Modul PLC Programming.pdf
- 1. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 1 CHAPTER 4 – PROGRAMMING Main Objective: Provide an overview of PLC programming method using programming languages commonly used. Specific Objectives: After completed this chapter, student will know the major component 1. Familiarise with the PLC Programming system 2. Able to explain PLC programming method using Ladder Diagram and mnemonic code., Instruction set and logic function. 3. Understand and use Ladder Diagram and mnemonic code to solve control systems circuits. 4. Explain the following logic instruction set: Load. Load Not, Out, And, And Not, Or, Or Not, And Ld and Or Ld. 5. Explain sequential instruction set: No Operation, End, Interlock, Jump, Keep, Set/Reset and Differential Up/Down. 6. Explain the timer and Counter instruction set and execute timer/counter application solution methods. 4.0 Introduction PLC programming process is to plan activities such as design and write a program to perform the required tasks. Here are the parts that should be there in a PLC program. Start Starting an operation Operating Mode Determining the origin of the device input / output and also the starting point The Reset Controlling the operation of start / stop it manually or automatically in the program Operations / Ordering Process Program design as required by the task Signal Output Trigger output devices. Status Output Display indicator light or alarm. End Stop the process./operation
- 2. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 2 4.1 Programming Language IEC 1131-3 is the international standard for programmable controller programming languages. The following is a list of programming languages specified by this standard: i. Ladder Diagram (LD) ii. Instruction List (IL) iii. Structured Text (ST) iv. Sequential Function Chart (SFC) v. Function Block Diagram (FBD) One of the primary benefits of the standard is that it allows multiple languages to be used within the same programmable controller. This allows the program developer to select the language best suited to each particular task. i. Ladder Diagram Ladder Diagram is kind of graphical programming language that changed the relay control wiring circuit diagram. Ladder Diagram contains tracks from left to right contact diagram (see Figure below). This platform is connected to contact elements available normally open - NO or available Normally closed - NC through the current path and loop elements. Ladder diagram also shows the control circuit and the display function and a combination of the sequence of operations for each branch of the horizontal lines separately. Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Instruction There are other methods to program PLCs. One of the earliest techniques involved mnemonic instructions. These instructions can be derived directly from the ladder logic diagrams and entered into the PLC through a simple programming terminal. ii. Instruction List This low-level language is similar to Assembly language and is useful in cases where small functions are repeated often. Although it is powerful, it is considered to be difficult to learn. +ve -ve INPUT CONDITION OUTPUT ACTION NO NC
- 3. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 3 Example Calculate new weight by subtracting tare weight from net weight. LD weigh_command JMPC WEIGH_NOW ST ENO RET WEIGH_NOW: LD gross_weight SUB tare_weight iii. Structured Text Structured Text (ST) is a high level textual language that is a Pascal like language. It is very flexible and intuitive for writing control algorithms. Structured Text uses operators such as logical branching, multiple branching, and loops. People trained in computer programming languages often find it the easiest language to use for programming control logic. When symbolic addressing is used, ST programs resemble sentences, making it highly intelligible to beginner users as well. ST is ideal for tasks requiring complex math, algorithms or decision-making. Its concise format allows a large algorithm to be displayed on a single. Benefits of Structured Text People trained in computer languages can easily program control logic Symbols make the programs easy to understand Programs can be created in any text editor Runs as fast as ladder Example 1 We have Motor that will be controlled manually by 2 push buttons (Start Push Button, and Stop Push Button). When the Start Push Button is pushed then the Motor will be turned ON. and when the Stop Push Button is Pushed then we want to stop the Motor. (Security logic has been taken off this logic, for the purpose of domonstration.) IF StartPb THEN Motor := 1; END_IF; IF StopPb THEN Motor := 0; END_IF;
