Sap overview
- 1. SAP Overview Srinivas VuppalaModule Trainer
- 2. SAP SAP has abbreviated as systems Analysis and Program Development in 1972 SAP has populated as Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing in 1977 Dietmar Hopp, Hans-Werner Hector, Hasso Plattner, KlausTschira and Claus Wellenreuther founded at walldrof, Germany in 1972 SAP is Public limited company known as SAP AG
- 3. SAP SAP is three dimensional integrated software The integration of core business systems within the organization from Financials, Human resources, Manufacturing and sales The seamless flow of data between two organizations that transact with each other Controversial approach of combining various business functions into one application and database
- 4. SAP Architecture SAP introduced the following architectures as per the market trend Single Tier 2 -Tier R/3 Architecture (Real-Time or 3-Tier or Multi-Tier Architecture)
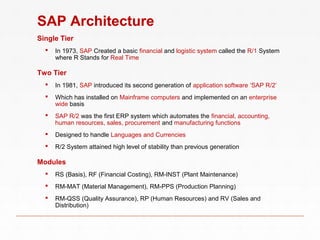
- 6. SAP Architecture Single Tier In 1973, SAP Created a basic financial and logistic system called the R/1 System where R Stands for Real Time Two Tier In 1981, SAP introduced its second generation of application software ‘SAP R/2’ Which has installed on Mainframe computers and implemented on an enterprise wide basis SAP R/2 was the first ERP system which automates the financial, accounting, human resources, sales, procurement and manufacturing functions Designed to handle Languages and Currencies R/2 System attained high level of stability than previous generation Modules RS (Basis), RF (Financial Costing), RM-INST (Plant Maintenance) RM-MAT (Material Management), RM-PPS (Production Planning) RM-QSS (Quality Assurance), RP (Human Resources) and RV (Sales and Distribution)
- 7. SAP Architecture 3-Tier / Real-Time / Multi-Tier Architecture SAP R/3 is integrated software solutions for client/server and distributed open systems The software is highly customizable, scalable using SAP’s proprietary programming language R/3 Comprised of application, presentation and database servers SAP R/3 is based on various hardware and software architectures, running on most type of UNIX, Windows and OS/400 SAP R/3 runs on several databases Oracle, Adabas D, Informix, DB2 for UNIX, DB2/400, Microsoft SQL Server 6.0 Servers are linked by Communication Networks Perform tasks without sacrificing data integration and processes within the system
- 8. 3-Tier Architecture The SAP R/3 architecture is based on a 3-tier client/server principle Presentation Server Application Server Database Server
- 10. Servers Overview Presentation Server GUI only At workstation Very light Sends requests to application server Obtains screens from application server and displays Application Server One application server is needed to operate an sap system Services are divided among several application servers Services are technically carried out by Work Processes (Components) Components are able to execute an application (Logic) Database Server Interface between application server and RDBMS Holds the vendor specific DB driver
- 11. Multi-tier Internet Architecture User Dialog: Graphical information processing Processing application logic: System Management Transaction Monitoring Handling Internet access Processing Internet Transactions Presentation Application Database Create Production Orders Release Production Orders Schedule Production Accept Customer Order Confirm Delivery Build Products Explode Bill-of- Material Reserve Material Customer Service Rep Plant Personnel Production Order Customer Order Part Material Task Internet Information Storage Database Backup Layer Internet Architecture Multi-tier 10-20% 60-70% 5-10% 10-20% Load Application Services Database Services Internet Server Web Server Web Browser Presentation Services Presentation Services Web Server Internet Server Application Services Database Services 2-tier 3-tier
- 12. SAP R/3 Conceptual Areas SAP Conceptual Areas Application Area (Initiate and execute SAP transactions) (Functional) Basis Area (The technical administration of the system) (Authorizations/Ids/etc) Development Area (A developer’s Workbench, Create & Test ABAP/4 programs) (Technical)
- 13. Systems in R/3 Development System (DC) Quality System (QC) Production System (IC) Client 110 100 etc.. Transport Request
- 14. Clients in R/3
- 16. SAP Modules SAP R/3SAP R/3 FIFI WFWF PSPS PMPM WMWM PPPP MMMM SDSD HRHR AMAM COCO QMQM PP – Production Planning WM – Warehouse Management PM – Plant Maintenance AM – Asset Management PS – Project System MM – Materials Management SD – Sales and Distribution QM – Quality Management WF – Workflow HR – Human Resources CO – Controlling FI – Financial Accounting
- 17. SAP R/3 Application Modules Financial accounting (FI) Controlling (CO) Materials management (MM) Sales and Distribution (SD) Human resources (HR) Production Planning (PP) Quality management (QM) Asset Management (AM) Project system (PS) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- 18. MM Material Procurement Inventory Management Batch Management Goods inspection Invoice Verification PP BOM/Work Center/Routing MRP Capacity Evaluations Production Orders QM in production SD Inquiry processing Sales Order Processing Delivery Processing Billing FI General Ledger Accounts Payable Accounts receivable Cash management CO Cost Center Accounting Product Costing Order Contribution Analysis Module Functionalities
- 19. SAP Standard Application Benchmarks Materials Management- MM Sales & Distribution- SD Production Planning- PP Warehouse Management-WM Assemble-To-Order - ATO Advanced Planning and Optimizing - APO Project System- PS Online Store Cross Application Time Sheets- CATS Payroll Business Information Warehouse- BW E-commerce mySAP Human Resources mySAP Business Intelligence Retail Banking - Bank Customer Accounts- BCA Utilities - Customer Care and Service - CCS Industry Solutions mySAP Supply Chain Management mySAP Product Lifecycle Management Financial Accounting - FI mySAP Financials Internet Sales Customer Interaction Center mySAP Customer Relationship Mgmt
- 23. Organizational Structure - Levels
Editor's Notes
- #16: The R/3 System architecture allows you to separate application from the presentation and the database. This is the prerequisite for distributing load onto several application servers in client/server configurations. Therefore, the system can be distributed, in hardware terms, at three different levels. This architecture means that the installed host service can be adjusted without any problems (scalability), especially where load profiles have changed as a result of increasing user numbers, or because additional components have been used. R/3 System scalability provides you with flexibility when choosing hardware and software. Examples of R/3 System scalability: . Brewery - 20 users . Small Telecom company - 415 users . Large Software Company - 2000 users . Oil & Gas Company - 2500 users . Large Engineering Company- 3200 users . Large Telecom Company- 5800 users
