Tech ed 2012 eim260 modeling in sap hana-exercise
- 1. MODELING IN SAP HANA EIM260 Exercises / Solutions
- 2. 2 Initial Setup During the exercises, you will work on a SAP HANA system with the following system properties: Host name: coe-he-083.wdf.sap.corp Instance number: 00 SAP System ID (SID): ANC Database user name: EIM260_XX (XX = your assigned student ID) Password: Welcome1 Database Schema EIM260 Exercise package eim260.sessionX.eim260-XX.exercise1-3 Solution package eim260.solution.exercise1-3 Session X (X = your assigned session ID) As preparatory steps, make sure a connection to the backend SAP HANA database system is defined with your assigned user (EIM260_XX). 1. Start the SAP HANA studio from the Windows Desktop 2. In order to add a new HANA system, right-click on the background of the white area in the “Navigator” view. Choose “Add System…” from the context menu.
- 3. 3 3. Register a new System. Enter the Hostname, Instance Number and Description. Host: coe-he-083.wdf.sap.corp Instance: 00 Click > Next. 4. Enter your assigned user and password credentials. Enter EIM260_XX where XX represents your assigned number Password: Welcome1 Click > Finish.
- 4. 4 5. Become familiar with the modelling environment. Ensure that the Modeler perspective is open. (Window > Open Perspective > Other > Modeler Modelling artefacts reside within the Content folder and within package eim260. The tables used in the exercises are located in schema EIM260. Note: The tables were replicated out of an SAP ERP system using SLT and are referred to as the EPM Demo model. Data for the exercises were generated through transaction SEPM_DG (SAP BASIS 7.02+). 6. Within your assigned session package create your own personal package named “eim260-XX” Right-click on the assigned session package folder Select “New” > “Package” from the context menu Remember: XX is your assigned student number 7. Within the Package creation window supply the following values: Name: eim260.sessionX.eim260-XX (where X = assigned session ID) (where XX = assigned student ID) Click OK.
- 5. 5 8. Create one more package for the first exercise (within the previously created package): In the creation wizard enter: Name: eim260.sessionX.eim260- XX.exercise1 (where X = assigned session ID) (where XX = assigned student ID) Click OK. 9. Ensure that your package structure looks as follows.
- 6. 6 Exercise 1: Variables & Input Parameters The exercise teaches students how variables can accelerate the joining of Sales data and Delivery data. Traditionally unions have been used to combine different subject areas that have corresponding dimensions. Students will therefore learn how to safely join Analytical Views that have different dimensions by using variables that will prompt the front end tools to supply values. As a result the variables are pushed down into the Database exploiting the underlying features of SAP HANA and will result in optimal performance. This exercise will also teach students how to work with Input Parameters and how they similarly can be leveraged via prompts from within font end tools such as Analysis for Office. As a result input parameters can be pushed down directly into low level Database calculations. 1.1 Create the Customer Attribute View 1. Navigate and select your previously created exercise1 package With the Right Mouse Button > Select New > Attribute View 2. Enter the name of the Attribute View: CUSTOMER_AT. Select Standard Attribute View Click Finish (As a result the Attribute View editor will appear)
- 7. 7 3. Manually add both the Business Partners and Address table. Expand the Tables folder underneath schema EIM260 and drag and drop the 2 tables into the Attribute View editor. Address Table (SNWD_AD) Business Partners (SNWD_BPA) 4. Create a Join (Referential) between the 2 tables. Re-arrange the tables so that the Business Partner Table is located on the left hand side. 5. Click and select the Address Guid field from the Business Partner table and drag/drop it to the Node Key field on the Address Table. Referential Join should be defaulted. 6. Set the Cardinality indicator between the tables. Make sure to select the JOIN line that links the 2 tables. At the bottom of the screen locate the Properties View and Change the Cardinality to (n..1). Note: The LEFT Business Partner table is the MANY (n) table and joins to the RIGHT (1) dimension table. 7. Add the KEY Attribute to the Attribute View. Select the key field NODE_KEY on the Business Partner table > right click on field. Choose Add as Key Attribute. Result: The NODE_KEY: (SNWD_BPA.NODE_KEY) appears in the Output frame.
