Rakesh Roshan MIS Slides
- 1. By Rakesh Roshan Management of Information System BY Rakesh Roshan
- 2. By Rakesh Roshan CONTENT Introduction: Fundamentals of MIS and various terminologies associated with MIS. 2. Business application development and management. Business applications modeling through IT and their development. 3. Fundamentals of strategic advantage. 4. Intranets , Extranets and Enterprise collaboration. 5. DS and artificial intelligence. 6. Developing system strategies and solutions. 7. Computer hardware / software and networks. 8.DBMS(Database Management System)
- 3. By Rakesh Roshan 1. Fundamentals of MIS
- 4. An IS Framework for business Professionals By Rakesh Roshan Information System Information Systems Management System Information Technologies Business Applications Development Processes Foundation Concepts
- 5. Foundation Concepts : Fundamental behavioural , technical, business and managerial concepts about the components and role of information systems. Examples include basic information system concepts derived from general system theory , or competitive strategy concepts used to develop business applications of IT for competitive advantage. Information Technologies : Major concepts, developments and management issues in information technology – that is hardware, software , networks , data management and many Internet-based technologies. Business Applications : The major uses of information systems for the operations, management and competitive advantage of a business. Applications of information technology in the functional areas of business like marketing , manufacturing and accounting. Development Processes : How business professionals and information specialists plan . Develop and implement information system to meet business opportunities. Several development technologies including the SDLC and prototyping approaches to business application development. By Rakesh Roshan
- 6. Management Challenges : The challenges of effectively and ethically managing information technology at the end user, enterprise and global levels of a business.Management chalenges focuses on security challenges and security management issues in the use of IT. By Rakesh Roshan
- 7. The Fundamental Roles of IS in Business By Rakesh Roshan Support Strategies For Competitive Advantage Support Business Decision Making Support Business Processes and Operations
- 8. Contd...…………………….. Support Business Processes : As a consumer , you regularly encounter information systems that support the business processes and operations at the many retail stores where you shop. Example : Customer purchase record, keep track of inventory , pay employees , evaluate sales trends etc. Support Decision Making : Information systems also help store managers and other business professionals make better decisions . Example: Decisions on what lines of merchandise need to be added or discontinued, or on what kind of investment they require , are typically made after an analysis provided by computer based information systems. Support Competitive Advantage : Gaining a strategic advantage over competitors requires innovative application on information technologies. Example: store management might make a decision to install touch screen kiosks in all of their stores , with links to their e-commerce website for online shopping. By Rakesh Roshan
- 9. By Rakesh Roshan The Role of e-Business in Business The Internet and related technologies and applications have changed the way businesses are operated and people work , how information systems support business processes, decision making and competitive advantages, The many businesses today using internet technologies to Web enable business processes and create innovative e-business applications. Supply Chain Management: Procurement , distribution and logistics Customer relationship management: Marketing Sales Customer service Engineering and Research Manufacturing and production Accounting and Finance Intranets Intranets Extranets Company Boundary Supplier and Other Business Partners The Internet Consumers and Business Customers
- 10. By Rakesh Roshan Types Of Information System The applications of IS that are implemented in today’s business world can be Classified in several different ways. Several types of IS can be classified as Either operations or management information system. Information System Operations Support System Management Support System Transaction Processing System Process Control Systems Enterprise Collaboration Systems Management Information Systems Decision Support System Executive Information System Support of Business Operation Support of Managerial Decision making Processing Business transactions Control of Industrial Processes Team and Workgroup Collaboration Prespecified Reporting For Managers Interactive Decision Support Information Tailored for Executives
- 11. Operation Support System Information systems have always been needed to process data generated by, and used in , business operations. Such operations support systems produce a variety of information products for internal and external use. Transaction Processing System : TPS are an important ex. of operations support systems that record and process data resulting from business transactions. They process transaction in two basic ways. In batch Processing , transactions data are accumulated over a period of time and processed periodically.In Real Time processing , data are processed immediately after a transaction occurs. For Example. Point of Sale (POS). Process Control System : PCS monitor and control physical processes. For ex , a petroleum refinary uses electronic sensors linked to computers to continually monitor chemical processes and make instant adjustments that control the refinery process. Enterprise collaboration system : ECS enhance team and workgroup communications and productivity , and include applications that are sometimes called office automation systems. For Ex. Knowledge workers in a project team may use electronic mail to send and receive electronic messages, and video conferencing to hold electronic meetings to coordinate their activities By Rakesh Roshan
- 12. Management support System When information system applications focus on providing information and support effective decision making by managers, they are called M anagement Support Systems. Management Information System : MIS provides information in the form of reports and displays to managers and many business professionals. For Ex. Sales managers may use their networked computers and Web browsers to get instaneous displays about the sales result of their products and to access their corporate internet for daily sales analysis reports that evaluate sales made by each sales person. Decision Support Systems : DSS gives direct computer support to managers during the decision making process. For ex. An advertising managers may use a DSS to perform a what if-analysis as part of a decision to determine where to spend advertising dollars. Executive Information System : EIS provides critical information from a wide variety of internal and external sources in easy-to-use displays to executives and managers. For ex. Top executives may use touch screen terminals to instantly view text and graphics displays that highlights key areas of organizational and competitive performance. By Rakesh Roshan
- 13. Managerial Challenges of IT By Rakesh Roshan (Challenges and Opportunities that business managers face in managing information systems and technologies to meet business goals) The Business Enterprise Strategies/ Processes/ Structure/ Culture Information technology Customer Value Business Value Speed and Flexibility requirements of product development , manufacturing and delivery cycles Reengineering and cross-functional integration of business processes using internet technologies Integration of e-business and e-commerce into the organization’s strategies,processec,structure and culture. Use of Internet,Intranets , extranets and the web as the primary IT infrastructure. Diffusion of Web technology to internetwork employees , customers and suppliers. Global networked computing , collaboration and decision support systems. Give customers what they want, when and how they want it , at the lowest cost. Coordination of manufacturing and business processes and suppliers and customers. Marketing channel partnerships with suppliers and distributers.
