Markup language classification, designing static and dynamic
- 1. MARKUP LANGUAGE CLASSIFICATION, DESIGNING STATIC AND DYNAMIC PAGES Ankita Bhalla
- 2. MARKUP LANGUAGES A markup language is a language that illustrates text so that the computer can manipulate the text. Most markup languages are human readable because the illustrations are written in a way to distinguish them from the text. In HTML, XML, and XHTML, the markup tags are enclosed between < and >. For example: <p> this is a paragraph of text written in HTML </p>
- 3. DIFFERENT MARKUP LANGUAGES Following are the different markup languages: •HTML •XML •XHTML •DHTML •VoiceXML •LaTeX
- 4. HTML (HYPERTEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE) HTML is a defined standard markup language. HyperText Markup Language is the language of the web. All web pages are written in HTML. HTML defines the way that images, multimedia, and text are displayed in web browsers.
- 5. XML (EXTENSIBLE MARKUP LANGUAGE) XML is a language for writing markup languages. Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human- readable and machine-readable. There are also several standardized languages already created with XML: MathML for defining mathematics, SMIL for working with multimedia, XHTML, and many others.
- 6. XHTML XHTML stands for extended hypertext markup language. XHTML 1.0 is HTML 4.0 redefined to meet the XML standard. XHTML is written in lower case. While HTML tags can be written in UPPER case, MiXeD case, or lower case, to be correct, XHTML tags must be all lower case. All XHTML elements must have an end tag. Elements with only one tag, such as HR and IMG need a closing slash (/) at the end of the tag: <hr /> <img /> XHTML requires that tags are nested correctly. If you open a bold (B) element and then an italics (I) element, you must close the italics element (</i>) before you close the bold (</b>).
- 7. DHTML DHTML stand for Dynamic Hypertext Markup Language. Dynamic HTML, or DHTML, is used to create interactive and animated web sites by using a combination of a static markup language (such as HTML), a client-side scripting language (such as JavaScript), a presentation definition language DHTML allows scripting languages to change variables in a web page's definition language, which in turn affects the look and function of page content, after the page has been fully loaded and during the viewing process.
- 8. VOICEXML VoiceXML is used in Voice interaction between humans and computer, mainly in systems that enable you to, for example check your credit card balance over the phone. The logive- like dialogue management and speech recognition- is defined by voiceXML. LaTeX A document markup language used mainly by mathematicians, authors, etc to typeset their content. It is suitable for representing mathematical formulas.
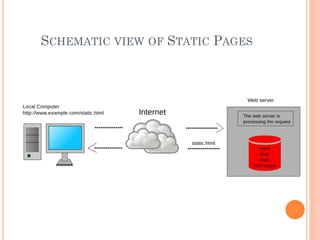
- 9. WHAT IS A STATIC WEBPAGE..?? A Static Webpage is a Webpage that is delivered to user exactly as stored. Static WebPages are HTML documents stored as files in file system and made available by the web server over HTTP.
- 10. SCHEMATIC VIEW OF STATIC PAGES
- 11. CREATING STATIC PAGES HTML documents can be created using a professional HTML editor like: * Adobe Dreamweaver * Microsoft Expression Web * CoffeeCup HTML Editor However, the most recommended and easily available editor is Notepad.
- 12. STEPS TO CREATE A STATIC PAGE IN NOTEPAD Step I: Start Notepad Start > All Programs > Accessories > Notepad Step II: Edit your HTML with Notepad
- 13. STEPS TO CREATE A STATIC PAGE IN NOTEPAD Step III: Save your HTML Select Save as… in Notepads File menu. You can use either .htm or .html extension to save your document as HTML page. Step IV: Run the HTML in your Browser
- 14. HTML ATTRRIBUTES HTML elements can have attributes. Attributes provide additional information about an element. Attributes are always specified in the start tag. Attributes come in name/value pairs like: attribute_name="value"
- 15. HTML HEADINGS Headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags. <h1> defines the most important heading, <h6> defines the least important heading.
- 16. Browsers automatically add some empty space (a margin) before and after each heading. HTML HEADINGS
- 17. HTML PARAGRAPHS Paragraphs are defined with <p> tag.
- 18. HTML HYPERLINKS A hyperlink (or link) is a word, group of words, or image that you can click on to jump to a new document or a new section within the current document. Links are specified in HTML using the <a> tag. Syntax: <a href="url">Link text</a>
- 19. HTML HYPERLINKS Example: <a href=“www.facebook.com”>Go to Facebook</a>
- 20. HTML HEAD The <head> element is a container for all the head elements. Elements inside <head> can include scripts, instruct the browser where to find style sheets, provide meta information, and more. <title>, <base>, <link>, <meta>, <script>, and <style> can be added to HTML Head
- 21. HTML <TITLE> TAG The <title> tag defines the title of the document. The <title> tag defines a title in the browser toolbar.
