Key functions in_oracle_sql
- 1. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 1 of 6 Key Functions in Oracle SQL Use this Quick Reference Guide to locate functions you can use in your queries. There are five tables in this guide: Grouping Functions, Numeric Functions, String Functions, Date Functions, and Conversion Functions. Grouping functions may include either of the keywords DISTINCT or ALL. ALL is the default if neither is specified and uses all selected rows in the calculation. DISTINCT uses only one row for each value in the calculation. Example: • AVG(ALL 2,2,3,3,4) and AVG(2,2,3,3,4) both return 2.8. • AVG(DISTINCT 2,2,3,3,4) returns 3. Grouping Meaning and Example Functions and Parameters AVG(expression) Returns the average of the values in a set of rows Example: • AVG(endowment_unit_value) COUNT(expression) Returns the number of rows in the set or COUNT(*) Note: If you include an expression, COUNT returns only the number of rows in which the expression is not null. COUNT(*) counts all rows. Since no HDW table contains nulls, COUNT(expression) and COUNT(*) are equivalent. Example: • COUNT(*) • COUNT(DISTINCT univ_id_no) MAX(expression) Returns the largest value from a set of rows Note: See the GREATEST function if you want the largest of a series of values in a single row. Example (returns the date on which the most recent change was made to dwfnd_rf_tub_cds): • MAX(tub_last_update_dt) (continued on next page) DD004QR3 - Key Functions In Oracle SQL.Doc 4-1 Rev 3, 10/1/99
- 2. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 2 of 6 Grouping Functions (continued) Grouping Meaning and Example Functions and Parameters MIN(expression) Returns the smallest value from a set of rows Note: See the LEAST function if you want the smallest of a series of values in a single row. Example (returns the lowest rate used for fringe-benefit assessments): • MIN(fringe_assessment_rate) SUM(expression) Adds the value for all rows in the query or for all rows with the same values for columns listed in the GROUP BY clause Example: • SUM(pcard_transaction_distr_amt) Numeric Meaning and Example Functions and Parameters ABS(number) Removes the sign, if any, returning a positive value Example (selects actual_amt values above 10,000 and below –10,000): • ABS(actual_amt) > 10000 GREATEST(value1, Returns the largest of the values in the list value2, …) Note: This function is used for multiple values in the same row. See the MAX function if you want the largest value from a group of rows. Example: • GREATEST(pcard_dt_modified, pcard_dt_reviewed) LEAST(value1, Returns the smallest of the values in the list value2, …) Note: This function is used for multiple values in the same row. See the MIN function if you want the smallest value from a group of rows. Example: • LEAST(pcard_dt_modified, pcard_dt_reviewed, pcard_swept_dt) (continued on next page) DD004QR3 - Key Functions 4-2 In Oracle SQL.Doc Rev 3, 10/1/99
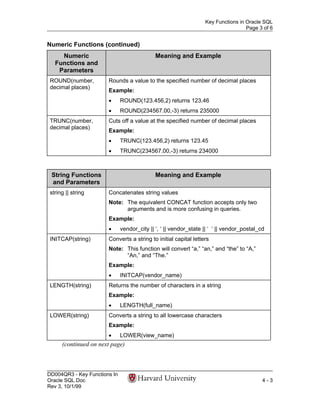
- 3. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 3 of 6 Numeric Functions (continued) Numeric Meaning and Example Functions and Parameters ROUND(number, Rounds a value to the specified number of decimal places decimal places) Example: • ROUND(123.456,2) returns 123.46 • ROUND(234567.00,-3) returns 235000 TRUNC(number, Cuts off a value at the specified number of decimal places decimal places) Example: • TRUNC(123.456,2) returns 123.45 • TRUNC(234567.00,-3) returns 234000 String Functions Meaning and Example and Parameters string || string Concatenates string values Note: The equivalent CONCAT function accepts only two arguments and is more confusing in queries. Example: • vendor_city || ‘, ‘ || vendor_state || ‘ ‘ || vendor_postal_cd INITCAP(string) Converts a string to initial capital letters Note: This function will convert “a,” “an,” and “the” to “A,” “An,” and “The.” Example: • INITCAP(vendor_name) LENGTH(string) Returns the number of characters in a string Example: • LENGTH(full_name) LOWER(string) Converts a string to all lowercase characters Example: • LOWER(view_name) (continued on next page) DD004QR3 - Key Functions In Oracle SQL.Doc 4-3 Rev 3, 10/1/99