- 14. Contd………. Success and failure of IT : The success of an information system should not be measured only by its efficiency in terms of minimizing costs , time and the use of information resources. Success should also be measured by the effectiveness of IT in supporting an organization business strategies , enabling its business processes , enhancing its organizational structure and culture and increasing the customer and business value of the enterprise. Developing IS Solutions : Developing successful Information system solutions to business problems is a major challenges for business managers and professional today. Challenges of Ethics and IT : As a prospective manager , business professional , and knowledge worker , you will be challenged by the ethical responsibilities generated by the use of IT.For ex. What uses of IT might be considered improper , irresponsible or harmful to other individuals or to society. Challenges of IT careers : IT have created interesting , challenging and lucrative career opportunities of millions of men and women all over the globe. At this point in your lige you may still be uncertain about the career path you wish to follow , so learning more about IT may help you decide if you want to persue an IT-related career. By Rakesh Roshan
- 15. Example of some of the ethical challenges that must be faced by Business Manager , when implement major applications of IT By Rakesh Roshan Customer Relationship Management Human Resource Management Business Intelligence Systems Infringements on privacy Inaccurate Information Collusion Consumer boycotts Work stoppages Government intervention Codes of ethics Incentives Certification Application of IT Potential Harms Potential Risks Possible Responses
- 16. By Rakesh Roshan A system is a group of interrelated components , with a clearly defined boundary ,working together toward a common goal by accepting inputs and producing outputs in an organized transformation process. Three Basic components of a system are: INPUT involves capturing and assembling elements that enter the system to be processed. For example , raw materials , energy , data and huamn effort must be secured and organized for processing. PROCESSING involves transformation process that convert input into output. Examples are a manufacturing process , the human breathing process , or mathematical calculations. OUTPUT involves transferring elements that have been produced by a transformation process their ultimate destination. For Example , finished products , human services and management information must be transmitted to their human users. The Two additional components are: FEEDBACK is data about the performance of a system. For example, data about sales performance is feedback to a sales manager. CONTROL involves monitoring and evaluating feedback to determine whether a system is moving toward the achievement of its goal. System
- 17. By Rakesh Roshan ORGANIZATIONAL SYSTEM The Community Competitors Management Information system Economic Resources: People Money Material Machines Land Facilities Energy Information Business Process: Market , Develop , Produce and Deliver Products and Services Support Customers Other Processes Goods and services: Products Services Payments Contributions Information Other Effects Financial Institutions Labor Unions Input Processing Output
- 18. By Rakesh Roshan Ata People Resources (End users and IS Specialist Software Resources (Program and Procedure) Network Resources Communications Media and Network Support Hardware Resources Machines and Media Data Resources Data and Knowledge Bases Control of system performance Input and Data Resources Processing Data into Information Output of Information Products Storage of Data Resources Component of Information System
- 19. Contd….. This information system model highlights the relationships among the components and activities of IS. It provides a framework that emphasizes four major concepts that can be applied to all types of information systems: People, hardware ,software , data, and networks are five basic resources of information system. People resources include end users and IS specialists , hardware resources consist of machines and media , software resources include both programs and procedures, data resources can include data and knowledge bases , and network resources include communications media and networks. Data resources and transformed by information processing activities into a variety of information products for end users. Information processing consists of the system activities of input, processing , output , storage , and control . By Rakesh Roshan
- 20. Information System Resources and Products People Resources Specialists-Systems analysts,software developers , system operators. End Users-anyone else who uses information systems Hardware Resources Machines-computers , video monitors , magnetic disk drives , printers,optical scanners. Media-Floppy disks , magnetic tape,optical disks,plastic cards , paper forms. Software resources Programs- operating system programs, spreadsheets programs , word processing programs , payroll programs Procedures- data entry procedures , error correction procedures, paycheck distribution procedures. Data Resources Product descriptions, customer records , employee files , inventory databases. Network Resources Communications media,communications processors, network access and control software Information Technology Management Reports and business documents using text and graphics displays , audio responses and paper forms By Rakesh Roshan
- 21. Information System activities Input of Data Resources Data about business transaction and other events must be captured and prepared for processing by the input activity.Input typically takes the form of data entry activities such as recording and editing. Processing of Data Information Data are typically subjected to processing activities such as calculating , comparing , sorting , classifying and summarizing. These activities organize , analyze , and manipulate data , thus converting them into information for end users. The quality of any data stored in an information system must also be maintained by a continual process of correcting and updating activities. Output of Information Products Information in various forms ids transmitted to end users and made available to them in the output activity. The goal of information system is the production of appropriate information products for end users. Common information products include message , reports , formas and graphic images , which may be provided by video displays , audio responses ,paper products and multimedia . By Rakesh Roshan
- 22. Contd…… Storage of Data resources Storage is a basic system component of Information system. Storage is the information system activity in which data and information are retained in an organized manner for later use. Control of System Performance An important information system activity is the control of system performance. An information system should produce feedback about input , processing , output and storage activities. This feedback must be monitored and evaluate to determine if the system is meeting established performance standards. Then appropriate system activities must be adjusted so that proper information products are produced for end users. By Rakesh Roshan
- 23. Enterprise Business system Introduction Contrary to popular opinion , e-business is not synonymous with e-commerce. E-business is much broader in scope , going beyond transaction to signify use of the Net, in combination with other technologies and forms of electronic communication , to enable any type of business activity. By Rakesh Roshan
- 24. Cross-Functional Enterprise Applications Many companies today are using IT to deploy integrated cross-functional enterprise systems that cross the boundaries of traditional business function in order to reengineer and improve vital business processes all across the enterprise. These organization view cross-functional enterprise systems as a strategic way to use IT to share information resources and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes , and develop strategic relationship with customers , suppliers , and business partners. By Rakesh Roshan Customer Feedback Market Research Market Test Component Design Product Test Product Release Process Design Equipment Design Production Start Marketing R & D Engineering Manufacturing
- 25. Contd……. Many companies first moved from functional mainframe based legacy systems to integrated cross-functional client/server applications. This typically involved installing enterprise resource planning , supply chain management or customer relationship management software from SAP America , PeopleSoft , Oracle and others. Instead of focusing on the information processing requirements of business function , such enterprise software focuses on supporting integrated clusters of business processes involved in the operation of a business. By Rakesh Roshan
- 26. Enterprise Application Architecture An Enterprise application architecture , which illustrates the interrelationships of the major cross-functional enterprise applications that many companies have or are installing today. This architecture does not provide a detailed or exhaustive application blueprint , but provides a conceptual framework to help you visualize the basic components , processes and interfaces of these major e-business applications , and their interrelationships to each other . This application architecture also spotlights the roles these business systems play in supporting the customers , suppliers , partners and employees of a business. By Rakesh Roshan
- 27. Architecture of Enterprise Application By Rakesh Roshan Suppliers Supply Chain Management Sourcing * Procurement Enterprise Resource Planning Customer Relationship Management Marketing*Sales*Service Customers Employees Partners Knowledge Management Collaboration*Decision support Partner Relationship Management Selling * distribution
- 28. Enterprise Application Integration Enterprise application integration software is being used by many companies to connect their major e-business application. EAI software enables user to model the business process involved in the interactions that should occur between business application . EAI also provides middleware that transforms data conversion and coordination , application communication and messaging service and access to the application interface involved . Thus EAI software can integrate a variety of enterprise application clusters by letting them exchange data according to rules derived from the business process models developed by users. For example, “ When an order is complete , have the order application tell the accounting system to send a bill and alert shipping to send out the product”. By Rakesh Roshan Front Office Customer Service Field Service Product Configuration Sales Order Entry Back Office Distribution Manufacturing Scheduling Finance EAI