- 8. 8 8. Add the regular Attributes to the Attribute View. Select COMPANY_NAME > Right Click > Add as Attribute Select both CITY and COUNTRY from the Address table > Right Click > Add as Attribute. 9. Save and Activate. Towards the top right corner of the Attribute editor click on the green horizontal arrow. Within the Job Log view at the bottom of the screen review the Activation status and ensure successful activation. Note: Details regarding unsuccessful Activations can be reviewed by double clicking on the Activation message. 10. Preview the Attribute View. Click on the Data Preview Icon in the title bar. As a result the Preview will show the results as follows.
- 9. 9 1.2 Create the Sales Analytic View 1. Select package exercise1 > Right Click > New > Analytic View 2. Enter SALES_AV for the name of the Analytical View within the creation wizard. You may leave the value for “Schema for currency conversion” unselected. Click > Next. 3. Find both tables (in schema EIM260), SNWD_SO (Sales Orders) and SNWD_SO_I (Sales Order Items) and click Add. Click Next.
- 10. 10 4. On the next screen of the wizard select the 2 Attribute Views located in different packages: First expand the folder (EIM260/sessionX/eim260- XX/exercise1) and select the attribute view CUSTOMER_AT. Then navigate to the solution/exercise1 directory and use the MATERIAL_AT Attribute view which was created for you. Click on Finish. As a result the Analytical View editor opens 5. Within the Data Foundation Tab create a JOIN between the Order Items and Order Header table. Ensure the Order Items table (SNWD_SO_I) is positioned to the left of the Order Header (SNWD_SO) table. Create a Referential JOIN between the Order Items table field (PARENT_KEY) and the Order Header table field (NODE_KEY) While selecting the JOIN line between the 2 tables, change the Cardinality to (n..1) - within the Properties View at the bottom of the Window.
- 11. 11 6. Next select and add the „private‟ attributes to be included in the Analytic view SNWD_SO_I.NODE_KEY SNWD_SO_I.PARENT_KEY SNWD_SO_I.PRODUCT_GUID SNWD_SO.BUYER_GUID SNWD_SO.CREATED_ON Right click on the fields > Add as Attribute 7. Note: Due to a field name conflict the NODE_KEY private attribute was automatically renamed to NODE_KEY_1. Select the NODE_KEY_1 Private Attribute and rename the field to ITEM_ID below within the Properties View. 8. Proceed to rename PARENT_KEY to ORDER_ID
- 12. 12 9. Within the Data Foundation tab add Measures from the fact table SNWD_SO_I. Select 3 measures > Right Click > Add as Measure. SNWD_SO_I.GROSS_AMOUNT SNWD_SO_I.NET_AMOUNT SNWD_SO_I.TAX_AMOUNT 10. Create a Calculated Measure to display the total quantity of items ordered. Right click on the folder Calculated Measures > New 11. Name the Calculated Measure > ORDER_QTY Supply the following values: Aggregation Type: SUM Data Type: DECIMAL (13,2) Expression: "NET_AMOUNT"/"PRICE" HINT: You can expand the Attribute View MATERIAL_AT and select the PRICE Attribute.
- 13. 13 12. Create a new Input Parameter (Country) that will be used for dynamic gross amount calculations depending on the Country value supplied. On the Input Parameters folder > Right Click > New 13. Supply the following values: Name: IP_COUNTRY Type: Attribute Value Attribute: CUSTOMER_AT.COUNTRY Click OK. Optional: Read only if you experience the above error. Due to a bug in the current version you may experience this error when you click on OK. As a work around you have 2 options Either delete and re-add the Input Parameter Or change the Type drop down and select to Currency > Then enter 1 into the Length field. Then change the Type drop down list back to Attribute Value. Then you should be able to click OK.
- 14. 14 14. Create a new Calculated Measure that will calculated the gross amount depending on the specific Country Value supplied: Calculated Measures > Right Click > New 15. Within the Calculated Measure supply the following values: Name: GROSS_AMOUNT_CM Aggregation Type: SUM Data Type: DECIMAL (13,2) Expression: if( "COUNTRY"= '$$IP_COUNTRY$$',"GROSS_AMOUNT",0 ) Note: The above expression will only calculated the gross amounts for the country value passed in via the input parameter. Click OK.