- 4. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 4 iv. Sequential Function Chart These are similar to flowcharts, but much more powerful. This method is much different from flowcharts because it does not have to follow a single path through the flowchart. SFC programming offers a graphical method of organizing the program. The three main components of an SFC are steps, actions and transitions. Steps are merely chunks of logic, i.e., a unit of programming logic that accomplishes a particular control task. Actions are the individual aspects of that task. Transitions are the mechanisms used to move from one task to another. Control logic for each Step, Action and Transition is programmed in one of the other languages such as Ladder Diagram or Structured Text. Is a kind of graphic language (see Figure 4.1.4). Elements are the steps, transitions, choice and parallel branch. Each step shows the status of the control program processes the active or inactive. One step consists of action based on the transition. The action consists of the sequence structure itself. v. Function Block Diagram Like SFC, FBD is a graphical language that allows programming in other languages (ladder, instruction list, or structured text) to be nested within the FBD. In FBD, program elements appear as blocks which are "wired" together in a manner resembling a circuit diagram. FBD is most useful in those applications involving a high degree of information/data flow between control components, such as process control. Step 1 MOTOR (Start) Step 2 Step 3 MOTOR (Stop) Transition 1 Transition 2 Action Sample Program In Sequencial Function Chart Language
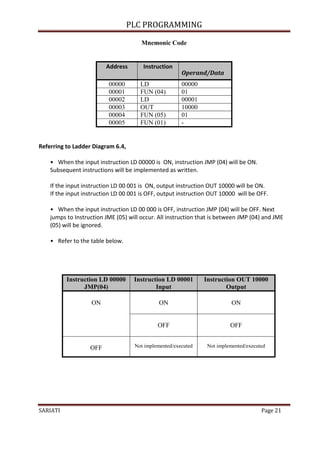
- 5. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 5 4.1.1 Basic Ladder Diagram A ladder diagram consists of a vertical line on the left and right are called bus bars and horizontal lines to the right, called the instruction lines. Along the lines of command are logical combinations of conditions (conditions) that will determine when and how the instructions on the right at all to be implemented. Based on the picture above, one should note that a ladder diagram consists of two basic parts: left section also called conditional, and a right section which has instructions. When a condition is fulfilled, instruction is executed. Example Ladder Diagram as shown in figure below . instruction 00000 00001 00002 00003 00004 00005 00006 00007 Sample Ladder Diagram 00007 00007
- 6. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 6 The pairs of vertical lines along the branch line is called the conditions. These conditions consist of two, namely: i. Normally open condition (NO) ii. Normally closed condition (NC) The numbers in each case to determine the bit operations per instruction. Each command in ladder diagram either ON or OFF depending on the status of specified bit operations. Notes: Normally open condition is ON if the bit operation is ON and will be OFF if the bit operation is OFF . Normally closed condition is ON if the bit operation is OFF and will be OFF if bit operation is ON. 4.2 Basic Terms 4.2.1 Execution Conditions Logical combination of the ON and OFF states gathered to establish an instruction to be implemented. This condition is called Execution Condition. Refer to figure below. Instructions will be in the Execution Conditions ON when IR 00000 is ON, IR 00001 is OFF and IR 00002 is ON. Instruction n Instruction n 00000 Normally Open Normally Closed 00000 Instruction executed when the IR bit 00000 is ON Instruction executed when the IR bit 00000 is OFF Example of Ladder Diagram instruction 00000 00001 00002 Examples of Execution Conditions
- 7. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 7 4.2.2 Operand Bits Bit operations for each instruction can consist of any of the bits in the memory area IR, SR, HR, TC or TR. This means that the conditions in Ladder Diagram can be determined by the bit I / O, flags , work bits , timer / counters and others. Table 4.3.2 shows the memory map refers to the PLC type SYSMAC OMRON-CQM1H. DATA AREA BIT FUNCTION Input Area IR00000 - IR01515 Used as the input bit Output Area IR10000 – IR11515 used as output bits. IR Area Work Area IR21600 – IR21915 Bit has no function specifically. Can be used freely in the program SR Area SR24400 – SR25507 This bit use to do certain functions, such as flags (flags) and control bits. TR Area TR 0 – TR 7 This bit is used to temporarily store the status ON / OFF on the branches of the program HR Area HR 0000 – HR 9915 This bits used to store data and maintain the status ON / OFF when the power is off. Timer/Counter Area TC 000 – TC 511 The same number used for the timer and counter. Use for TC000 to TC002. `interval timer '