- 29. HOW EAI WORKS: By Rakesh Roshan 1.An order comes in via the call center ,email , the Web or fax. 2.Customer information captured in the order process is sent to a “ new customer” process , which distributes the new customer information to multiple application and databases. 3.Once the order is validated,relevant details are sent to order fulfillment- which may pick the requested items from inventory ,schedule them for manufacture , or simply forward them. 4. Fulfillment return status and shipment info to the order entry system…… 5. …..and to the call center , which needs to know about outstanding orders. EAI Call Center Billing Finance Order & Fulfillment Routing Manufacturing Shipping 2 3 1 4 5 E-Mail Fax Web Call Center
- 30. Transaction Processing System Transaction processing systems(TPS) are cross functional information systems that process data resulting from the occurrence of business transactions.TPS as one of the major application categories of information systems in business. Transactions are events that occur as part of doing business such as sales , purchases,deposits,withdrawls,refunds and payments.Ex. Of the data generated whenever a business sells something to a customer on credit, whether in a retail store or at an e-commerce site on the web. Data about the customer,product,salesperson,store and so on,mustbe captured and processed.Therefore, transaction processing systems play a vital role in supporting the operations of an e-business enterprise. By Rakesh Roshan
- 31. OLTP(Online transaction processing systems) OLTP plays a strategic role in electronic commerce. Many firms are using the Internet , extranets and other networks that tie them electronically to their customers or suppliers for online transaction processing. Such real time systems , which capture and process transactions immediately, can help firms provide superior service to customers and other trading partners.This capability adds value to their products and services , thus gives them an important way to differentiate themselves from their competitors. By Rakesh Roshan
- 32. Transaction Processing Cycle By Rakesh Roshan Data Entry Transaction Processing Batch Online/Real-Time Database Maintenance Document and Report Generation Inquiry Processing 1 2 4 3 5
- 33. Contd…. Data Entry: The first step of the Transaction Processing Cycle is the capture of business data. For ex. Transaction data can be collected from the point of sale terminals using optical scanning of bar code and credit card readers at a retail store or other business. Transaction Processing : TPS process systems process data in two basic ways : (1) Batch Processing(processed over a period of time) (2) Real time Processing(online processing) Database maintenance : An organization’s data must be maintained by its transaction processing systems so that they are always correct and up-to-date. Document and Report Generation : TPS produce a variety of documents and reports. Examples of transaction documents include purchase orders , pay checks, sales receipts ,invoices and customer statements. Inquiry Processing : Many transaction processing systems allow you to use the Internet,Intranet,extranet and Web browsers or database management query languages to make inquiries and receives responses concerning the results of transaction processing activity. By Rakesh Roshan
- 34. Functional Business Systems Functional Business systems is a variety of types of information systems that support the business functions of accounting ,finance, marketing, operations management and Human resource management By Rakesh Roshan Functional Business Systems Customer Relationship Management Interactive Marketing Sates force automation Compensation Analysis Employee skills inventory Personal requirements forecasting Cash Management Credit Management Investment Management Capital budgeting Financial forecasting Order processing Inventory control Accounts receivable Accounts payable Payroll General Ledger Manufacturing Resource Planning Manufacturing Execution Systems Process Control Marketing Production/Operations Human Resource Management Accounting Finance
- 35. Manufacturing Systems Manufacturing information systems supports the production/operation function that include all activities concerned with the planning and control of the processes producing goods and services. Thus the production/ operations functions is concerned with the management of the operational processes and systems of all business firms. Computer Integrated Manufacturing A variety of Manufacturing Information systems, many of them Web enabled, are used to support Computer Integrated Manufacturing(CIM). CIM is an overall concept that stresses that the objectives of computer based systems in manufacturing must be to: * Simplify production processes , product designs, and factory organization as a vital foundation to automation and integration. * Automate production process and the business functions that support them with computers, machines and robots. * Integrate all production and support processes using computer networks , cross functional business software and other information technologies . By Rakesh Roshan
- 36. How Manufacturing Information Systems support computer integrated manufacturing By Rakesh Roshan Shop Floor Control Computer Aided Design Process Control Machine Control Capacity Planning Production Cost Control Quality Control Robotics Control Material Requirements Planning Production Forecasting Production Scheduling Shop Floor Scheduling Computer Aided Engineering Computer Aided Process Planning Product Simulation and Prototyping Computer Integrated Manufacturing Manufacturing Resource Planning Systems Manufacturing Execution Systems Engineering Systems
- 37. Contd….. Computer are used to help engineers design better products using both computer aided engineering and computer aided design systems, and better production processes with computer aided process planning . They are also used to help plan the material needed in the production process, which is called material requirement planning(MRP). Computer Aided Manufacturing Systems are those that automate the production processed. Ex.This could be accomplished by monitoring and controlling the production process in the factory. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) are performance monitoring information systems for factory floor operations. The monitor, track and control the five essential components involved in a production process: Material, equipment , personnel, instructions and specifications and production facilities.MES includes shop floor scheduling and control , machine control , robotics control and process control systems. Process Control is the use of computer to control an ongoing physical process. Process control computers control physical processes in petroleum refineries, cements plants, steels mills , chemicals plants , food product manufacturing plants , pulp and paper mills , electric power plants and so on. Machine control is the use of computers to control the actions of machines. This is also popularly called numerical control. By Rakesh Roshan
- 38. Human Resource Systems The HRM function involoes the recruitment ,placement, evaluation, compensation, and development of the employees of an organization. The goal of human resource management isa the effactive and efficient use of the human resources of a company. Thus Human resource information systems are designed to support: (i) Planning to meet the personnel need of the business. (ii) development of employees to their full potential. (iii) Control of all personnel policies and programs. Many firms have gone these traditional personnel management functions and hace developed HRIS that support (i) Recruitment,selection and hiring. (ii) Job placement. (iii) Performance appraisals. (iv) Employee benefits analysis. (v) Training and development. (vi) Health , safety and security. By Rakesh Roshan
- 39. HRM and the Internet The Internet has become a major force for change in HRM. Ex. Online HRM systems may involve recruiting for employees through recruitment sections of corporate websites. Companies are also using commercial recruiting services and databases on the WWW , posting messages in selected Internet newsgroups , and communicating with job applicants via e-mail. HRM and Corporate Intranets Intranet technologies allow companies to process most common HRM applications over their corporate intranets. Intranets allow the HRM department to provide around the clock services to their customers: the employees. They can also disseminate valuable information faster than through previous company channels. Intranet can collect information online from employees for input to their HRM files, and they can enable managers and other employees to perform HRM tasks with little intervention by the HRM department. By Rakesh Roshan
- 40. Supply Chain Management Definition: Supply Chain Management is a cross-functional inter enterprise system that uses information technology to help support and mange the links between some of the company’s key business processes and those of its suppliers, customers , and business partners. NOTE : The Goal of SCM is to create a fast , a efficient and low-cost network of business relationships or supply chain to get a company’s products from concept to market By Rakesh Roshan
- 41. By Rakesh Roshan Commit Schedule Make Deliver Strategic Sourcing and Procurement Forecast and Demand Planning Customer Order Fulfillment/Service Distribution Network and Warehouse Operations Production Logistics Transportation and Shipment Management Shared Market Data Collaborative Fulfillment The Internet Supplier Manufacturer Retailer Customer Supply Chain Life Cycle SCM Functional Processes SCM Integration Solution
- 42. Objectives and Outcomes of SCM (Role of SCM) By Rakesh Roshan What? Establish objectives , policies , and operating footprint How much? Deploy resources to match supply to demand When ? Where? Schedule ,monitor , control and Adjust production Do Build and transport Objectives Supply policies (Service levels) Network design Demand forecast Production , procurement , logistics plan Inventory targets Work center scheduling Order/inventory tracking Order cycle Material movement Strategic Tactical Operational Execution SCM Objectives SCM Outcomes
- 43. Trends In SCM By Rakesh Roshan Information Sharing Products/Sales Data Sourcing Help Logistics Order Fulfillment Order Management Inventory Management Resource Allocation Systems Use and Integration Collaborative Marketing Sales and Service SCM Optimization Collaborative Design and Delivery SCM Stage 1 Current supply chain improvement Supply chain, e-commerce loosely coupled SCM Stage 2 Intranet/extranet links to trading partners Supplier network expansion SCM Stage3 Collaborative planning and fulfillment Extranet and exchange-based collaboration
- 44. By Rakesh Roshan E-Commerce Introduction to E-commerce E-commerce is changing the shape of competition , the speed of Action, and the streamlining of interactions, products and payments from customers to companies and from companies to suppliers. Categories of e-Commerce Many companies today are participating in or sponsoring three Basic categories of electronic commerce applications: 1. Business-to-Consumer(B2C) e-Commerce : In this form of electronic Commerce , businesses must develop attractive electronic marketplace to sell products and services to consumers. For example many companies offer e-commerce websites that provide virtual storefronts and multimedia catalogs, interactive order processing, secure electronic payment systems and online customer support.