- 22. HTML IMAGES Images are defined with the <img> tag. The <img> tag has no closing tag. To display an image on a page, you need to use the src attribute. Src stands for "source". The value of the src attribute is the URL of the image you want to display. Syntax: <img src="url" alt="some_text"> The required ‘alt’ attribute specifies an alternate text for an image, if the image cannot be displayed.
- 23. HTML IMAGES Example: <img src="batman.jpg" alt="Batman“ height=200 width=400> The height and width attributes are used to specify the height and width of an image.
- 24. HTML STYLES - CSS Cascading Style Sheets(CSS) is used to style HTML elements. CSS can be added to HTML using the style attribute in HTML elements. Example: <p style="color:orange;margin-left:200px;">This is a paragraph.</p>
- 25. CSS PROPERTIES PROPERTY DESCRIPTION background-color Specifies the background color of HTML element background-image Sets the background image for an element opacity Sets the opacity level for an element height Sets the height of an element width Sets the width of an element font-family Specifies the font family for text font-size Specifies the font size for text font-weight Specifies the font weight of a font Color Sets the color of text text-decoration Specifies the decoration added to text. text-align Specifies the alignment of text.
- 26. HTML TABLES Tables are defined with the <table> tag. A table is divided into rows with the <tr> tag, and each row is divided into data cells with the <td> tag. A <td> tag can contain text, links, images, lists, forms, other tables, etc.
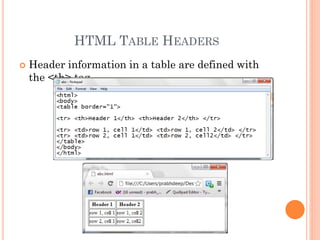
- 28. HTML TABLE HEADERS Header information in a table are defined with the <th> tag.
- 29. HTML TABLE ATTRIBUTES ATTRIBUTE PURPOSE Border Specifies the size of table border (in pixels) Width Specifies table width (in pixels) Cell spacing Specifies the distance between two cells Cell padding Specifies the space between cell content and table border Align Used to specify alignment of the table
- 30. HTML TEXT FORMATTING HTML Text Formatting Tags TAG DESCRIPTION <b> Defines bold text <big> Defines big text <emp> Defines Emphasized text <i> Defines italicised text <small> Defines small text <strong> Defines strong text <sub> Defines subscripted text <sup> Defines superscripted text <ins> Defines inderted text <del> Defines deleted text
- 31. HTML LISTS The most common HTML lists are ordered and unordered lists: An ordered list: 1. First List Item 2. Second List Item 3. Third List Item An Unordered lost: * List Item * List Item * List Item
- 32. UNORDERED LIST
- 33. ORDERED LIST
- 34. HTML LAYOUTS - USING <DIV> ELEMENTS The <div> element is a block level element used for grouping HTML elements. Multiple columns are created by using <div> elements. CSS are used to position elements, or to create backgrounds or colorful look for the pages.
- 35. HTML LAYOUTS - USING <DIV> ELEMENTS
- 36. HTML LAYOUTS - USING <DIV> ELEMENTS
- 38. INTRODUCTION o Dynamic web pages are pages that are generated at the time of access by a user or change as a result of interaction with the user. o For example, the page may change with the time of day, the user that accesses the webpage, or the type of user interaction.
- 39. TYPES Client side scripting Scripts that are interpreted on client side i.e browser of client. Example: JavaScript Server side scripting Scripts that run at server end and return the HTML document as the output. Example: asp, php
- 40. DRAWBACK OF STATIC PAGES Difficult to maintain when a site gets large. Difficult to keep consistent and up to date. Offers little visitor personalization (all would have to be client side)
- 41. USE OF DYNAMIC PAGES Offers highly personalized and customized visitor options. Database access improves the personalized experience (as opposed to using just client side cookies) Scripts can read in data sources and display it differently depending on how it is run. Can create the illusion of being updated regularly using time and date sensitive routines (or even randomisers) to display pre- written text.
- 42. STATIC VS DYNAMIC PAGE PROCESSING
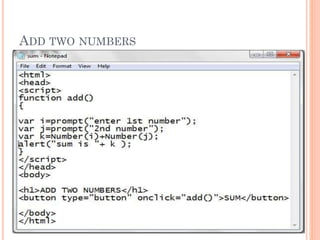
- 43. JAVASCRIPT CREATING DYNAMIC PAGES Syntax: <html> <head> </head> <title> </title> <body> <script> …..code….. </script> </body> </html>
- 46. ADD TWO NUMBERS
- 48. DYNAMIC IMAGES Dynamic images means the images on a page that are displayed on a web page at run time or are changed at run time. We can rotate pics, or zoom a pic on functions like mouseover, mouseclick etc.
- 49. CASCADING STYLE SHEETS Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation semantics (the look and formatting) of a document written in a mark up language. Its most common application is to style web pages written in HTML and XHTML
- 50. DYNAMIC IMAGES USING CSS
- 51. .
- 52. … .
- 53. THANK YOU !!