- 8. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 8 4.2.3 Logic Block The respond to an instruction is determined by the relationship between the conditions on the instruction line that connects them. Any group of conditions that formed to produce a logical result is called a logical block. Refer to Figure 4.3.3. 4.2.4 Instruction Block A block of instruction is composed of all the instructions contained in a block. Block is obtained by drawing a horizontal line without cutting a vertical line and vice versa. Refer to Figure 4.3.3. 4.2.5 Mnemonic Code Ladder diagram can not be read by the Programming Console. Thus the ladder diagram should be changed to mnemonic code. Mnemonic code provides the same information as ladder diagram and can be typed directly on Programming Console. ADDRESS INSTRUCTION OPERASI / DATA 00000 LD 00000 00001 OR 00001 00002 AND 00003 00003 AND LD 00004 OUT 10000 00005 TIM 000 #0050 00006 CNT 002 #0010 00007 FUN 01 instruction 00000 00002 0000 1 0000 3 Example Logic Block Example Mnemonic Code
- 9. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 9 ANSWER ALL THESE QUESTIONS 1. What do you understand about Ladder Diagram and draw one (1) example of a Ladder Diagram. 2. Explain the purpose of the following terms: i. The logic blocks ii. The Instruction block Reference; 1. http://www.kronotech.com/ST/st.htm
- 10. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 10 UNIT 5: BASIC INSTRUCTIONS SET OBJECTIVE: Describe the set of instructions used in PLC programming SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of this unit student should be able to: i. Know the functions of the instruction LOAD, LOAD NOT, OUT, AND, AND NOT, OR, NOT and OR END ii. Know the function block instruction AND LD and OR LD. iii. Convert Ladder diagram to Mnemonic Code. NOTE: These instructions will be explained later is based on OMRON PLC brands – SYSMAC CQM1H 5.0 Introduction There are a lot of instructions used to develop the PLC program. Each instruction has a respective function. 5.1 LD - LOAD Instruction These instructions are use to start a line of the program. It is used in the first contacts in the normally open condition (NO). Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation: The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when IR 00000 is ON. instruction 00000 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 instruction
- 11. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 11 5.2 LD NOT - LOAD NOT Instruction These instructions are use to start a line of the program. It is used in the first contacts in the normally closed condition (NC). Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when IR 00000 is OFF 5.3 AND - AND Instruction These instructions are used in the second contact in a normally open (NO) and a series with previous contacts Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when IR 00000 and IR 00001 are ON instruction n 00000 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD NOT 00000 00001 instruction instruction n 00000 00001 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 AND 00001 00002 instruction
- 12. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 12 5.4 AND NOT - AND NOT Instruction These instructions are used in the second contact in a normally closed (NC) and in series with previous contacts Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when IR 00000 ON and IR 00001 are OFF. 5.5 OR - OR Instruction These instructions are used in the second contact in a normally open (NO) and in line (parallel) with previous contacts. . Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when either IR 00000 or IR 00001 are ON. instruction n 00000 00001 Address Instruction Operand/ Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 AND NOT 00001 00002 instruction instruction n 00000 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 OR 00001 00002 instruction 00001