- 45. 2. Business-to-Business(B2B) e-Commerce : This category of electronic Commerce involves both electronic business marketplaces and direct market Links between businesses. For example, many companies offer secure Internet Or extranet e-commerce catalog websites for their business customers and Suppliers. Also very important are B2B e-commerce portals that provide auction and exchange marketplaces for businesses. 3. Consumer-to-Consumer(C2C) e-Commerce : The huge success of online auctions like eBay , where consumers can buy and sell with each other in an auction process at an auction website ,makes this e-commerce model an important e-commerce business strategy. Thus, participating in or sponsoring consumer or business auctions is an important e-commerce alternative for B2B, C2B or B2B e-commerce. Electronic personal advertising of products or services to buy or sell by consumers at electronic newspaper sites, consumer e-commerce portals, or personal websites is also an important form of C2C e-commerce. By Rakesh Roshan
- 46. By Rakesh Roshan Electronic Buying and Selling of goods and services Selling Process Buying Process Market/ Product Research Customer Service and Support Market Stimulation / Education Terms Negotiation Order Billing/ Payment Mgmt Order Receipts Order Scheduling/ Fulfillment delivery Order Selection and Priority Product Discovery Product Services and Support Product Evaluation Terms Negotiation Order Payment Order Placement Product Receipt Order Tracking
- 47. E-Commerce Process Architecture By Rakesh Roshan Access Control And Security Access Control Authentication Security Measures Profiling and Personalizing Profile Management Personalization Behavior Tracking Search Management Content-Based Search Parametric-Based Search Role-and rule-Based Search Content Management Dynamic Content Generation Data Repository Catalog Management Pricing Calculation Product Configuration Catalog Generation Payment Shopping Cart Payment Method Support Payment Verification Collaboration And Trading Mediation Negotiation Bidding/Auctioning Collaborative Buying Online Community Workflow Management Buying Process Automation Document Management Rule and Role-Based Content Routing Event Management Event Driven Transaction Processing Message to eMail Message Boards Newsgroups
- 48. E-Commerce Applications and Issues By Rakesh Roshan E-Commerce is changing how companies do business both internally and externally with their customers, suppliers , and other business partners. How companies apply e-Commerce to their business is also subject to change As their managers confront a variety of e-Commerce alternatives. The application of e-Commerce by many companies have gone through several major stages as e-Commerce matures in the world of business. For Example, E-Commerce between businesses and Consumers(B2C) moved from merely offering multimedia company information at corporate websites to offering Products and services at web store front sides via electronic catalogs and online sales transactions. B2B e-Commerce , on the other hand , started with website Support to help business customers serve themselves ,and than moved toward automating intranet and extranet procurement systems.
- 49. By Rakesh Roshan High Business Value Low Time to Implement High B2C B2B Web Storefront & e-Catalog Interactive Marketing Interactive Web Store Self-Service Web Sales B2C Portal E-Business Empowerment B2B Portal Extranets And Exchanges Procurement Automation Customer Self-Service Short Term Project Operations automation Short Term Strategies Long Term Strategies SCM CRM Web Brochures Trends in B2C and B2B e-commerce
- 50. By Rakesh Roshan e-Commerce Success Factors Selection and Value : Attractive product selections , competitive prices, satisfaction guarantees and customer support after the sale. Performance and Service : Fast, easy navigation , shopping and purchasing, and prompt shipping and delivery. Look and Feel : Attractive Web storefront , website shopping areas, multimedia product catalog pages and shopping features Advertising and Incentives : Targeted Web page advertising and e-mail promotions , discounts and special offers, including advertising at affiliates sites. Personal Attention : Personal Web pages , personalized product recommendations, Web advertising and e-mail notices and interactive support for all customers. Community Relationship : Virtual communities of customers, suppliers, company representatives and other via newsgroups, chat rooms and links to related sites. Security and Reliability : Security of customer information and website transactions, trustworthy product information and reliable order fulfillment
- 51. Strategic IT: We view information system as more than a set of technologies that support efficient business operations , workgroup and enterprise collaboration , or effective business decision making . IT can change the way businesses compete . So, we should also view IS strategically, that is , as vital competitive networks, as a means of organizational renewal , and as a necessary investment in technologies that help a company adopt strategies and business processes that enable it to reengineer or reinvent itself in order to survive and succeed in today’s dynamic business environment. Competitive Strategy Concepts: The major role of IS applications in business is to provide effective support of a company’s strategies for gaining competitive advantage. This strategic role of IS involves using IT to develop products ,services and capabilities that give a company major advantages over the competitive forces it faces in the global marketplace. By Rakesh Roshan Fundamentals of Strategic Advantages
- 52. Competitive Forces and Strategies By Rakesh Roshan Cost Leadership Differentiation Innovation Growth Alliances Other Strategies Rivalry of Competitors Threats of New Entrants Threat of Substitutes Bargaining Power of Customers Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 53. Strategic Uses of IT By Rakesh Roshan Basic strategies in the Business Use of Information Technology Lower Costs Use IT to substantially reduce the cost of business process Use IT to lower the costs of customer or suppliers Differentiate Develop new IT features to differentiate products and services. Use IT features to reduce the differentiation advantages of competitors. Use IT features to focus products and services at selected market places. Innovate Create new products and services that include IT components. Develop unique new markets or market niches with the help of IT. Make radical changes to business processes with IT that dramatically cut costs, improve quality, efficiency or customer service or shorten time to market. Promote Growth Use IT to manage regional and global business expansion. Use IT to diversify and integrate into other products and services. Develop Alliances Use IT to create virtual organizations of business partners. Develop inter enterprise information systems linked by the Internet and extranets that support strategic business relationships with customers ,suppliers .subcontractors and others.
- 54. Building a Customer Focused Business For many companies ,the chief business value of becoming a customer focused business lies in its ability to help them keep customers loyal, anticipate their future needs , respond to customer concerns and provide top-quality customer service. This strategic focus on customer value recognizes that quality , rather than price has become the primary determinant in the customer’s perception of value. Companies that consistently offer the best value from the customer’s perspective are those that keep track of their customer’s individual preferences, keep up with market trends, supply products ,services and information anytime, anywhere, and provide customer services tailored to individual needs. And So Internet technologies have created a strategic opportunity for companies, large and small , to offer fast ,responsive, high quality products and services tailored to individual customer preferences. By Rakesh Roshan
- 55. How a customer-focused business builds customer value and loyalty using Internet technologies? By Rakesh Roshan Let customers place orders directly Let customers place orders through distribution partners Link employee and distribution partners to databases and customers Let customers check order history and delivery status Make loyal customers feel special with websites personalization Give all employees a complete view of each customer Build a customer database segmented by preferences and profitability Build a Web community of customers, employees and partners Transaction Database Customer Database Internet Internet Internet Extranets Intranets Extranets Intranets
- 56. Value Chain and Strategic IS The value chain concept was developed by Michael Porter. It views a firm as a series, chain, or network of basic activities that add value to its products and services , and thus add a margin of value both to the firm and its customers. In the value chain conceptual framework , some business activities are primary processes; others are support processes . The framework can highlight where competitive strategies can best be applied in the business. Managers and business professional should try to develop a variety of strategic uses of Internet and other technologies for those basic processes that add the most value to a company’s products or services , and thus to the overall business value of the company. By Rakesh Roshan
- 57. Value Chain of a firm By Rakesh Roshan Support Processes Primary Business Processes Inbound Logistics Automated Just-in-time Warehousing Operations Computer Aided Flexible Manufacturing Marketing and Sales Online Point-of-sale and order Processing Marketing and sales Targeted Marketing Customer Service CRM Competitive Advantage Administrative Coordination and support Services Collaborative Workflow Intranet Human resource Management Employee Benefits intranet Technology Development Product Development Extranet with Partners Procurement of Resources E-Commerce Web Portals for Suppliers
- 58. Strategic Use of IT There are many ways that organizations may view and use IT. For Ex, Companies may choose to use Information Systems strategically, or they may be content to use IT to support efficient every day operations. But if a company emphasized strategic business uses of IT, Its management would view IT as a major competitive differentiator. They would then device business strategies that would use IT to develop products, services ,and capabilities that would give the companies major advantages in the markets in which it competes. By Rakesh Roshan Reengineering Business Processes One of the most important implementations of competitive strategies is business Process reengineering(BPR), most often simply called reengineering. Reengineering is a fundamental rethinking and radical redesign of business processes to achieve Dramatic improvements in cost, quality, speed, and services. So BPR combines a strategy of promoting business innovation with a strategy of making major improvements to business processes so that a company can become a much stronger and more successful competitor in the marketplace.