- #17: Let us see a few of the R/3 Modules in brief Financial Accounting Financial Accounting is designed for automated management and external reporting of general ledger, accounts receivable, accounts payable and other sub-ledger accounts with a user defined chart of accounts. As entries are made relating to sales production and payments journal entries are automatically posted. This connection means that the "books" are designed to reflect the real situation. Controlling Controlling represents the company's flow of cost and revenue. It is a management instrument for organizational decisions. It is also automatically updated as events occur. Assets Management Asset Management is designed to manage and supervise individual aspects of fixed assets including purchase and sale of assets, depreciation and investment management. Sales and Distribution Sales and Distribution helps to optimize all the tasks and activities carried out in sales, delivery and billing. The key elements are; pre-sales support, inquiry processing, quotation processing, sales order processing, delivery processing, billing and sales information system. Materials Management Materials Management supports the procurement and inventory functions occurring in day-to-day business operations such as purchasing, inventory management, reorder point processing, etc. Production Planning Production Planning is used to plan and control the manufacturing activities of a company. This module includes; bills of material, routings, work centers, sales and operations planning, master production scheduling, material requirements planning, shop floor control, production orders, product costing, etc Quality Management Quality Management is a quality control and information system supporting quality planning, inspection, and control for manufacturing and procurement. Plant Maintenance In a complex manufacturing process, maintenance means more than sweeping the floors. Equipment must be services and rebuilt. These tasks affect the production plans. Plant Maintenance module supports and supervises these maintenance. Warehouse Management Warehouse Management provides flexible, automated support to assist in processing all goods movements and in maintaining current stock inventories in the warehousing complex. Human Resources Human Resources is a complete integrated system for supporting the planning and control of personnel activities. Workflow Workflow is a solution which has been integrated fully in the R/3 System and which enables customer-specific business process flows to be coordinated and controlled on a cross-application and cross-workplace basis. Project System Project System is designed to support the planning, control and monitoring of long-term, highly complex projects with defined goals.
- #21: The R/3 System is a client system. The client concept enables the joint operation, in one system, of several enterprises that are independent of each other in business terms. During each user session you can only access the data of the client selected during the logon. A client is in organizational terms an independent unit in the R/3 System. Each client has its own data environment and therefore its own master data and transaction data, assigned user master records and charts of accounts and specific customizing parameters. A user master record linked to the relevant client must be created for users to be able to log on to the system. To protect access, a password is required for logon. The password is hidden as you type (you only see asterisks). SAP systems are available in several languages. Use the Language input field to select the logon language for each session. Multiple logons are always logged in the system beginning with Release 4.6. This is for security as well as licensing reasons. A warning message appears if the same user attempts to log on twice or more. This message offers three options: Continue with current logon and end any other logons in the system Continue with current logon without ending any other logons in the system (logged in system) Terminate current logon
- #22: SAP Easy Access is the standard entry screen displayed after logon. Using the menu path Extras® Set start transaction you can select a transaction of your choice to be the default entry screen after logon. You navigate through the system using a compact tree structure that you can adapt to your own specific requirements. Use the menu path Extras® Settings to change your view of the tree structure. You can use this to display technical names (transaction codes). You can also create a Favorites list of the transactions, reports, files and Web sites you use most. You can add items to your favorites list using the Favorites menu option or by simply dragging & dropping them with the mouse.
- #23: Command field: You can use the command field to go to applications directly by entering the transaction code. You can find the transaction code either in the SAP Easy Access menu tree (see next slide) or in the relevant application under System® Status. Menu bar: The menus shown here depend on which application you are working in. These menus contain cascading menu options. Standard toolbar: The icons in the system function bar are available on all R/3 screens. Any icons that you cannot use on a particular screen are dimmed. If you leave the cursor on an icon for a moment, a small flag will appear with the name (or function) of that icon. You will also see the corresponding function key. The application toolbar shows you which functions are available in the current application. Title bar: The title bar displays your current position and activity in the system. Check boxes: Checkboxes allow you to select several options simultaneously within a group. Radio buttons: Radio buttons allow you to select one option only. Status bar: The status bar displays information on the current system status, for example, warning and error messages. A tab provides a clearer overview of several information screens. Options: You can set your font size, list colors, and so on here.
- #24: The highest-level element of all organizational units is the client. The client can be an enterprise group with several subsidiaries. All of the enterprise data in an R/3 System implementation is split into at least the client area, and usually into lower level organizational structures as well. Flexible organizational units in the R/3 System enable more complex enterprise structures to be represented. If there are many organizational units, the legal and organizational structure of an enterprise can be presented in different views. By linking the organizational units, the separate enterprise areas can be integrated and the structure of the whole enterprise represented in the R/3 System.