- 13. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 13 5.6 OR NOT - OR NOT Instruction These instructions are used in the second contact in a normally closed (NC) and in line (parallel) with previous contacts Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Explanation The Execution Conditions of the instruction on the right will be ON when either IR 00000 is ON or IR 00001 is OFF or IR 00000 ON, IR 00001 OFF simultaneously 5.7 OUT - OUTPUT Instruction These instructions are used for the coil output. Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code IR 10000 will ON when IR 00000 is ON . 5.8 END END instruction has no physical contact device. It is the last instruction required for completion of a program. If no END instruction, the program cannot be implemented instruction n 00000 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 OR NOT 00001 00002 instruction 0000 1 00000 Address Instruction Operand/ Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 OUT 10000 10000
- 14. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 14 Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code For PLC type OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, the instruction FUN 01 is the END instruction. 5.9 OR LD - BLOCK LOGIC OR Instruction The OR LD instruction has no physical contact device. Only a programming tool for solving complex OR function as a series of contacts LD (or LD NOT), in parallel with a series of other contacts. Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code END 00000 00001 Address Instruction Operand/ Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 AND NOT 00001 00002 OUT 10000 00003 FUN 01 1000 0 END 00000 00001 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 AND 00001 00002 LD 00002 00003 AND 00003 00004 OR LD 00005 OUT 10000 00006 FUN 01 1000 0 00002 00003
- 15. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 15 5.10 AND LD - BLOCK LOGIC AND Instruction The AND LD no physical contact device. Only a programming tool for solving complex functions such as AND connects a number of OR, OR NOT, OR LD in the series. Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code 00001 5.11 OR LD and AND LD When both logic block instruction is to be used in Ladder Diagram, a program must be written from the bottom up to merge logic blocks. For example, ladder diagram below: Logic block of instruction for the last two blocks (blocks b1 and b2 blocks) are written first and then followed by the first logic block instruction (block a). END 00000 00001 Address Instruction Operand/ Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 OR 00002 00002 LD 00001 00003 OR 00003 00004 AND LD 00005 OUT 10000 00006 FUN 01 10000 00002 00003
- 16. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 16 Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Example. END 00000 00001 1000 0 00002 00003 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD NOT 00000 00001 AND 00001 00002 LD 00002 00003 AND NOT 00003 00004 LD NOT 00004 00005 AND 00005 00006 OR LD 00007 AND LD 00008 OUT 10000 00009 FUN 01 00004 00005 Block a Block b2 Block b1 Block b2 Block a Block b1 Block b2 + Block b1 = Block b Block b, Block a
- 17. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 17 UNIT 6 (4.3) : SEQUENTIAL INSTRUCTION SET Objective Describe the sequence instruction set NO OPERATION, END, INTERLOCK, JUMP, KEEP, SET / RESET and DIFFERENTIATE UP / DOWN Specific Objectives: At the end of this unit you should be able to understand set of instructions the following sequence: NO OPERATION END INTERLOCK JUMP KEEP SET/RESET DIFFERENTIATE UP / DOWN 6.0 Introduction In this unit you will be exposed to a sequence of instructions which usually acts as the last instruction in the instruction line. Instruction sequence SET, RESET, KEEP, DIFFERENTIATE UP, DOWN DIFFERENTIATE, used to ON and OFF state output bits in the IR. These instructions are used to control the status of the other bits in the IR or in other areas. INTERLOCK instruction sequences can overcome the problem of storing execution conditions, in the branches of the ladder diagram. JUMP instruction sequence can be used to control devices that require a product that can last a long time. 6.1 NO OPERATION – NOP ( 00 ) These instructions do not have a ladder diagram symbols and will not do any operations. When you remove the memory in this instruction will be displayed on the console screen PLC programming.