- 59. Business Improvement Vs Business Process reengineering By Rakesh Roshan Business Improvement Business Process Reengineering Level Of Change Incremental Radical Process Change Improved new version of process Brand new process Starting Point Existing Processes Clean slate Frequency of Change One-Time or continuous Periodic one-time change Time Required Short Long Typical Scope Narrow, within functions Broad, cross functional Horizon Past and present Future Participation Bottom-up Top-down Path to Execution Cultural Cultural, structural Primary Enabler Statistical control Information Technology Risk Moderate High
- 60. Example By Rakesh Roshan Reengineering Order Management Customer relationship management systems using corporate intranets and the Internet. Supplier managed inventory systems using the Internet and extranets. Cross-functional ERP software for integrating manufacturing, distribution, finance and human resource processes. Customer-accessible e-commerce websites for order entry, status checking, payment and services. Customer, product, and order status databases accessed via intranets and extranets by employees and suppliers.
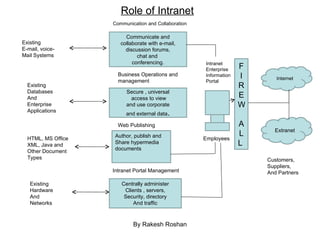
- 61. Intranet An intranet is a network inside an organization that uses Internet technologies to provide an Internet-like environment within the enterprise for information sharing, communications, collaboration and the support of business process. An intranet is protected by security measures such as passwords, encryption and firewalls and thus can be accessed by authorized users through the Internet The Business Value Of Intranets Organizations of all kinds are implementing a board range of intranet uses. One Way that companies organize intranet application is to group them conceptually into a few user services categories that reflect the basic services that intranets offer to their users. These services are provided by the intranet’s portal,browser and server software as well as by other system and application software and groupware that are part of a company’s intranet software environment By Rakesh Roshan
- 62. Role of Intranet By Rakesh Roshan Communicate and collaborate with e-mail, discussion forums, chat and conferencing. Secure , universal access to view and use corporate and external data . Author, publish and Share hypermedia documents Centrally administer Clients , servers, Security, directory And traffic Existing E-mail, voice- Mail Systems Existing Databases And Enterprise Applications HTML, MS Office XML, Java and Other Document Types Existing Hardware And Networks Intranet Enterprise Information Portal F I R E W A L L Internet Extranet Customers, Suppliers, And Partners Communication and Collaboration Business Operations and management Web Publishing Intranet Portal Management Employees
- 63. Extranet Extranets are network links use internet technologies to interconnect the intranet of a business with the intranets of its customer, suppliers, or other business partners. Companies can establish direct private network links between themselves or create private secure Internet links between them called virtual private network By Rakesh Roshan Business Value of Extranets The business value of extranets is derived from several factors. First, the Web Browser technology of extranets makes customer and supplier access of intranet Resources a lot easier and faster than previous business methods. Second, as you will see in two upcoming examples , extranets enable a company to offer new kinds of interactive Web-enabled services to their business partners.
- 64. Extranets connect the interconnected enterprises to consumers, business customers, suppliers and other business partners (Role of Extranet) By Rakesh Roshan Partners Consultants Contractors Joint design Outsourcing Suppliers and Distributers Distributer management SCM Procurement Consumers Customer Self-Service Online Sales and Marketing Sales Force Automation Build-to-Order products Just-in-Time Ordering Business Customers Internetworked Enterprise
- 65. Enterprise Collaboration Systems Enterprise collaboration system(ECS ) are cross-functional information Systems that enhance communication, coordination and collaboration among The members of business teams and workgroups. Information technology , especially Internet technologies , provide tool to help us collaborate - to Communicate ideas , share ideas , share resources and coordinate our cooperative work efforts as members of the many formal and informal process and projects team and workgroup that makes up many of today’s organizations. Thus, the goal of ECS is to enable us top work together more easily and Effectively by helping us to: Communication: Sharing information with each other. Coordinate: Coordinating our individual work efforts and use of resources with each other. Collaborative : Working together cooperatively on joint projects and assignments By Rakesh Roshan
- 66. Tools for Enterprise Collaboration By Rakesh Roshan Enterprise Collaboration System Collaborative Work Management Tools Electronic Conferencing Tools Electronic Communications Tools E-Mail Instant Messaging Voice mail Faxing Web Publishing Paging Data Conferencing Voice conferencing Video conferencing Discussion Forums Chat Systems Electronic Meeting Systems Calendaring and scheduling Task and Project Management Workflow Systems Document Sharing Knowledge Management
- 67. Decision Support System To success in business today, companies need information systems that can support the diverse information and decision-making needs of their managers and business professionals. The type of information required by decision makers in the company is directly related to the level of management decision and the amount of structure in the decision situations they face. you should realize that the framework of the classical managerial pyramid applies even in today’s downsized organization and flattened or nonhierarchical organizational structures. Thus the level of managerial decision making that must be supported by information technology in a successful organization are: Strategic Management : Typically , a board of directors and an executive committee of the CEO and top executives develop overall organizational goals, strategies, policies and objectives as part of a strategic planning process. Tactical management : Increasingly , business professionals in self-directed teams as well as business unit managers develop short- and medium range plans, schedules and budgets and specify the policies, procedures and business objectives for their subunits of the company By Rakesh Roshan
- 68. Operational Management : The members of self-directed teams or operating managers develop short-range plans such as weekly production schedules. They direct the use of resources and the performance of tasks according to procedures and within budgets and schedules they establish for the teams and other workgroups of the organization By Rakesh Roshan Strategic Management Executives and directors Tactical Management Business Unit Managers And self-Directed Teams Operational Management Operating Managers and Self-Directed Teams Decision Structure Information Characteristics Unstructured Semi structured Structured Decision Information Ad Hoc Un scheduled Summarized Infrequent Forward Looking External Wide Scope Prespecified Scheduled Detailed Frequent Historical Internal Narrow Focus
- 69. Decision Support in Business Using information systems to support business decision making has been one of the primary thrusts of the business use of IT. However during the 1990s , both academic researchers and business practitioners began reporting that the traditional managerial focus originating in classic management information systems(1960s), decision support systems (1970s) and executive information systems(1980s) was expanding. The fast pace of new information technologies like PC H/W and S/w suites , client/server networks and networked PC versions of DSS/EIS software made decision support available to lower levels of management , as well as to nonmanagerial individuals and self-directed teams of business professionals. By Rakesh Roshan
- 70. A business must meet the information and data analysis requirements of their stakeholders with more personalized and proactive Web-based decision support By Rakesh Roshan Business Stakeholder Requirements Information at your Fingertips Do-it-yourself Data Analysis Decision Support Response Personalized, Proactive Decision Analytics and Web-based Applications
- 71. Decision Support Systems Contd…….. DSS are computer-based information systems that provide interactive support to managers and business professionals during the decision making process. Decision support systems use (i) Analytical models (ii) Specialized database (iii) a decision maker’s own insights and judgments (iv) an interface , computer based modeling process to support the making of semi structured business decisions Example : Sales manager typically rely on MIS to produce sales analysis reports. These reports contain sales performance figures by product line, salesperson ,sales region and so on. A DSS , on the other hand, would also interactively shows a sales manager the effects on sales performance of change in a variety of factors. The DSS could then use several criteria to evaluate and rank several alternative combinations of sales performance factors By Rakesh Roshan
- 72. Components of DSS By Rakesh Roshan Legacy Software Web Browser Other Software User Interface Functions Hyperlinked Multimedia ,3-D Visualization Data Management Functions Data Extraction, Validation, Sanitation, Integration, and replication Model Management Functions Analytical Modeling, Statistical Analysis Operational Data Customer Account Data Sales Data Market Data Data Mart and Other Databases
- 73. Online Analytical Processing The competitive and dynamic nature of today’s global business environment is driving demands by business managers and analysts for information systems that can provide fast answers to complex business queries. The IS is responded to these demands with developments like analytical database, data marts, data warehouse, data mining techniques and multidimensional database structures and with specialized servers and Web enabled software products that support online analytical processing. Online analytical processing enables managers and analysts to interactively examine and manipulate large amounts of detailed and consolidated data from many perspectives. OLAP involves analyzing complex relationships among thousands or even millions of data items stored in data marts, data warehouse and other multidimensional databases to discover patterns ,trends and exception conditions. An OLAP session takes place online in real time, with rapid responses to a manager’s or analyst’s queries ,so that their analytical or decision making process is undistributed. By Rakesh Roshan
- 74. Online Analytical Processing By Rakesh Roshan Corporate Dtabases Multi- Dimensional Dtabases Spreadsheets Statistical packages Web-enabled OLAP Software Data are retrieved from Corporate databases and Staged in an OLAP Multidimensional Database for retrieval by Front-end systems Operational databases Data marts Data warehouse Client PCs OLAP Server
- 75. Activities and examples of the major types of analytical modeling (Using DSS) By Rakesh Roshan Type of Analytical Modeling Activities and examples What-if Analysis Observing how changes to selected variables affect other variables. Example : What if we cut advertising by 10 percent? What would happen to sales? Sensitivity analysis Observing how repeated changes to a single variable affect other variables. Example : Let’s cut advertising by $100 repeatedly so we can see its relationship to sales. Goal-Seek analysis Making repeated changes to selected variables until a chosen variable reaches a target value. Example : Let’s try increases in advertising until sales reach $1 million. Optimization analysis Finding an optimum value for selected variables, given certain constraints. Example : What’s the best amount of advertising to have, given our budget and choice of media?
