. Bits and Bytes both measure amounts of data. However, they are typically used in two different contexts. Bits, kilobits (Kbps), and megabits (Mbps) are most often used to measure data transfer speeds. This may refer to how fast you are downloading a file, or how fast your Internet connection.
- 27. Bytes, on the other hand, are used to measure data storage. The other important difference is that bytes contain eight bits of data. Therefore, a 240Kbps download is only transferring 30KB of data per second.
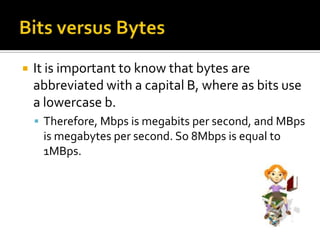
- 28. It is important to know that bytes are abbreviated with a capital B, where as bits use a lowercase b. Therefore, Mbps is megabits per second, and MBps is megabytes per second. So 8Mbps is equal to 1MBps.
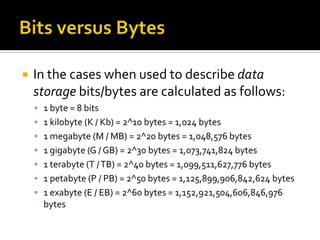
- 29. In the cases when used to describe data storage bits/bytes are calculated as follows: 1 byte = 8 bits 1 kilobyte (K / Kb) = 2^10 bytes = 1,024 bytes 1 megabyte (M / MB) = 2^20 bytes = 1,048,576 bytes 1 gigabyte (G / GB) = 2^30 bytes = 1,073,741,824 bytes 1 terabyte (T / TB) = 2^40 bytes = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes 1 petabyte (P / PB) = 2^50 bytes = 1,125,899,906,842,624 bytes 1 exabyte (E / EB) = 2^60 bytes = 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bytes
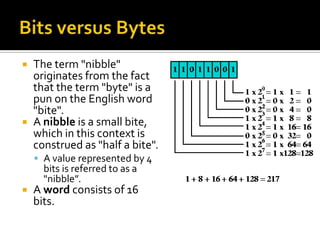
- 30. The term "nibble" originates from the fact that the term "byte" is a pun on the English word "bite". A nibble is a small bite, which in this context is construed as "half a bite". A value represented by 4 bits is referred to as a "nibble”. A word consists of 16 bits.
- 31. A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. The International System of Units (SI) specifies a set of unit prefixes known as SI prefixes or metric prefixes. An SI prefix is a name that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a decimal multiple or fraction of the unit. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to the unit symbol.
- 32. Digital electronics represent signals by discrete levels, rather than by a continuous range. In most cases these states are represented by two voltage levels: one near to zero volts and a higher level near the supply voltage.
- 33. A digital circuit is often constructed from small electronic circuits called logic gates. Each logic gate represents a function of Boolean logic. A logic gate is an arrangement of electrically controlled switches.
- 34. This model of the typical digital computer is often called the von Neumann computer. Programs and data are stored in the same memory: primary memory. The computer can only perform one instruction at a time. Primary Memory Input CPU Output Units (Central Processing Unit) Units
- 35. Input/Output (I/O): Refers to the process of getting information into and out of the computer. Input: Those parts of the computer receiving information to programs. Output: Those parts of the computer that provide results of computation to the person using the computer. Floppy disk drives and Hard disk drives.
- 36. Display monitors: Hi-resolution monitors come in two types: ▪ Cathode ray tube (CRT) - Streams of electrons make phosphors glow on a large vacuum tube. ▪ Liquid crystal display (LCD) - A flat panel display that uses crystals to let varying amounts of different colored light to pass through it. ▪ Developed primarily for portable computers. Audio Output Disk Output (CD-R, CD-RW)
- 37. The Central Processing Unit ( CPU) Often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. Responsible for controlling all activities of the computer system. The three major components of the CPU are: 1. Arithmetic Logic Unit (Computations performed) Accumulator (Results of computations kept here) 2. Control Unit (Has two locations where numbers are kept) Instruction Register (Instruction placed here for analysis) Program Counter (Which instruction will be performed next?) 3. Instruction Decoding Unit (Decodes the instruction) Motherboard: The place where most of the electronics including the CPU are mounted.