- 18. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 18 6.2 END – END(01) Acting as the last instruction for each program (see figure 6.2) There is no instruction will be written after the END instruction (01) implemented. If there is no END instruction (01) in the program, the task would not be implemented and verse NO END LIST is displayed on the programming PLC console screen. Ladder Diagram shows the END instruction Mnemonic Code 6.3 INTERLOCK [ IL ( 02 ) ] DAN INTERLOCK CLEAR [ ILC ( 03 ) ] IL (02) and ILC (03) must be used together. These instructions are used to solve the problem of storing execution conditions at branch points. When the INTERLOCK instruction is ON as shown in Ladder Diagram 6.3, the implementation of the INTERLOCK instruction will control all of the instruction execution until the instruction ‘INTERLOCK CLEAR’. When the INTERLOCK instruction is OFF, INTERLOCK CLEAR instruction will reset the program operation. To set the INTERLOCK instruction for PLC tpe OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H is FUN 02 for INTERLOCK instruction and FUN 03 is INTERLOCK CLEAR instruction. 00000 END 10000 Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD NOT 00000 00001 OUT 10000 00002 FUN(01)
- 19. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 19 00000 00001 10000 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 FUN 02 - 00002 LD 00001 00003 OUT 10000 00004 FUN 03 - 00005 FUN 01 - Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.3, When the instruction input LD 00 000 is ON, the instruction IL (02) will be ON. Instruction output OUT 10 000 will depend on the instruction input ON LD 00001 and LD 00000. If the input instruction LD 00 001 ON, output OUT 10000 will be ON. If the input instruction LD 00 001 OFF, output OUT 10000 will be OFF. In the event that the input instructions LD 00 000 OFF, instruction IL (02) is OFF. Instructions to the output OUT 10 000 will be OFF. Next program ILC (03) will reset the program. IL (02) ILC (03) END Figure 6.3 : Ladder Diagram shows IL ( 02 ) dan ILC ( 03 ) instruction
- 20. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 20 Refer the table below: Instructions LD 00000 IL(02) Instructions LD 00001 Input Instructions OUT 10000 Output ON ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF 6.4 JUMP [ JMP (04) ] DAN JUMP END [ JME (05) ] Instructions JMP (04) is usually used in pairs with the command JME (05) for the jump. JMP (04) is a command to determine the starting point of the jump and JME (05) is the instruction that the direction of the jump.( where to jump). When the instruction JMP (04) is ON, no jump will occur and the program will be implemented as written. When the instruction JMP (04) is OFF, a jump to the instruction JME (05) which has the same number will be done. Further instructions are the instructions JME (05) will be implemented. Instructions JUMP and JUMP END can use the numbers from the range of 00 to 99. To set the instruction for PLC type OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, is FUN 04 for JUMP instruction and FUN 05 instruction is the JUMP END instruction. 00000 00001 10000 JMP (04) 01 JME (05) 01 END Figure 6.4 : Ladder Diagram shows JUMP instruction
- 21. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 21 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 FUN (04) 01 00002 LD 00001 00003 OUT 10000 00004 FUN (05) 01 00005 FUN (01) - Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.4, • When the input instruction LD 00000 is ON, instruction JMP (04) will be ON. Subsequent instructions will be implemented as written. If the input instruction LD 00 001 is ON, output instruction OUT 10000 will be ON. If the input instruction LD 00 001 is OFF, output instruction OUT 10000 will be OFF. • When the input instruction LD 00 000 is OFF, instruction JMP (04) will be OFF. Next jumps to Instruction JME (05) will occur. All instruction that is between JMP (04) and JME (05) will be ignored. • Refer to the table below. Instruction LD 00000 JMP(04) Instruction LD 00001 Input Instruction OUT 10000 Output ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF Not implemented/executed Not implemented/executed
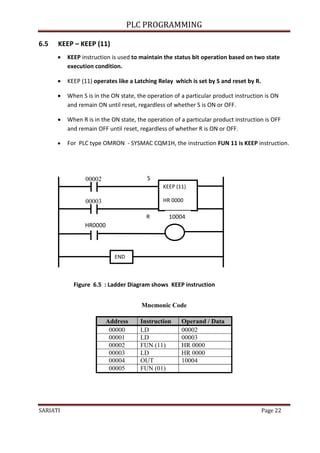
- 22. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 22 6.5 KEEP – KEEP (11) KEEP instruction is used to maintain the status bit operation based on two state execution condition. KEEP (11) operates like a Latching Relay which is set by S and reset by R. When S is in the ON state, the operation of a particular product instruction is ON and remain ON until reset, regardless of whether S is ON or OFF. When R is in the ON state, the operation of a particular product instruction is OFF and remain OFF until reset, regardless of whether R is ON or OFF. For PLC type OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, the instruction FUN 11 is KEEP instruction. 00002 00003 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand / Data 00000 LD 00002 00001 LD 00003 00002 FUN (11) HR 0000 00003 LD HR 0000 00004 OUT 10004 00005 FUN (01) Figure 6.5 : Ladder Diagram shows KEEP instruction HR0000 KEEP (11) HR 0000 S R END 10004