- 15. 15 16. Next join the Dimensional Attribute Views. Choose the Logical View Select the NODE_KEY field within the CUSTOMER_AT Dimension and drag a line to the BUYER_GUID defined on the Data Foundation. Continue to join the Material Attribute View Dimension. Select the MATERIAL_NODE_KEY field within the MATERIAL_AT Dimension and drag a line to the PRODUCT_GUID field defined on the Data Foundation. 17. Save > Activate > Preview: When you Preview you will be Prompted to supply a Country value Enter „US‟ in the From field Click OK Review the Preview output data. GROSS_AMOUNT_CM is only calculated for those Countries that equal the Input Parameter Value.
- 16. 16 1.3 Create a Calculation View that combines Sales and Delivery Analytical Views 1. Create a new Calculation View within package exercise1 2. Use the wizard and enter SALES_DELIVERY_CV for the name of the Graphical Calculation View. Leave the “Schema for conversion” field unselected. Click Next. 3. In the second step of the Calculation view wizard add 2 Analytical Views from within 2 different packages: First expand your own package and select your SALES_AV and add that to the right hand side of the screen. Proceed to also include the DELIVERY_AV Analytical View located in the solution package that was created for you. Click Finish
- 17. 17 4. As a result of the previous step the Graphical Calculation View editor opens. Create a Join between the Deliveries and the Sales Analytical View by dragging the Join Node from the Tools Palette into the work area. 5. Next, with the mouse hover over the Delivery Analytical view until you see the „Create connection‟ icon. Drag a line to the Join node. Do the same for the Sales Analytical view by dragging a line to the Join node. 6. Click on the Join node and define the Join KEY and attributes. To create the join drag a line between both ITEM_IDs.
- 18. 18 7. Next select/add the required attributes > Right Click on the field > Add to Output. Tip: Add all the fields except the following fields in the list below. SALES_AV.PRICE SALES_AV.SUPPLIER_GUID SALES_AV.MATERIAL_NODE_KEY SALES_AV.NODE_KEY row.count DELIVERY_AV.DELIVERY_ID 8. Connect the Join node to the Output node by dragging a connection line. 9. Next click on the Output node and distinguish the fields either as attributes or measures. Select the fields listed below > right click > add as Measure GROSS_AMOUNT NET_AMOUNT TAX_AMOUNT ORDER_QTY QUANTITY GROSS_AMOUNT_CM 10. Proceed to add the rest of the fields as regular Attributes. ITEM_ID, CATEGORY, ORDER_ID, PRODUCT_ID,COUNTRY, COMPANY_NAME, CITY, DELIVERY_DATE, CREATED_ON
- 19. 19 11. Rename the QUANTITY field to DELIVER_QTY. Click on the measure Quantity. Within the Properties view rename the measure to DELIVER_QTY 12. Define one variable for each Analytical view. Start with the Delivery Date field from the Delivery Analytical View. Note: This will allow the front end tools to filter the data-set by the delivery date. Within the Output node > Attributes > right click on Delivery Date > “Create Variable – Apply Filter” 13. The Variables pop-up window appear: Supply the values shown in the image. You many leave the default Name, Description and Attribute field as is. Change the Selection Type drop down list to INTERVAL (This will allow front end tool to specify both to-and-from delivery dates) Click OK.
- 20. 20 14. Next proceed to create a second Variable for the Sales Analytical view‟s Created On field. Note: this filter will allow front end tools to filter by the order creation date. Remember to change the Selection Type drop down list to INTERVAL Click OK. Save, Activate 1.6 Advanced Office Analysis 1. Open Advanced Office Analysis > from the Windows Start Menu > SAP Business Objects Analysis for Microsoft Excel 2. Click on Analysis. 3. Underneath the File menu click Insert and select Data Source …..