- 4. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 4 of 6 String Functions (continued) String Functions Meaning and Example and Parameters SUBSTR(string, Extracts a portion of a string starting value, Note: If the starting value is 0, it is treated as 1. If the number of starting-value is negative, Oracle counts backward characters) from the end of the string. If the starting value is positive, Oracle counts forward from the beginning of the string. Example: • SUBSTR(‘ABCDEF’,2,3) returns ‘BCD’ • SUBSTR(‘abcdef’,-4,3) returns ‘cde’ UPPER(string) Converts a string to all uppercase characters Example: • WHERE UPPER(lodging_location) LIKE ‘%CHICAGO%’ Date Functions Meaning and Example and Parameters ADD_MONTHS Adds the specified number of months to the date value (date, number of (subtracts months if the number of months is negative) months) Note: If the result would be a date beyond the end of the month, Oracle returns the last day of the resulting month. Example (selects expense reports not settled for more than two months after trip end): • WHERE report_gl_export_dt > ADD_MONTHS(report_ trip_end_or_expense_dt, 2) LAST_DAY(date) Returns the last day of the month that contains the date Example (returns ‘29-FEB-2000’): • LAST_DAY(‘15-FEB-2000’) (continued on next page) DD004QR3 - Key Functions 4-4 In Oracle SQL.Doc Rev 3, 10/1/99
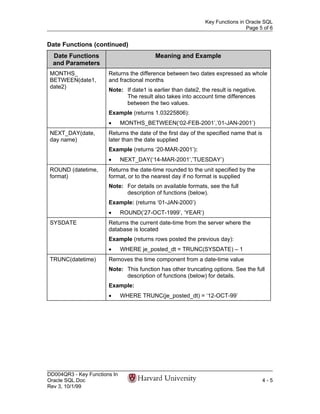
- 5. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 5 of 6 Date Functions (continued) Date Functions Meaning and Example and Parameters MONTHS_ Returns the difference between two dates expressed as whole BETWEEN(date1, and fractional months date2) Note: If date1 is earlier than date2, the result is negative. The result also takes into account time differences between the two values. Example (returns 1.03225806): • MONTHS_BETWEEN(‘02-FEB-2001’,’01-JAN-2001’) NEXT_DAY(date, Returns the date of the first day of the specified name that is day name) later than the date supplied Example (returns ‘20-MAR-2001’): • NEXT_DAY(‘14-MAR-2001’,’TUESDAY’) ROUND (datetime, Returns the date-time rounded to the unit specified by the format) format, or to the nearest day if no format is supplied Note: For details on available formats, see the full description of functions (below). Example: (returns ‘01-JAN-2000’) • ROUND(‘27-OCT-1999’, ‘YEAR’) SYSDATE Returns the current date-time from the server where the database is located Example (returns rows posted the previous day): • WHERE je_posted_dt = TRUNC(SYSDATE) – 1 TRUNC(datetime) Removes the time component from a date-time value Note: This function has other truncating options. See the full description of functions (below) for details. Example: • WHERE TRUNC(je_posted_dt) = ‘12-OCT-99’ DD004QR3 - Key Functions In Oracle SQL.Doc 4-5 Rev 3, 10/1/99
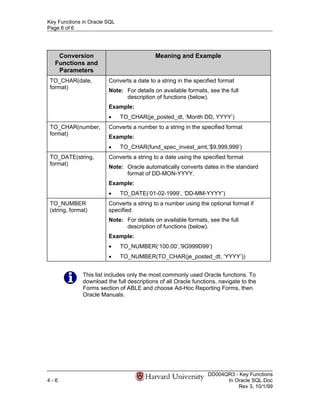
- 6. Key Functions in Oracle SQL Page 6 of 6 Conversion Meaning and Example Functions and Parameters TO_CHAR(date, Converts a date to a string in the specified format format) Note: For details on available formats, see the full description of functions (below). Example: • TO_CHAR(je_posted_dt, ‘Month DD, YYYY’) TO_CHAR(number, Converts a number to a string in the specified format format) Example: • TO_CHAR(fund_spec_invest_amt,’$9,999,999’) TO_DATE(string, Converts a string to a date using the specified format format) Note: Oracle automatically converts dates in the standard format of DD-MON-YYYY. Example: • TO_DATE(‘01-02-1999’, ‘DD-MM-YYYY’) TO_NUMBER Converts a string to a number using the optional format if (string, format) specified Note: For details on available formats, see the full description of functions (below). Example: • TO_NUMBER(‘100.00’,’9G999D99’) • TO_NUMBER(TO_CHAR(je_posted_dt, ‘YYYY’)) This list includes only the most commonly used Oracle functions. To download the full descriptions of all Oracle functions, navigate to the Forms section of ABLE and choose Ad-Hoc Reporting Forms, then Oracle Manuals. DD004QR3 - Key Functions 4-6 In Oracle SQL.Doc Rev 3, 10/1/99