- 23. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 23 With reference to Figure 6.5, Instruction LD 00 002 acts as S (Set)-and the LD 00 003 acts as R (Reset). When the instruction LD 00 002 ON, the output instruction OUT 10004 will be ON and will remain ON even if the instruction LD 00 002 is OFF. When the instruction LD 00 003 ON, then the output OUT 10004 instruction OFF and will remain OFF even though the instruction LD 00 002 in OFF or ON state. Instruction LD 00003 Reset Instruction LD 00002 Set Instruction OUT 10004 Output ON ON OFF OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF OFF 6.6 SET and RESET SET and RESET instruction will change the status of bit operations only when the implementation is ON. In the OFF condition, the instructions will not change the bit operation status. 00000 00001 Figure 6.6 : Ladder Diagram shows the Set and Reset instruction SET 10000 RESET 10000
- 24. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 24 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand / Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 SET 10000 00002 LD 00001 00003 RESET 10000 Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.6, When the input instruction LD 00 000 is ON, SET instruction command to ON and always ON regardless of whether the input instruction LD 00 000 is ON or OFF. When the inputs instruction LD 00 001 is ON, RESET instruction is ON and SET instruction will be off . Its operations can be understood clearly in the KEEP instruction. 6.7 DIFFERENTIATE UP [ DIFU (13) ] DAN DIFFERENTIATE DOWN [DIFD (14) ] DIFU instructions (13) and DIFD (14) will ON the output within a very short time. Instructions DIFU (13) will turn the output to ON when the input signal changes from OFF to ON. Instructions DIFD (14) will turn the output to ON when the input signal changes from ON to OFF. For PLC type of OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, instruction FUN 13 is instruction DIFFERENTIATE UP and FUN 14 is instruction DIFFERENTIATE DOWN. Input DIF U DIF D
- 25. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 25 00000 Figure 6.7a : Ladder Diagram shows DIFFERENTIATE UP instruction Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand / Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 FUN (13) 01000 00002 LD 01000 00003 OUT 10000 Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.7a, When the input instruction LD 00000 is ON (has changes from OFF to ON), operand bit 01 000 will be ON, the output OUT 10000 will be ON within a very short time and then OFF. We can not see the situation in the products. After that the operand bit 01 000 will be OFF regardless of the status of the input instruction LD 00 000. 00000 Figure 6.7b : Ladder Diagram shows the DIFFERENTIATE DOWN instruction DIFU (13) 01OOO END 01000 10000 DIFU (14) 01OOO END 01000 10000
- 26. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 26 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand / Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 FUN (14) 01000 00002 LD 01000 00003 OUT 10000 Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.7b, When the input instruction LD 00 000 is OFF (change from ON to OFF), operand bit 01000 will be ON, the output OUT 10000 will be ON within a very short time and then OFF. We can not see the situation in the products. After that the operand bit 01000 will be OFF regardless of the status of the input instruction LD 00 000.
- 27. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 27 UNIT 7(4.4) : TIMER AND COUNTER OBJECTIVE: Describe the instruction set of timer and counter. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES: At the end of this unit you should be able to: 1. Describe the instruction timer (TIMER – TIM) 2. Describe the instruction counter (COUNTER - CNT). 3. Converts Ladder Diagram to mnemonic code. 7.0 Instruction TIMER (TIM) and COUNTER (CNT) is the instructions that require numbers TIM / CNT (N) and the set value(SV). The range of numbers TIM / CNT is from 000 to 511, while the range of set values for the TIM / CNT is 0000 to 9999 The numbers TIM / CNT can not be used twice. When a number has been used as definer, such as number 000 for instructions on TIM / CNT, the number can not be used again. When a number is defined as the number of TIM / CNT, it can be used as often as required as an operator operand in other instructions from the command TIMER or COUNTER. 7.1 TIMER - TIM Symbol Timer numbers (N) is between 000 and 015. The set value (SV) is between 0000 to 9999. All numbers TIM / CNT can be used as definer in only one TIMER or COUNTER instruction. TIM N SV SV