- 76. Executive Information System Executive Information Systems(EIS) are information systems that combine many of the features of management information systems and decision support systems. When they were first developed, their focus was on meeting the strategic information systems was to provide top executives information systems was to provide top executives with immediate and easy access to information about a firm’s critical success factors(CSF), that is , key factors that are critical to accomplishing an organization’s strategic objectives. For examples: the executives of a retail store chain would probably consider factors such as its e-commerce versus traditional sales results or its product line mix to the critical to its survival and success. By Rakesh Roshan Features of an EIS In an EIS, information is presented in forms tailored to the preferences of the Executives using the system. For example, most executive information systems stress the use of a graphical user interface and graphics displays that can be customized to the information preferences of executives using the EIS. Other Information presentations methods used by an EIS include exception reporting And trend analysis. The ability to drill down, which allow executives to quickly Retrieve displays of related information at lower levels of detail, is another important capability.
- 77. Enterprise Information Portal An Enterprise Information Portal(EIP) is a Web-based interface and integration of MIS, DSS , EIS and other technologies that gives all intranet users and selected extranet users access to a variety of internal and external business applications and services By Rakesh Roshan
- 78. Components of Enterprise Information Portal(EIP) By Rakesh Roshan Sales VP Managers Sales Reps Other Employees Suppliers Customers Engineering VP Managers Engineers Corporate VPs Managers Analysts Marketing VP Managers Analysts Universal Interface Components Search Query Calendaring Channels/News e-Mail/Chat APIs Administration Security Load Balancing Meta Data Management Contextualization Inferencing Dynamic Profiling Portal Gateway DSS Tools Data Mining OLAP Other Tools Hyperlinking Indexing Taxamony Search Agents Enterprise Portal Server Operational Database Analytic Database Data Warehouse Business Application Intranets Extranets Internet web
- 79. Knowledge Management Systems Knowledge Management Systems as the use of information technology to help gather, organize and share business knowledge within an organization. In many organizations, hypermedia databases at corporate intranet websites have become the knowledge bases for storage and dissemination of business knowledge. This knowledge frequently takes the form of best practices, policies and business solutions at the project , team, business unit and enterprise levels of the company. For many companies, enterprise information portals are the entry to corporate intranets that serve as their knowledge management systems. That’s why such portals are called enterprise knowledge portals by their vendors. By Rakesh Roshan
- 80. Knowledge Management System Portals By Rakesh Roshan Enterprise knowledge portal Single point of access to all corporate data Personalized views of news and data Collaboration tools Community work areas ERP Databases CRM Databases Other Databases E-mail Groupware File System Documents Presentations Web Internet Intranet Extranet Enterprise Knowledge Base Structured data Sources Unstructured Data Sources Enterprise Knowledge Portal server with knowledge management Engine/server component Automatically crawls(searches) structured or unstructured data sources Categorizes searched data, tags and hyperlinks information Automatically builds user profiles based in activity. Web User(employee/customer) Data Sources
- 81. Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence(AI) is a field of science and technology based on disciplines such as computer science, biology, psychology, linguistics, mathematics and engineering. The goal of AI is to develop computers that can simulate the ability to think, as well as see, hear, walk, feel and talk. A major thrust of AI is the simulation of computer functions normally associated with human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning and problem solving. By Rakesh Roshan Attribute of Intelligent Behaviour Think and reason. Use reason to solve problem. Learn and Understand from experiences. Acquire and apply knowledge. Exhibit creativity and imagination. Deal with complex or perplexing situations. Respond quickly and successfully to new situations. Recognize the relative importance of elements in a situation. Handle ambiguous, incomplete, or erroneous information.
- 82. Business and AI AI-enabled applications are at work in information distribution and retrieval, database mining, product design, manufacturing, inspection, training, user support , surgical planning, resource scheduling and complex resource management. Indeed, for any one who schedules, plans, allocates resources, designs new products, use the Internet, develops software, is responsible for product quality, is an investment professional, heads up IT , use IT or operates in any of a score of other capacities and arenas, AI technologies already may be in place and providing competitive advantage. By Rakesh Roshan The Domains of Artificial Intelligence The major Domains of AI research and development are: Cognitive Science : This area of AI is based on research in biology, neurology, psychology, mathematics, and many allied disciplines. It focuses on researching how the human brain works and how humans think and learn. This results of such research in human information processing are the basis for the development of a variety of computer–based applications in AI. Robotics : AI, engineering and physiology are the basic disciplines of robotics. This technology produces robot machines with computer intelligence and computer controlled, human like physical capabilities.
- 83. 3. Natural Interfaces ; The development of natural interfaces is considered a major areas of AI applications and is essential to the natural use of computers by humans. For example, the development of natural languages and speech recognition are major thrusts of this area of AI. Being able to talk to computers and robots in conversational human languages and have them “understand” us as easily as we understand each other is a goal of AI research. By Rakesh Roshan Artificial Intelligence Natural Interface Applications Robotics Applications Cognitive Science Applications Expert System Learning Systems Neural Network Visual Perception Tactility Navigation Natural Languages Speech Recognition Virtual Reality
- 84. Expert System An expert system(ES) is a knowledge-based information system that uses its knowledge about a specific, complex application area to act as an expert consultant to end users. Expert systems provide answers to questions in a very specific problem area by making humanlike inferences about knowledge contained in a specialized knowledge base. They must able to explain their reasoning process and conclusions to a user. So, expert systems can provide decision support to end users in the form of advice from an expert consultant in a specific problem area. By Rakesh Roshan Component of an Expert System Knowledge Base : The knowledge base of an expert system contains (1) facts about a specific subject area and (2) heuristics (rules of thumb) that express the reasoning procedures of an expert on the subject. There are many ways that such knowledge is represented in expert systems. Examples are rule-based, frame-based, object-based and case based methods of knowledge representation. Software Resources : An expert system software package contain an inference engine and other programs for refining knowledge and communication with users. The inference engine program processes the knowledge related to a specific problem.