- 21. 21 4. (Optional) Skip the SAP Business Objects logon Window if being prompted to Login. Instead you will connect directly to the SAP HANA database via an ODBC connection that is already setup. Note: See the Appendix for ODBC configuration instructions. 5. Select the data source EIM260. (Refer to the appendix for instructions how to setup a ODBC Data Source to SAP HANA.) 6. Enter your assigned User ID (EIM260_XX) and enter Welcome1 for the password. 7. Next select the Calculation View SALES_DELIVERY_CV from within your exercise1 package. Tip: Click on the Search tab and enter eim260-xx to list all your models Click OK. 8. When the Prompts window appear supply the following values: DELIVERY DATE (Variable): 20120101 20120501 CREATED ON (Variable): 20120101 20120501 COUNTRY (Input Parameter): US
- 22. 22 9. Drag the Category dimension and add it to the Rows area: Notice the Total Gross Amount for Flat screens across all countries, then notice the Gross Amount Calculated Measure that represents the „US‟ input parameter that was entered. Note: To change any of the variables or input parameter click on the Prompts Icon in the Ribbon:
- 23. 23 Exercise 2: Current year previous year sales comparison This exercise will teach students how to create dynamic models to compare current year sales versus previous year sales by quarter. Student will learn how to create time based attribute views, work with expression logic and use unions to combine sales figures. 2.1 Create a Time based Attribute view 1. Create a package called exercise2 2. Create a new Attribute View within the package exercise2 called TIME_AT and supply the parameters as shown in the image. Select „Time‟ Attribute View type. Calendar Type: Gregorian Granularity: Date Check Auto Create. Click Finish. 3. Within the Attribute View editor review the Attributes within the Output. As a result of checking „Auto Create‟ in the previous step the system automatically added fields in the Output structure. Remove all the attributes and leave the following list of Attributes YEAR, QUARTER, MONTH WEEK, DAY, DATE_SAP (Key) To remove an Attribute: Right click on the Attribute > Remove Save, Activate & Preview. 4. Review the output. Notice the KEY field DATE_SAP; in the next step it will be used to join the Time Dimension to the Analytical View.
- 24. 24 2.2 Create a copy of your Analytical View 1. Create a copy of the previously created SALES_AV Analytical View from exercise1. Select package exercise2 > right click > New > Analytical View Select the „Copy From‟ radio button and click on the „Browse‟ button to select the Analytical View to copy. Expand the folders under eim260 and select your SALES_AV within the exercise1 package. Click OK. Click Finish on the Next Screen. 2. As a result the Analytical View editor is opened. On the Data Foundation Tab Remove both the Gross Amount Calculated Measure and then IP_COUNTRY Input Parameter. 3. Within the Logical View add the previously created TIME_AT Attribute View as a dimension to the Analytical View. Click on the Logical View tab. Expand package exercise2 and drag and drop the TIME_AT Attribute view into the Logical View work area. Create a JOIN from the TIME_AT Dimension to the Data Foundation by dragging a line from the DATE_SAP field of the TIME_AT to the CREATED_ON field in the Data Foundation. Save, Activate, Preview.
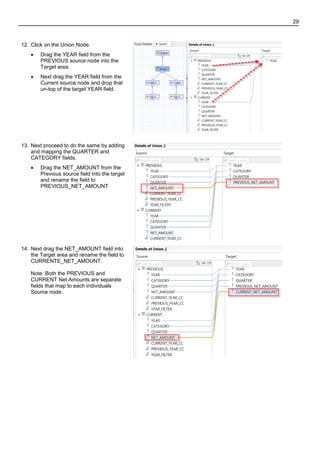
- 25. 25 2.3 Create a Graphical Calculation View to combine the current year sales with previous year sales 1. Within the exercise2 package create a new Graphical Calculation View named PREVIOUS_CURRENT_YEAR_SALES_CV 2. As a result the Graphical Calculation View Editor opens. Drag and drop the SALES_AV Analytical View 2 times into the work area. From the Tools Palette select 2 Projection Nodes and add them to the work area as shown in the image Next add a UNION node Connect all the nodes using a connection line. 3. Important! Rename the Projection node on the left to PREVIOUS, and rename the Projection node on the right to CURRENT. Hint. To enable the Projection node name to be editable, click on the Projection node once with the left mouse button, and then once more click with the left mouse button on the name of the Projection node using the left mouse button.
- 26. 26 4. Click on the PREVIOUS Projection Node: Define the Projection Node fields, select them > Right click > and add to the Output QUARTER, YEAR, CATEGORY, NET_AMOUNT 5. Next add 3 different Calculated Columns that will be used to determine if an order was created the current year or the previous year. Add a New Calculated Column to the Output of the PREVIOUS Projection Node. Right Click on the Calculated Columns folder > New 6. As a result the Calculated Column Editor Window Opens. Supply the following values for the Calculated Column: Name: CURRENT_YEAR_CC Data Type: VARCHAR Length: 4 Expression: midstr(string(now()),1,4) Hint: You can either select the midst() function underneath the String Functions list or you can manually type the expression syntax. Hint: The expression would return 2012 When finished click Add.