- 28. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 28 Example 7.1.1 TIMER is enabled/activated when the execution condition is ON and will be reset to set value (SV) when the execution condition is OFF. The set value (SV) of TIMER is the BCD between # 0000 to # 9999. For example, if TIMER be set to 5 seconds, then the set value (SV) is # 0050. Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 TIM 000 # 0050 00002 LD TIM 000 00003 OUT 10000 00004 FUN 01 Operating Condition: When the input (LD 00000) is ON, the timer contact will be activated after 5 seconds. Next the output (OUT 10000) will be ON END 00000 TIM 000 10000 Tim 000 # 0050 (5 saat)
- 29. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 29 Example 7.1.2 Ladder Diagram TIM 000 10001 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 TIM 000 # 0050 00002 LD TIM 000 00003 OUT 10000 00004 LD NOT TIM 000 00005 OUT 10001 00006 FUN 01 Operating Condition: When the input (LD 00000) ON, the timer (TIM 000) will be activated after 5 seconds and the output (OUT 10000) will be ON. While the output (OUT 10 001) will be ON as soon as the supply is supplied and will be OFF after 5 seconds. Timer will continue to be active as long as the input 00000 state is ON. END 00000 TIM 000 10000 Tim 000 #0050 (5 saat)
- 30. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 30 Example 7.1.3 Ladder Diagram Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 TIM 000 # 0050 00002 LD TIM 000 00003 AND NOT TIM 001 00004 OUT 10000 00005 LD 10000 00006 TIM 001 #0030 00007 OUT 10001 00008 FUN 01 00000 TIM 000 10000 Tim 000 # 0050 (5 saat) Tim 001 # 0030 (3 saat) TIM 001 10000 END
- 31. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 31 Operating Condition: When the input (LD 00000) ON, the timer (TIM 000) will be activated after 5 seconds. Next the output (OUT 10000) will be ON. After 3 seconds the output (OUT 10000) ON, the timer (TIM 001) will be activated the next output (OUT 10000) will be OFF and the timer (TIM 001) will be OFF. When the timer TM001 OFF, contact TIM 001 (NC) will be ON and the output (OUT 10000) is ON state. Output (OUT 10000) will continue ON and OFF until the input (LD 00000) in the OFF state. 7.2 COUNTER - CNT Symbol Number TIM / CNT can be used as definer for either timer or counter. Counter numbers are range from 000 to 015. Counters are used to calculate the count down from the set value (SV) on the execution condition on the counting pulse (CP) when it is changed from OFF to ON. The set value (SV) is range 0000 to 9999. Counters will reset to the reset (R). Ladder Diagram CP R CNT N SV CP R CNT 001 # 0010 (10 kiraan) END 0000 0 00001 CNT 001 10000
- 32. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 32 Mnemonic Code Address Instruction Operand/Data 00000 LD 00000 00001 LD 00001 00002 CNT 000 #0010 00003 LD CNT 001 00004 OUT 10000 00005 FUN 01 Operating Condition Counter set to count 10. When the input (LD 00,000) is the pulse of ten, a counter will be activated and thus the output (OUT 10000) will be ON. When reset (LD 00,001) ON, a counter will be in original condition
- 33. PLC PROGRAMMING SARIATI Page 33 7.3 The Application Of Timer And Counter Instructions The number of Counter cannot be the same number to the number of timer because both share the same data in the PLC memory. R Operating Condition: Counter set to count 5. When the input (LD 00,000) is the pulse of five, a counter will be activated and thus the output (OUT 10000) will be ON. When the output (OUT 10000) ON, TIM 001 will be activated after 3 seconds and then the output (OUT 10 001) will be ON. Both the output (OUT 10000) and (OUT 10 001) will always be ON until reset (LD 00001) in the ON state. Reset will return the counter to its original condition. CNT 000 # 0005 (5 kiraan) CP 0000 0 0000 1 TIM 001 # 0050 ( 5 saat ) END CNT 000 10000 1000 0 TIM 001 10001















![PLC PROGRAMMING
SARIATI Page 18
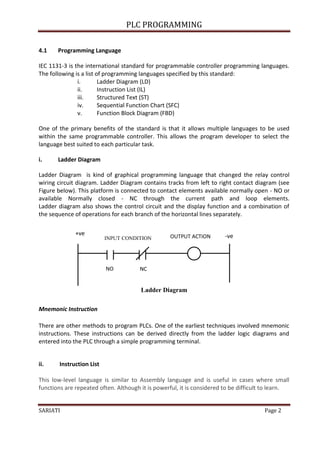
6.2 END – END(01)
Acting as the last instruction for each program (see figure 6.2)
There is no instruction will be written after the END instruction (01) implemented.
If there is no END instruction (01) in the program, the task would not be implemented
and verse NO END LIST is displayed on the programming PLC console screen.
Ladder Diagram shows the END instruction
Mnemonic Code
6.3 INTERLOCK [ IL ( 02 ) ] DAN INTERLOCK CLEAR [ ILC ( 03 ) ]
IL (02) and ILC (03) must be used together.
These instructions are used to solve the problem of storing execution conditions at
branch points.
