Unit V
- 1. Unit V Management System and Integration of Application
- 2. Management System • Management Information System (MIS) gives emphasis to the collection, organization, analysis and distribution of information for the planning and control of business and organizational operations.
- 3. Goals of an MS • Provide managers with information • Regular, routine operations • Control, organize and plan better
- 4. Objectives of MS • Capturing Data • Processing Data • Information Storage • Information Retrieval • Information Propagation
- 5. Types • Electronic Data Interchange Systems (EDI) • Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Executive Information Systems (EIS) • Idea Processing Systems
- 6. EDI
- 7. DSS
- 8. EIS
- 10. Components of MS • Hardware • Software • Procedures • Personnel
- 11. Advantages of MS • It facilitates planning • In Minimizes information overload • MIS Encourages Decentralization • It brings Co-ordination • It makes control easier
- 12. Limitations of MS • Highly sensitive requires constant monitoring. • Buddgeting of MIS extremely difficult. • Quality of outputs governed by quality of inputs. • Lack of flexibility to update it. • Effectiveness decreases due to frequent changes in top management
- 14. What is Application Integration
- 15. • enterprise application integration is the unification of data sets across all different applications used by a company. OR • Integrating applications means entering data once and having it available across all platforms. It can also be defined as merging data and workflows between disparate software applications. SAP application integration, java application integration, oracle application integration are a few examples of how data is integrated across multiple channels within an organization.
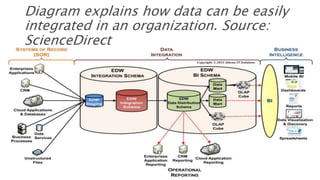
- 16. Diagram explains how data can be easily integrated in an organization. Source: ScienceDirect
- 17. Advantages of Enterprise Application Integration 1.Tackling data silos: Without integration, there is a possibility that information in application A will not match the updated data in application B, thereby reducing the reliability of application A reports and analytics. If a company has 50 different applications, they can have 50 disparate but similar data sets, each having their own drawbacks. To take it up a notch, if employees from different departments choose different data sets to process information they need, the data variances can multiply exponentially. 2.Reducing Redundancy: Traditionally, businesses had to input data for each application separately, redoing the same task to get all applications up to speed. This is a problem for businesses in terms of time invested on replicating data, cost of resources involved, and unreliability of analytics. 3.Data cleansing at source: Data cleansing is pertinent before data transformation can take place. All data collected by a company may not be usable – data cleansing ensures only relevant data is fed into the system. Data transformations will then convert all the ingested data into business insights. Imagine a company having 50 different data sets, all need to be cleansed individually before the applications can deliver reliable insights. Integration ensures there is one data set across all applications, so all data errors need to be addressed once.
- 18. Applications Integration Framework 1.Data consistency: First and foremost, data across all systems must be consistent. All manipulations need to be applied uniformly so every department within the organization is “on the same page”. 2.Data access: There’s no point of having 50 different systems if you have no visibility in the functioning of 20 of these systems. There needs to be a dashboard where all data and information is adequately represented as processed by each of the applications. 3.Workflow integration: Typically, businesses use a combination of specialized applications across different functions. These applications should be integrated in a manner that facilitates information exchange so that appropriate workflow notifications are triggered based on predefined conditions.
- 19. How to Integrate Multiple Applications? • There are two ways to integrate applications on an enterprise level: 1.Manually: this involves a hefty amount of data feeding, updating, refeeding, and tracking how and what type of data has been ingested. Most businesses can’t afford time losses that occur alongside. 2.Automatically: this involves the creation of a technical mediator that “talks” to all apps within the company, keeping each of these up-to- date with the latest data sets. This typically involves APIs and Web applications or the use of Middleware. Automating application integration can offer real-time (or near real-time) data synchronization across all sources, facilitating the generation of appropriate reporting and meaningful analytics.
- 20. Who Needs Enterprise Application Integration? • Enterprises • Multinationals • Governments • Schools & Universities • Banks & financial firms • Energy firms & grid stations • In short, any business using more than one application will need application integration, if not right away, then at some point in future. Period. • Business competition is all about making a well-informed decision at the right time. Business Intelligence (BI) aims to reduce the risk involved in such decisions with predictive analysis and data insights. These analytics, in turn, are based on the data captured by different business applications over extended time periods. Without integration, all of the data is not accounted for, which may lead businesses to make wrong, even lethal, decisions.
- 21. Challenges of Enterprise Application Integration 1.Presentation-Level integration: This involves creation of a middleware where all data is stored and processed, thereafter distributed to all other business applications. 2.Business Process integration: This involves the use of cloud technologies and automation to enhance business processes that can improve data efficiencies and reduce errors/roadblocks. 3.Data integration: Each application speaks a different language. Data integration bridges the gap with code or integration tools, allowing all applications to sync seamlessly via data translation. 4.Communications-Level integration: All information may not be used by each application. This level of integration ensures each application can receive just what it needs to function properly.
- 22. Enterprise Application Integration Approaches 1.Point-to-point integration: This involves the creation of links between the applications so that information exchange can take place seamlessly. The applications become co-dependent in this case, so all data transformation and translation is only possible when integration works properly. 2.Service bus integration: This involves using a middleware solution where all applications are required to tune in and read data from a central source. Whether the business chooses to migrate all data from legacy systems into newer systems and retire the old ones, or chooses to keep every application in place but has them all synchronized as much as possible, this approach ensures there is one data set available to all employees/departments within the organization.