- 38. Primary storage or memory: Is where the data and program that are currently in operation or being accessed are stored during use. Consists of electronic circuits: Extremely fast and expensive. Two types: ▪ RAM (non-permanent) ▪ Programs and data can be stored here for the computer’s use. ▪ Volatile: All information will be lost once the computer shuts down. ▪ ROM (permanent) ▪ Contents do not change.
- 39. Software consists of computer programs. The process of writing (or coding) programs called programming. Individual who perform this task are called programmers. Computer programs include documentation, which is written descriptions of the function of the program.
- 40. There are two major types of software. System Software – is set of instructions that serves primarily as a intermediary between computer hardware and application programs, and may also be directly manipulated by knowledge users. Application Software – is a set of computer instructions that provide more specific functionality to a user.
- 41. Is the class of programs that control and support the computer software and its information- processing activities. System software an be grouped into two major functional categories : System control programs ▪ It control the use of hardware, software, and data resource of a computer system. ▪ The main system control is the operating system that provides an interface between the user and the hardware. System support programs ▪ It supports the operations, management, and users of a computer system providing a variety of support services.
- 42. Application software includes: Proprietary application software ▪ Addresses a specific or unique business need of a company. Such specific software programs developed for a particular company by a vendor are called contract software.
- 43. Off-the-shelf application software ▪ Can be purchased, leased or rented from a vendor includes the special purpose programs or packages such as inventory control or payroll. ▪ General purpose, off-the-shelf application programs that supports general types of the processing are referred to personal application software. ▪ Personal application software is designed is to help individual users increase their productivity.
- 44. Support Module An auxillary set of instructions used in conjunction with the main software program. Data Module Contains data (not supplied by the user) necessary for the execution of certain tasks.
- 45. A computer program (also a software program, or just a program) is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task for a computer.
- 46. Computer programming (often shortened to programming or coding) is the process of designing, writing, testing, debugging / troubleshooting, and maintaining the source code of computer programs.
- 47. SDLC is a methodolgy that is typically used to develop, maintain and replace information system for improving the quality of the software design and development process. Software development is an intricate process that requires a lot of planning, implementation and testing.
- 48. What is the importance of SDLC? The software development life cycle (SDLC) is a pre-set framework that is used by all software development companies for through understanding and developing effective information systems and software.
- 49. SDLC involves five phases. Each plays an important role in creating a good system. The said phase are: Planning – This phase includes the information about the requirement for the proposed system. This is also known as feasibility phase.
- 50. Analysis – The main goal in this phase is to identify the requirements for new software or simply change several aspect in the current working software. ▪ The activities performed by the analyst during this phase are: ▪ Study the current software ▪ Determine software requirement ▪ Write requirement report
- 51. Design – During this phase, the developer of the software translates the result of the previous phase into actual design or specifications of the software. ▪ The activites performed in this phase are: ▪ Identify potential solutions ▪ Evaluate solutions and select best ▪ Select hardware and software ▪ Develop application specification ▪ Obtain approval implement the new software
- 52. Implementation – During this phase, implementing the software will include several phase: ▪ Coding – Creation of the actual program ▪ Testing – Both programmer and analyst submit the software to various “quality testing” to discover if there are any bugs within the software ▪ Installation – after coding and testing is done, the actual software must be installed and slowly or completely replace the old software
- 53. Maintenance – This phase is used to make necessary patches ato remove found errors. ▪ This is where the software is systematically repaired and improved based on errors or possible new requirement found.
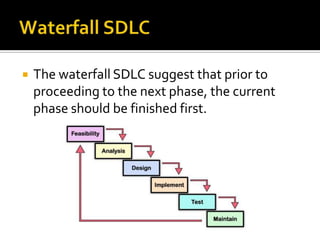
- 54. The waterfall SDLC suggest that prior to proceeding to the next phase, the current phase should be finished first.