When the INTERLOCK instruction is ON as shown in Ladder Diagram 6.3, the
implementation of the INTERLOCK instruction will control all of the instruction
execution until the instruction ‘INTERLOCK CLEAR’. When the INTERLOCK instruction is
OFF, INTERLOCK CLEAR instruction will reset the program operation.
To set the INTERLOCK instruction for PLC tpe OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H is FUN 02 for
INTERLOCK instruction and FUN 03 is INTERLOCK CLEAR instruction.
00000
END
10000
Address Instruction
Operand/Data
00000 LD NOT 00000
00001 OUT 10000
00002 FUN(01)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulplcprogramming-220511150326-46681d7f/85/Modul-PLC-Programming-pdf-18-320.jpg)

![PLC PROGRAMMING
SARIATI Page 20
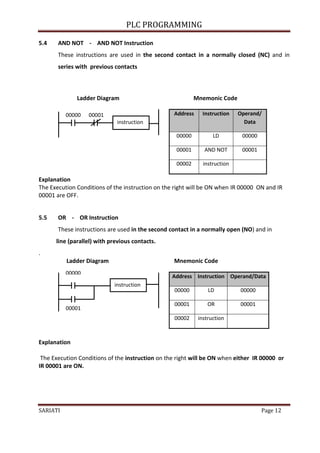
Refer the table below:
Instructions
LD 00000
IL(02)
Instructions
LD 00001
Input
Instructions
OUT 10000
Output
ON ON
ON
OFF OFF
ON OFF
OFF
OFF OFF
6.4 JUMP [ JMP (04) ] DAN JUMP END [ JME (05) ]
Instructions JMP (04) is usually used in pairs with the command JME (05) for the jump.
JMP (04) is a command to determine the starting point of the jump and JME (05) is the
instruction that the direction of the jump.( where to jump).
When the instruction JMP (04) is ON, no jump will occur and the program will be
implemented as written.
When the instruction JMP (04) is OFF, a jump to the instruction JME (05) which has the
same number will be done. Further instructions are the instructions JME (05) will be
implemented.
Instructions JUMP and JUMP END can use the numbers from the range of 00 to 99.
To set the instruction for PLC type OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, is FUN 04 for JUMP
instruction and FUN 05 instruction is the JUMP END instruction.
00000
00001 10000
JMP (04)
01
JME (05) 01
END
Figure 6.4 : Ladder Diagram shows JUMP instruction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulplcprogramming-220511150326-46681d7f/85/Modul-PLC-Programming-pdf-20-320.jpg)

![PLC PROGRAMMING
SARIATI Page 24
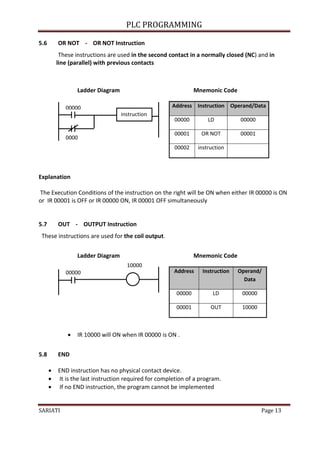
Mnemonic Code
Address Instruction Operand / Data
00000 LD 00000
00001 SET 10000
00002 LD 00001
00003 RESET 10000
Referring to Ladder Diagram 6.6,
When the input instruction LD 00 000 is ON, SET instruction command to ON and always
ON regardless of whether the input instruction LD 00 000 is ON or OFF.
When the inputs instruction LD 00 001 is ON, RESET instruction is ON and SET
instruction will be off .
Its operations can be understood clearly in the KEEP instruction.
6.7 DIFFERENTIATE UP [ DIFU (13) ] DAN DIFFERENTIATE DOWN [DIFD (14) ]
DIFU instructions (13) and DIFD (14) will ON the output within a very short time.
Instructions DIFU (13) will turn the output to ON when the input signal changes from
OFF to ON.
Instructions DIFD (14) will turn the output to ON when the input signal changes from
ON to OFF.
For PLC type of OMRON - SYSMAC CQM1H, instruction FUN 13 is instruction
DIFFERENTIATE UP and FUN 14 is instruction DIFFERENTIATE DOWN.
Input
DIF U
DIF D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulplcprogramming-220511150326-46681d7f/85/Modul-PLC-Programming-pdf-24-320.jpg)