Lecture 1 - Introduction to architecture
- 2. 1. INTRODUCTION TO ARCHITECTURE Lecture Contents: 1.1 What is architecture? 1.2 Basics design elements and design principles 1.3 Architecture and civil engineering
- 3. Qn. Why do you need Fundamentals of Architecture? Describing architecture as ‘fundamental’ might suggest that there is a simplicity that underlies its expression. Architecture is a language that we understand because we inhabit buildings, they surround us and create our world. To achieve a piece of architecture requires engaging with a process of thinking, drawing and designing, a process that ultimately produces a building.
- 4. The etymology of the word ‘architecture’ can be defined as arkhi meaning chief and tekton meaning builder. Architecture is the art and science of designing buildings and other Physical structures. It is both a SCIENCE & an ART: Science - must produce structures which are: well planned, practical & strong… ART – it must produce structures which are aesthetically pleasing, Creative, … It Shows us the struggle or history of the society. Architecture is a reflection of our society in attitude, customs, desires, needs and technology. for Buildings to fulfill architecture, it must contain these three things: Firmness – structural integrity & durability. Space – spatial functionality Delight – aesthetics Plus the use of materials, technology, textures, light & shadow.
- 5. Architecture is about the making of places where people spend their lives. Architecture is not only concerned with the exterior and interior design of a building, but the environment as a whole. Architecture is mostly about human beings living in a better way than before.”
- 6. Other examples: Falling Water by Frank Lioyd Wright Stair and wall Interior space Interaction with nature
- 7. 1.2 Basics design elements and design principles The Concept of Design Many people would think of design as some kind of effort in beautifying the outward appearance of things. Certainly mere beautification is one aspect of design, but design is much more than this. Design is not just ornamentation. The well-designed chair not only has a pleasing outward appearance, but stands firmly on the ground and provides adequate comfort for whoever sits on it. Furthermore, it should be safe and quite durable, able to be produced at a comparatively economic cost, packed and shipped conveniently and it should have a specific function, whether for working, resting, dining or other human activities.
- 8. Cont. Design: is an activity that attempts to modify the environment, so that it becomes a better place to exist in. Major characteristic features about design: 1. PROCESS Any process is expected to have a definite beginning that sets it in motion and a definite end where the motion stops. 2. PROBLEM SOLVING This in turn implies that the activity that we call design starts by identifying a problem to be solved and tries to use inputs from the human mind (the designer) to come up with possible solutions 3. CREATIVE ACTIVITY There might be more than one possible solution to a specific problem. A designer is expected to explore possibilities and use his power of imagination to generate the best solution that is unique and original at the same time.
- 9. Elements The elements are components or parts which can be isolated and defined in any work of art i.e. specific "parts" of a design solution. They are the structure of the work, and can carry a wide variety of messages. Architectural design elements include: - Point - Line - Shape(plane) - Form - Space - Color - Texture
- 10. A Point - A point is an element that marks a position in the visual space. - perceived as having no length, width or depth. - Static, centralized and direction less. - Expresses stability and calmness
- 11. LINE - a point in motion creates the appearance of a line. - So Line is an extension of a point. - a line is considered to have a single dimension.(i.e. Distance) Physical Characteristics - Length: - Value - Direction - Position - Types of line curved, bent, irregular, wavy, etc
- 12. Vertical – Represents dignity, formality, stability, and strength Horizontal – Represents calm , peace, and relaxation
- 13. Diagonal – Represents action, activity, excitement, and movement Curved – Represents freedom, the natural, having the appearance of softness, and creates a soothing feeling or mood
- 14. Shape/plane When a line is extended in a direction other than its intrinsic one, it forms a plane. Physical Characteristics - Surface - Orientation Primary Shapes Circle Triangle Square Volume / Solid A plane in motion creates a volume/solid
- 15. Primary solids - Includes cube, sphere, cone, cylinder, and pyramid - Created from primary shapes. - Regular - Symmetrical - Stable Primary solids - Circles - generate spheres and cylinders. - Triangles - generate cones and pyramids. - Square - generates cube.
- 16. Solid / volume Used to: - Define or enclose space - Study relationships between components of a volume - Create a complex form in the three dimensional visual field
- 17. Color Color is considered the most important element of design. Each color has three characteristics: - hue, - value, and - intensity. Warm Colors Reds, oranges, yellows Cool Colors Blues, purples, greens
- 18. TEXTURE Tactile quality of an object surface Is the roughness or smoothness of a surface as perceived by our sense of sight. Due to the visual and tactile features of texture different feeling could be suggested. Physical and psychological comfort - Smooth textures in an interior can seem cold - Rough texture have a warmth about them that makes most people feel at ease.