- 27. 27 7. Next create another Calculated Column named PREVIOUS_YEAR_CC Supply the following values for the Calculated Column: Data Type: VARCHAR Length: 4 Expression: string(double(“CURRENT_YEAR_CC”)-1) Note: The expression subtracts 1 from the current year calculated columns. Therefore the expression would return 2011. Click Add. 8. Next Define the last Calculated Column named YEAR_FILTER: Supply the following values for the Calculated Column: Data Type: INTEGER Expression: if("CURRENT_YEAR_CC"="YEAR",1, if("PREVIOUS_YEAR_CC"="YEAR",2,-1),-1) Note: Both the current year value and the previous year value will be compared to the YEAR field from the TIME_AT Attribute View. Current year sales will be flagged as 1 and previous year sales will be flagged as 2. Therefore in the next step you can filter by 1 and 2 in order to filter the data for this year and last year. Click Add.
- 28. 28 9. Continue to work the PREVIOUS Projection Node Define a filter for YEAR_FILTER Calculated Column. Right Click on YEAR_FILTER > Apply Filter 10. As a result the Apply Filter Window appears. Select the Equal Operator Enter the value 2 Click Ok. Note: The number 2 represents the previous year‟s sales. 11. Click on the CURRENT Projection node Add YEAR, CATEGORY, QUARTER and NET_AMOUNT as output columns. Define exactly the same calculated columns as you did on the PREVIOUS projection node. CURRENT_YEAR_CC PREVIOUS_YEAR_CC YEAR_FILTER Apply a filter on the YEAR_FILTER Calculated Column and set the Equal Operator to 1 to filter the current year sales.
- 29. 29 12. Click on the Union Node. Drag the YEAR field from the PREVIOUS source node into the Target area. Next drag the YEAR field from the Current source node and drop that un-top of the target YEAR field. 13. Next proceed to do the same by adding and mapping the QUARTER and CATEGORY fields. Drag the NET_AMOUNT from the Previous source field into the target and rename the field to PREVIOUS_NET_AMOUNT 14. Next drag the NET_AMOUNT field into the Target area and rename the field to CURRENTE_NET_AMOUNT. Note: Both the PREVIOUS and CURRENT Net Amounts are separate fields that map to each individuals Source node.
- 30. 30 15. Click on the Output node. Define CATEGORY and QUARTER as Attributes Define PREVIOUS_NET_AMOUNT and CURRENT_NET_AMOUNT as Measures. Save, Activate & Preview 16. Click on the Info button to access the generated SQL statement. 17. Copy the SQL statement. 18. Open the SQL Editor. Select the Connection > Click on the SQL Icon.
- 31. 31 19. Paste (CTRL+V) the SQL statement into the SQL Editor. Delete all references of CATEGORY from both the field selection and the GROUP BY. Move QUARTER to the first field. Then execute the statement or press F8. As a result you will see the net amount per quarter for both the current year and previous year. Note: Replace X with your assigned numbers. SELECT "QUARTER", sum("PREVIOUS_NET_AMOUNT") AS "PREVIOUS_NET_AMOUNT", sum("CURRENT_NET_AMOUNT") AS "CURRENT_NET_AMOUNT" FROM "_SYS_BIC"."eim260.sessionX.eim260-XX.exercise2/PREVIOUS_CURRENT_YEAR_SALES_CV" GROUP BY "QUARTER"
- 32. 32 Exercise 3: Master data reporting This exercise will teach students how to create non OLAP models and build a report showing the number of business partners versus customers. Students will model directly against raw column tables; learn how to use exceptional aggregation including how to create custom counters. 3.1 Create a Calculation View 1. Create a package called exercise3 2. Create a new Graphical Calculation View named BUSINESS_PARTNER_CV Select the Address Table (SNWD_AD) and the Business Partners (SNWD_BPA) table to be used within the Calculation View. Click Finish. 3. Within the Graphical Calculation View editor add a JOIN node and a Projection node to the work area. Connect all the nodes using a connection line as shown in the image.
