Programming with matlab session 4
- 1. SESSION-4 :MATLAB Conditional Statements By: Prof. Ganesh Ingle
- 2. Session objective Introdcution Operators Conditional Statements If, if else, if elseif else and nested statements Switch case statement Menu driven Program SUMMARY
- 3. Operators Sr.No. Operator & Description 1 < Less than 2 <= Less than or equal to 3 > Greater than 4 >= Greater than or equal to 5 == Equal to 6 ~= Not equal to p q p & q p | q p ^ q 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 Logical OperatorsRelational Operators
- 4. Operators Sr.No. Operator & Description 1 + Addition or unary plus. A+B adds the values stored in variables A and B. A and B must have the same size, unless one is a scalar. A scalar can be added to a matrix of any size. 2 - Subtraction or unary minus. A-B subtracts the value of B from A. A and B must have the same size, unless one is a scalar. A scalar can be subtracted from a matrix of any size. 3 * Matrix multiplication. C = A*B is the linear algebraic product of the matrices A and B. More precisely, For non-scalar A and B, the number of columns of A must be equal to the number of rows of B. A scalar can multiply a matrix of any size. 4 .* Array multiplication. A.*B is the element-by-element product of the arrays A and B. A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. 5 / Slash or matrix right division. B/A is roughly the same as B*inv(A). More precisely, B/A = (A'B')'. 6 ./ Array right division. A./B is the matrix with elements A(i,j)/B(i,j). A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar.
- 5. Operators Sr.No. Operator & Description 7 Backslash or matrix left division. If A is a square matrix, AB is roughly the same as inv(A)*B, except it is computed in a different way. If A is an n-by-n matrix and B is a column vector with n components, or a matrix with several such columns, then X = AB is the solution to the equation AX = B. A warning message is displayed if A is badly scaled or nearly singular. 8 . Array left division. A.B is the matrix with elements B(i,j)/A(i,j). A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. 9 ^ Matrix power. X^p is X to the power p, if p is a scalar. If p is an integer, the power is computed by repeated squaring. If the integer is negative, X is inverted first. For other values of p, the calculation involves eigenvalues and eigenvectors, such that if [V,D] = eig(X), then X^p = V*D.^p/V. 10 .^ Array power. A.^B is the matrix with elements A(i,j) to the B(i,j) power. A and B must have the same size, unless one of them is a scalar. 11 ' Matrix transpose. A' is the linear algebraic transpose of A. For complex matrices, this is the complex conjugate transpose. 12 .' Array transpose. A.' is the array transpose of A. For complex matrices, this does not involve conjugation.
- 6. Conditional Statement Definition: A conditional statement, symbolized by p q, is an if-then statement in which p is a hypothesis and q is a conclusion. The logical connector in a conditional statement is denoted by the symbol . The conditional is defined to be true unless a true hypothesis leads to a false conclusion. Types of conditional statements: 1. If 2. If else 3. If elseif else ladder 4. Nested if else 5. Switch case statement
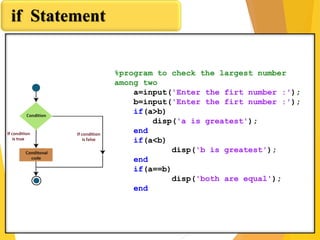
- 7. if Statement
- 8. if Statement %program to check the largest number among two a=input('Enter the firt number :'); b=input('Enter the firt number :'); if(a>b) disp('a is greatest'); end if(a<b) disp('b is greatest'); end if(a==b) disp('both are equal'); end
- 9. if else Statement If the conditional expression is an array, it is true only if all the elements of the array are true!
- 10. if else Statement If the conditional expression is an array, it is true only if all the elements of the array are true! %program to check the largest number among two distinct numbers a=input('Enter the firt number :'); b=input('Enter the firt number :'); if(a>b) disp('a is greatest'); else disp('b is greatest'); end
- 11. if elseif else Statement
- 12. if elseif else Statement
- 13. if elseif else Statement %program to check the largest number among two a=input('Enter the firt number :'); b=input('Enter the firt number :'); if(a>b) disp('a is greatest'); elseif(a<b) disp('b is greatest'); else disp('both are equal'); end
- 14. if elseif else Statement
- 15. Nested if else Statement
- 17. Switch Case Statement %calculator program using switch case construct menu driven a=input('Enter the firt number :'); b=input('Enter the second number :'); fprintf('Enter choice 1 if you want to perform addition of two numbers n'); fprintf('Enter choice 2 if you want to perform subtraction of two numbers n'); fprintf('Enter choice 3 if you want to perform multiplication of two numbers n'); fprintf('Enter choice 4 if you want to perform division of two numbers n'); choice=input('Enter the choice :'); switch (choice) case 1 add=a+b;disp('The addtion of two number is');disp(add); case 2 sub=a-b;disp('The Subtraction of two number is');disp(sub); case 3 mult=a*b;disp('The multiplication of two number is');disp(mult); case 4 div=a/b;disp('The Division of two number is');disp(div); otherwise disp('wrong choice'); end





![Operators
Sr.No. Operator & Description
7
Backslash or matrix left division. If A is a square matrix, AB is roughly the same as inv(A)*B,
except it is computed in a different way. If A is an n-by-n matrix and B is a column vector with n
components, or a matrix with several such columns, then X = AB is the solution to the equation
AX = B. A warning message is displayed if A is badly scaled or nearly singular.
8
.
Array left division. A.B is the matrix with elements B(i,j)/A(i,j). A and B must have the same
size, unless one of them is a scalar.
9
^
Matrix power. X^p is X to the power p, if p is a scalar. If p is an integer, the power is computed by
repeated squaring. If the integer is negative, X is inverted first. For other values of p, the
calculation involves eigenvalues and eigenvectors, such that if [V,D] = eig(X), then X^p =
V*D.^p/V.
10
.^
Array power. A.^B is the matrix with elements A(i,j) to the B(i,j) power. A and B must have the
same size, unless one of them is a scalar.
11
'
Matrix transpose. A' is the linear algebraic transpose of A. For complex matrices, this is the
complex conjugate transpose.
12
.'
Array transpose. A.' is the array transpose of A. For complex matrices, this does not involve
conjugation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingwithmatlabsession4-200906050021/85/Programming-with-matlab-session-4-5-320.jpg)