- 19. Principles/ Organization of Design Elements of Design are placed under the rules or principles of design. So, design is the organization of the elements of art according to the laws or principles of design. The principles of good design are the tools used by an artist or designer to create an effective composition or design. The principles are: balance, movement, repetition, emphasis, simplicity, contrast, proportion, space, and unity.
- 20. 1. Balance - a feeling of equality of weight, attention, or attraction of the various elements within the composition as a means of accomplishing unity 2. Movement - the suggestion of action or direction, the path our eyes follow when we look at a work of art 3. Repetition and rhythm - the act of repeating an element either regularly or irregularly resulting in a rhythm of the repeating elements. 4. Emphasis - the stress placed on a single area of a work or unifying visual theme 5. Simplicity (a.k.a. visual economy) - the elimination of all non-essential elements or details to reveal the essence of a form 6. Contrast - the difference between elements or the opposition to various elements 7. Proportion - the relation of two things in size, number, amount, or degree 8. Space - the interval or measurable distance between objects or forms (two dimensional or three dimensional) 9. Unity - the relationship between the individual parts and the whole of a composition
- 21. Ordering Principles In a composition that uses elements, regardless of the logic of organization, we can establish an ordered relationship between the elements by the use of Ordering Principles. Axis: - A line defined between two points in space about which forms can be arranged in a symmetrical or balanced manner. This line can be actual or implied. The overall impact of the introduction of an axis is that it establishes an order of significance between the elements of design.
- 22. Cont. SYMMETRY: - It is nothing but the arrangement of objects that are equidistant from an actual or implied axis.
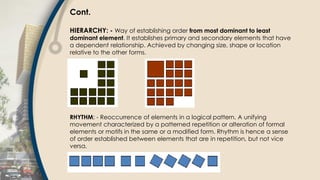
- 23. Cont. HIERARCHY: - Way of establishing order from most dominant to least dominant element. It establishes primary and secondary elements that have a dependent relationship. Achieved by changing size, shape or location relative to the other forms. RHYTHM: - Reoccurrence of elements in a logical pattern. A unifying movement characterized by a patterned repetition or alteration of formal elements or motifs in the same or a modified form. Rhythm is hence a sense of order established between elements that are in repetition, but not vice versa.
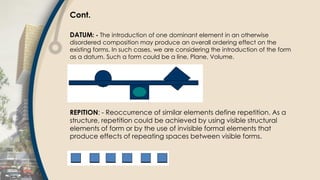
- 24. Cont. DATUM: - The introduction of one dominant element in an otherwise disordered composition may produce an overall ordering effect on the existing forms. In such cases, we are considering the introduction of the form as a datum. Such a form could be a line, Plane, Volume. REPITION: - Reoccurrence of similar elements define repetition. As a structure, repetition could be achieved by using visible structural elements of form or by the use of invisible formal elements that produce effects of repeating spaces between visible forms.
- 25. 3. Architecture and Civil Engineering In the construction industry, development projects usually require the knowledge and understanding of civil engineering and architecture. These are important disciplines that deal with the process of creating structures, such as buildings, airports, churches and houses. Both professions have critical functions that are essential in any construction job and they rely on one another to accomplish a given task. Civil engineers: - Measure and map the earth’s surface. - Design and supervise the construction of bridges, tunnels, large buildings, dams, and coastal structures. - Plan, layout, construct, and maintain railroads, highways, and airports. - Devise systems for the control and efficient flow of traffic. - Plan and build river navigation and flood control projects. - Provide plants and systems for water supply and sewage and refuse disposal.
- 26. Cont. Civil engineering is a diverse field. Most specialties fall under the categories of: • Structural • Environmental • Geotechnical • Water Resources • Transportation • Construction
- 27. Architecture and Civil Engineering: Similarity - Both Civil Engineering and Architecture are involved in planning and designing structures. - They rely on one-another to accomplish a given task. Differences - They have well-defined roles that make them distinguishable from each other. Architecture focuses more on the spatial functionality and aesthetics of the development work and is more concerned with the artistry, look, feel and functionality of the design, - While Civil Engineering concentrates on the structural elements of the design, making certain that the structure can endure normal and extreme conditions.
- 28. Summary, Architecture's primary concern is designing the development work while civil engineering's responsibility is ensuring that the design can be implemented in a safe and reliable manner. Civil engineers and architects may sometimes overlap each other's work but a good relationship between the two professions will make the construction job more effective and successful.
- 29. Any Question?