- 85. By Rakesh Roshan Components of an expert system……….. The Expert System Expert System Development User User Interface Programs Interface Engine Program Knowledge Base Knowledge Acquisition Program Knowledge Engineering Expert and/or Knowledge Engineer Workstations Expert System Software Workstations
- 86. By Rakesh Roshan Application Categories of Expert System Decision Management- Systems that appraise situations or consider alternatives and make recommendations based on criteria supplied during the discovery process: Loan portfolio analysis Employee performance evaluation Insurance underwriting Demographic forecasts Diagnostic/troubleshooting- Systems that infer underlying causes from reported symptoms and history: Equipment calibration Help desk operations Software debugging Medical diagnosis Design/configuration- Systems that help configure equipment components, given existing constraints: Computer option installation Manufacturability studies Communications networks Optimum assembly plan Selection/classification- Systems that help users choose products or processes , often from among large or complex sets of alternatives: Material selection Delinquent account identification Information classification Suspect identification Process monitoring/control- Systems that monitor and control procedures or processes: Machine control(including robotics) Inventory control Production monitoring Chemical testing
- 87. Benefits of Expert Systems : An expert system captures the enterprise of an expert or group of experts in a computer-based information system. Thus, it can outperform a single human expert in many problem situations. That’s because an expert system is faster and more consistent, can have the knowledge of several experts, and does not get tired or distracted by overwork of stress. Expert systems also help preserve and reproduce the knowledge of experts. They allow a company to preserve the expertise of an expert before she leaves the organization. Limitations of Expert Systems : The major limitations of expert systems arise from their limited focus, inability to learn, maintenance problems and development cost. Expert systems excel only in solving specific types of problems in a limited domain of knowledge . They fail miserably in solving problems requiring a broad knowledge base and subjective problem solving. They do well with specific types of operational or analytical tasks, but falter at subjective managerial decision making By Rakesh Roshan
- 88. Neural Networks Neural networks are computing systems modeled after the brain’s mesh like network of interconnected processing elements, called neurons. Of course, neural networks are a lot simpler in architecture( the human brain is estimated to have over 100 billion neuron brain cells!). However, like the brain, the interconnected processors in a neural network operate in parallel and interact dynamically with each other. This enables the network to “learn” from data it processes. That is, it learns to recognize patterns and relationships in this data. Example : A neural network can be trained to learn which credit characteristics result in good or bad loans. Developers of a credit evaluation neural network could provide it with data from many examples of credit applications and loan results to process, and opportunities to adjust the signal strengths between its neurons. By Rakesh Roshan
- 89. By Rakesh Roshan Development System Strategies
- 90. Organizational Planning By Rakesh Roshan Analyze the Organization’s Environment Develop Strategies Policies Tactics Articulate the Organization’s Plan Develop Implementation Methods and Controls Forecast Internal And external Developments Evaluate Accomplishments And Resources Team Building Modeling and Consensus Establish Vision Mission Goals Objectives Feedback
- 91. SWOT Analysis SWOT analysis ( strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats) is used to evaluate the impact that each possible strategic opportunity can have on a company and its use of information technology. A company’s strengths are its core competencies and resources in which it is one of the market or industry leaders. Weakness are areas of substandard business performance compared to others in their industry or market segments. Opportunities are the potential for new business markets or innovative breakthroughs that might greatly expand present markets. Threats are the potential for business and market losses posed by the action of competitors and other competitive forces, changes in government policies , disruptive new technologies and so on. Examples: Dell Computer Corp. is a good example of how a company can uses SWOT analysis to carve out a strong business strategy opportunity: the huge demand for PCs by Internet Connected Consumers and businesses. Dell recognized that its strengths was selling directly to consumers and businesses and keeping its cost lower than those of other hardware vendors.. As for weakness , the company acknowledged that it lacked solid dealer relationships. By Rakesh Roshan
- 92. Business Models and Planning A business model is a conceptual framework that express the underlying economic logic and system that prove how a business can deliver value to customers at an appropriate cost and make money. A business model answers vital questions about the fundamental components of a business, such as : who are our customers? What do our customers value? How much will it cost to deliver that value to our customers? How do we make money in this business? A business model is a valuable planning tool because it focuses attention on how all the essential components of a business fit into a complete system. Done properly , it forces entrepreneurs and managers to think rigorously and systematically about the value and viability of the business initiatives they are planning. Then the strategic planning process can be used to develop unique business strategies that capitalize on a firm’s business model to help it gain competitive advantages in its industry and the markets it wants to dominate. By Rakesh Roshan
- 93. By Rakesh Roshan Component of Business Model Questions for all Business Models Customer Value Is the firm offering its customers something distinctive or at a lower cost than its companies? Scope To which customers is the firm offering this value? What is the range of products/services offered that embody this value? Pricing How does the firm price the value? Revenue Source Where do the dollars come from? Who pays for what value and when? What are the margins in each market and what drives them? What drives value in each source? Connected activities What set of activities does the firm have to perform to offer this value and when? How connected are these activities? Implementation What organizational structure, systems, people and environment does the firm need to carry out these activities? What is the fit between them? Capabilities What are the firm’s capabilities and capabilities gaps that need to be filled? How does a firm fill these capabilities gaps? Is there something distinctive about these capabilities that allows the firm to offer the value better than other firms and that makes them difficult to imitate? What are the sources of these capabilities? Sustainability What is it about the firm that makes it difficult for other firms to imitate it? How does the firm keep making money? How does the firm sustain its competitive advantage?