- 33. 33 4. Click on the JOIN node Join the Business Partner table to the Address table using the Address Guid field from the SNWD_BPA table and the NODE_KEY field from the SNWD_AD table. Drag a line between these fields mentioned to indicate the JOIN fields. 5. Proceed to add the following additional fields to the Output of the JOIN SNWD_BPA.BP_ROLE SNWD_BPA.COMPANY_NAME SNWD_AD.CITY SNWD_AD.POSTAL_CODE SNWD_AD.STREET SNWD_AD.COUNTRY 6. Click on the Projection Node and add all the fields to the Output Right click on the field > Add to Output
- 34. 34 7. Within the Projection node create a new Calculated Column named BP_CUSTOMER Select INTEGER as the data type Enter the following expression “BP_ROLE” = „01‟ Note: The above expression will either return 0 or 1 depending on the value of BP_ROLE. Click Add. 8. Next create another Calculated Column also within the Projection node named BP_SUPPLIER Select INTEGER as the data type Enter the following expression “BP_ROLE” = „02‟ Click Add.
- 35. 35 9. Click on the Output node. Add Country and Company name as Attributes Add both the Calculated Columns BP_CUSTOMER and BP_SUPPLIER as Measures. 10. Next create a counter. Right click on Counters > New Name the Counter TOTAL Click on the Add Attribute button and select COMPANY_NAME Click OK. 11. Hide the Company Name Attribute. Click on the Company Name > within the properties window > set the Display Attribute value to false > Also set Hidden > true.
- 36. 36 12. Save, Activate. Preview
- 37. 37 Exercise 4: (Optional) SQL Editor This exercise is an extension to the first exercise and will show students how variables and input parameters are used within SQL statements. 4.1 Preview SALES_DELIVERY_CV 1. Expand your exercise1 package and perform a Data Preview on the Calculation View 2. Within the Prompts window supply the same values as you did before and click OK to execute the query. DELIVERY DATE (Variable): 20120101 - 20120501 CREATED ON (Variable): 20120101 – 20120501 COUNTRY (Input Paramater): US 3. After the results are returned click on the Icon to copy the SQL statement. Note: The default SQL statement generated by the standard Preview returns all possible dimensions; we therefore need to change the SQL query to something more optimal within the SQL Editor. Click on Copy.
- 38. 38 4. Open the SQL Editor. Ensure to first click on the connection > SQL icon in the top menu bar. 5. Paste (CTRL+V) the SQL statement into the SQL Editor 6. Modify the SQL statement to include several measures but only 1 dimension (COUNTRY). Notice how the Date Variable are passed down into the Database through WHERE clauses Notice how the Country Input Parameters are passed into the Database through the PLACEHOLDER syntax. SELECT sum("ORDER_QTY") AS "ORDER_QTY", sum("TAX_AMOUNT") AS "TAX_AMOUNT", sum("NET_AMOUNT") AS "NET_AMOUNT", sum("GROSS_AMOUNT") AS "GROSS_AMOUNT", sum("DELIVER_QTY") AS "DELIVER_QTY", sum("GROSS_AMOUNT_CM") AS "GROSS_AMOUNT_CM", "COUNTRY" FROM "_SYS_BIC"."eim260.sessionX.eim260-XX.exercise1/SALES_DELIVERY_CV" ('PLACEHOLDER' = ('$$IP_COUNTRY$$', 'US')) WHERE ("CREATED_ON" BETWEEN ('20120101') and ('20120501')) AND ("DELIVERY_DATE" BETWEEN ('20120101') and ('20120501')) GROUP BY "COUNTRY" 7. Press F8 to execute the query.
- 39. 39 Appendix Setting up an ODBC Connection (Prerequisite: Install the HANA Client Driver) When the 32x Microsoft Office is used ensure to install the 32x HANA Client Driver. Also ensure to use the 32x ODBC Configuration within the SysWOW64 directory. Click on the odbc32.exe to open up the ODBC Data Source Administrator. Add HANA ODBC Connection under SYSTEM DSN.
- 40. 40 Select the HDBODBC32 driver and click Finish. Enter the server name followed by „:‟ and the port. Click Connect to test the connection and supply your user credentials. (The user information entered here is merely for testing and will not be stored). The configuration is complete when you see a successful connection the message.
- 41. © 2012 by SAP AG. All rights reserved. SAP and the SAP logo are registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries. Business Objects and the Business Objects logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Business Objects Software Ltd. Business Objects is an SAP company. Sybase and the Sybase logo are registered trademarks of Sybase Inc. Sybase is an SAP company. Crossgate is a registered trademark of Crossgate AG in Germany and other countries. Crossgate is an SAP company.