- 94. Business/IT planning By Rakesh Roshan The Business/IT planning process , which focuses on discovering innovative approaches to satisfying a company’s customer value and business value goals. This planning process leads to development of strategies and business models for new e-business and e-commerce platforms, processes, products and services. The business/IT planning process has three major components: Strategy development : Developing business strategies that support a company’s business vision Resource management : Developing strategic plans for managing or outsourcing a company’s IT resources, including IS personnel , hardware, software, data and network resources Technology architecture : Making strategic IT choices that reflect an information technology architecture designed to support a company’s e-business and other business/IT initiatives . Customer And Business Value Visioning Business Strategies And Models Business/IT Strategies and Architecture Business Application Development and Deployment Key Insights Key Objectives Priorities More Questions Feedback Feedback
- 95. Identifying Business/IT Strategies Companies need a strategic framework that can bridge the gap between simple connecting to the Internet and harnessing its power for competitive advantage. The most valuable Internet applications allow companies to transcend communication barriers and establish connections that will enhance productivity, stimulate innovative development and improve customer relations. Strategic positioning matrix that can help a company identify where to concentrate its strategic use of Internet technologies to gain a competitive advantage. By Rakesh Roshan Global Market Penetration Product and service Transformation Cost and Efficiency Improvements Performance Improvement in Business Effectiveness HIGH LOW HIGH E-business processes/ collaboration/cost containment Internal Drivers External Drivers Customer connectivity/competition/technology
- 96. Business Application Planning The business application planning process begins after the strategic phase of business/IT planning has occurred. The application planning process includes the evaluation of proposals made by the IT management of a company for using information technology to accomplish the strategic business priorities developed. By Rakesh Roshan IT Proposals For Addressing Strategic Business Priorities Business Case for Investing in e-business projects Planning for Application Development and Implementation Key Objectives Action Plan Feedback Feedback
- 97. Developing System Solution By Rakesh Roshan
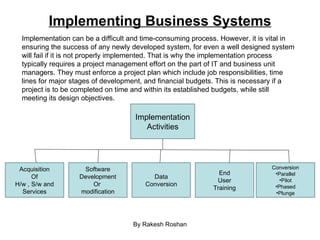
- 98. System Development Life Cycle By Rakesh Roshan Using the systems approach to develop information system solutions can be viewed as a multistep Process called the information systems development cycle, also known as the System development Life cycle(SDLC). SDLC includes the steps of (1) investigation (2) analysis (3) design (4) implementation And (5) maintenance. Systems Investigation Product: Feasibility Study Systems Analysis Product: Functional Requirement Systems Design Product: System Specifications Systems Implementations Product: Operational System Systems Maintenance Product: Improved System Determine how to address business opportunities and priorities Conduct a feasibility study to determine whether a new or improved business system is a feasible solution Develop a project management plan and obtain management approval Analyze the information needs of employees, customers and other business stakeholders. Develop the functional requirements of a system that can meet business priorities and the needs of all stakeholders. Develop specifications for the hardware, software, people, network and data resources, and the information products that will satisfy the functional requirements of the proposed business information system. Acquire hardware and software. Test the system, and train people to operate and use it. Convert to the new business system. Manage the effects of system changes on end users. Use a post implementation review process to monitor, evaluate and modify the business system as needed Understand the Business Problem or Opportunity Develop an Information System solution Implement The Information System Solution
- 99. Prototyping By Rakesh Roshan Identifying an End User’s Business Requirements Use and Maintain The Accepted Business System Revise the Prototypes to Better Meet End User Requirements Develop Business system Prototypes Investigation/Analysis: End users identify their business needs and assess the feasibility of several alternatives information system solutions Analysis/Design: End users and/or IS specialists use application development tools to interactively design and test prototypes of information system components that meet end user business needs. Design/Implementation: The business system prototypes are tested , evaluated and modified repeatedly until end users find them acceptable. Implementation/Maintenance: The accepted business system can be modified easily since most system Documentation is stored on disk. Prototyping Cycle Maintenance Cycle
- 100. By Rakesh Roshan Feasibility Studies Because the process of development can be costly, the systems investigation stage typically requires a preliminary study called a feasibility study. A feasibility study is a preliminary study where the information needs of prospective users and the resources requirements ,costs, benefits, and feasibility of a proposed project are determined. The feasibility of a proposed business system can be evaluated in terms of four major categories. Organizational Feasibility Economic Feasibility How well the proposed system support the business priorities of the organization. Cost savings Increased revenue Decreased investment requirements Increased profits Technical Feasibility Operational Feasibility Hardware ,software and network capability, reliability and availability Employee, customer, supplier acceptance Management support Government or other requirements
- 101. By Rakesh Roshan System Analysis Whether you want to develop a new application quickly or are involved in a long-term project, you will need to perform several basic activities of system analysis. Many of these activities are in extension of those used in conducting a feasibility study. However , systems analysis is not a preliminary study. It is an in-depth study of end user information needs that produces functional requirements that are used as the basis for the design of a new information system. Systems analysis traditional involves a detailed study of: The information needs of a company and end users like yourself. The activities resources and products of one or more of the present information systems being used. The information system capabilities required to meet your information needs , and those of other business stakeholders that may use the system. System Design System analysis describes what a system should do to meet the information needs of users. Systems design specifies how the system will accomplish this objective. Systems design consists of design activities that produce system specifications satisfying the functional requirements that were developed in the systems analysis process User Interface Design Data Design Process Design Screen , Form, Report and Dialog Design Data Element Structure Design Program and Procedure Design
- 102. By Rakesh Roshan End User Development In end user development, IS professionals play a consulting role, while you do your own application development. Sometimes a staff of user consultants may be available to help you and other end users with your application development efforts. This may include training in the use of application packages; selection of hardware and software ; assistance in gaining access to organization databases and of course , assistance in analysis, design and implementing the business application of IT that you read. Control What control are needed to protect against accidental loss or damage? Is there a need to control access to data used by the application? Processing What operations on the inputs are needed to produce the desired output? What software can most effectively support those operations? Storage Does the application use previously stored data? Does it create data that must be stored for future use by this or other applications? Output What information is needed by end users and in what form should the output be presented? Input What data are available, in what form?
- 103. Implementing Business Systems By Rakesh Roshan Implementation can be a difficult and time-consuming process. However, it is vital in ensuring the success of any newly developed system, for even a well designed system will fail if it is not properly implemented. That is why the implementation process typically requires a project management effort on the part of IT and business unit managers. They must enforce a project plan which include job responsibilities, time lines for major stages of development, and financial budgets. This is necessary if a project is to be completed on time and within its established budgets, while still meeting its design objectives. Implementation Activities Acquisition Of H/w , S/w and Services Software Development Or modification Data Conversion End User Training Conversion Parallel Pilot Phased Plunge
- 104. Evaluating Hardware, Software and Services By Rakesh Roshan Companies may use a scoring system of evaluation when there are several competing proposals for a hardware or software acquisition. They give each evaluation factor a certain number of maximum possible points. Then they assign each competing proposal points of each factor, depending on how well it meets the user’s specifications. Scoring evaluation factors for several proposals helps organize and document the evaluation process. It also spotlights the strength and weaknesses of each proposals. Large companies frequently evaluating proposed hardware and software by requiring the processing of special benchmark test programs and test data. Benchmarking simulates the processing of typical jobs on several computers and evaluates their performances. Users can then evaluate test results to determine which hardware device or software package displayed the best performance characteristics.
- 105. By Rakesh Roshan Hardware Evaluation Factor Performance What is its speed, capacity and throughput? Cost What is its lease or purchase price? What will be its cost of operations and maintenance? Reliability What are the risk of malfunction and its maintenance requirements? What are its error control and diagnostics features? Compatibility Is it compatible with existing hardware and software? Is it compatible with hardware and software provided by competing suppliers? Technology In what year of its product life cycle is it? Does it use a new untested technology or does it run the risk of obsolescence? Ergonomics Has it been “ human factor engineered” with the user in mind? Is it user-friendly, designed to be safe ,comfortable and easy to use? Connectivity Can it be easily connected to wide area and local area networks that use different types of network technology and bandwidths alternatives? Scalability Can it handle the processing demands of a wide range of end users, transactions, queries and other information processing requirements? Software Is system and application software available that can best use this hardware? Support Are the services required to support and maintain it available?
- 106. By Rakesh Roshan Software Evaluation Factors Quality Is it bug free, does it have many errors in its program code? Efficiency Is the software is well developed system of program code that does not use much CPU time, memory capacity or disk space? Flexibility Can it handle our business process easily, without major modification? Security Does it provide control procedures for errors , malfunctions and improper use? Connectivity Is it web enabled so it is easily access internet, Intranet and extranets, on its own , or by working with web browsers or other network software? Maintenance Will new features and bug fixes be easily implemented by our own software developers? Documentation Is the software well documented ? Does it include help screens and helpful software agents? Hardware Does existing hardware have the features required to best use this software? Other Factors
- 107. By Rakesh Roshan Evaluation Factors for IS Services Performance What has been their past performance in view of their past promises? Systems Development Are websites and other e-business developers available? What are their quality and cost? Maintenance Is equipment maintenance provided? What are its quality and cost? Conversion What systems development and installation services will they provide during the conversion period? Training Is the necessary training of personnel provided? What are its quality and cost? Backup Are similar computer facilities available nearby for emergency backup purposes? Accessibility Does the vendor provide local or regional sites that offer sales, systems development and hardware maintenance services? Business Position Is the vendor financially strong, wit good industry market prospects? Hardware Software
- 108. By Rakesh Roshan Software Software is the general term for various kinds of programs used to operate and manipulate computers and related devices. Computer Software Application Software System Software General Purpose Application Programs Application Specific Programs System Management Programs System Development Programs Software Suites Web Browsers E-Mail Word Spreadsheet Business- Accounting TPS,CRM,ERO etc Science Engg. Education Entertainment Operating System N/w mngt. Programs Database Mngt Programs Application Servers Programming Language Translators Programming Editors CASE
Editor's Notes
- #2: BY Rakesh Rosha