"What to Do before Project Starts?" or Problem Definition for Innovation
- 1. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 1 Andrey Schukin Esslingen, 09. January 2013 bytics engineering ag Bachweg 5 CH-8133 Esslingen T +41 44 905 64 64 Standort Problem Definition for Product Innovation or What to Do before Project Starts?
- 2. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 2 bytics engineering ag • Swiss-based engineering and management consulting firm, founded 1988 • 35 employees • Two offices: Zürich city centre and Zürich suburbs, EMC test lab • Three departments: Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & Software, Simulation & Calculations • Over 350 customers: industry and universities (ABB, Alstom, Bombardier, Carl Zeiss, Honeywell, Leica, Lindt & Sprüngli, MAN, Siemens, Sulzer, Wärtsilä, etc.)
- 3. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 3 Contents 2 Innovation Process 3 What is Innovation? 4 Project Requirements: Different Levels 5 Capturing Customer Needs 6 Multiple Stakeholders 7 Technical System Description 8 Successful Product 1 Our Challenges
- 4. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 4 Challenges that we face • New products/solutions, start from scratch • Often no detailed requirement specification from the customer • “Hidden” implicit requirements (ease of use, aesthetics, etc.) • Whether the solution is “good” or “innovative” is defined by customer, not us • Competition: other consulting firms AND sometimes customer’s own engineers with a lot of experience in their area
- 5. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 5 Why Projects Fail • Reasons for project failures (Fraunhofer Institute, Germany) : • 50% is due to insufficient problem definition • 20% due to the lack of ideas • 30% due to poor execution quality and technical faults • That means: 70% of all failing projects could be saved if more attention was paid to Problem Definition and Problem Solving. Problem Definition Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Phase 4 Phase 5 Idea Generation Concept Definition Development & Tests Production Service
- 6. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 6 Customer Focus Innovation Process
- 7. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 7 Innovation Process E5 Innovation ProcessTM Define Research the problem Define the requirements 1 Discover Discover the range of possible (and impossible) solutions 2 Select Evaluate, select and refine the most promising idea 3 ProduceDevelop Develop solution in more detail 4 5 Prototype Manufacturing Generation of Customer Value Tiefenanalyse und Requirements Engineering Ideefindung und Grobkonzept Konzeptentwurf und Fertigungsunterlagen Prototyp, Nullserie und Herstellung
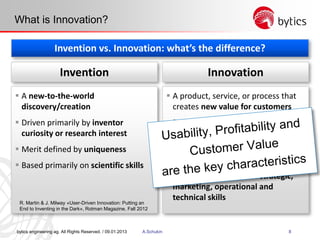
- 8. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 8 What is Innovation? Invention vs. Innovation: what’s the difference? A product, service, or process that creates new value for customers Driven primarily by a desire to add customer value Merit defined by profitable deployment Based on a broad set of strategic, marketing, operational and technical skills InnovationInvention A new-to-the-world discovery/creation Driven primarily by inventor curiosity or research interest Merit defined by uniqueness Based primarily on scientific skills R. Martin & J. Milway «User-Driven Innovation: Putting an End to Inventing in the Dark», Rotman Magazine, Fall 2012
- 9. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 9 Project Requirements Pyramid Impact on business operation and profitability. Project Scope, Objectives and Constraints. Business Requirements Product qualities and functions that, combined, satisfy needs of the end user. User Requirements Technical parameters to be achieved that would satisfy user requirements. Technical Requirements Summarising technical parameters that would guarantee user satisfaction is not easy – direct user input is often required.
- 10. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 17 Problem Definition: System Description • For any problem, we aim to get the desired outcome with the minimum possible input (costs) and minimum possible undesired outcome (harms). • Our ultimate (and mostly unachievable) goal is Ideal System, which does not have any costs or harmful effects, just benefits. • Problems are just gaps between existing system and system we want. undesired outcome input desired outcome costs harms benefits System 𝑰𝒅𝒆𝒂𝒍𝒊𝒕𝒚 = ↑ 𝒃𝒆𝒏𝒆𝒇𝒊𝒕𝒔 ↓ 𝒄𝒐𝒔𝒕𝒔 + ↓ 𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒎𝒔
- 11. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 18 • Step 1: Definition of Ideal Outcome: what we want, without any costs or harms • Step 2: Function Split: we split our future system into sub-functions • Step 3: Undesired Outcome: acceptable harms and possible risks • Step 4: Input • Interactions: People. Who will use the product? How are the inputs from people are delivered to the System? Ergonomics. • Interactions: Environment. How are the inputs from environment are delivered to the System? • Available Resources and “Disturbances” – variation in parameters: uneven floors, unexpected events, etc. • Step 5: History: existing system, previous tries to achieve result. Why failed? undesired outcome input desired outcome costs harms benefits System Problem Definition: System Description
- 12. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 19 User Requirements Business Requirements Successful Product Technical Requirements SCENEWhat is “well designed” product? Every commercially successful products is a result of finding a “golden middle” of the business requirements, user needs, and technology available.
- 13. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 21 Understanding Business Requirements Project delivered on specification, budget and in time Instead of immediately accepting customer’s solution, ask: what benefits is he looking for? Then search for other solutions that bring same benefits. The common end goal is to provide competitive advantage for the customer. Keep it in mind at all times. SCENEDevelopment projects – not just engineering
- 14. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 22 Understanding User Requirements Focus on Usability: the product should be useful, usable and desirable. Involve users or user representative at the beginning of every project, in concept and evaluation stages Take a closer look at additional customer needs: aesthetics, ergonomics, serviceability, reliability, etc. Aim to transform most vague wishes into actionable, specific and easy to understand technical requirements SCENEDevelopment projects – not just engineering
- 15. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 23 Understanding Technical Requirements Step by Step: 1.Describe the problem before coming up with solutions, then 2.Generate several ideas before choosing one to develop further. Borrow solutions from other industries or nature Generate ideas in a systematic way, and set yourself a goal on a number of ideas to be generated Think User Value, Novelty and Cost-Effective Implementation SCENEDevelopment projects – not just engineering
- 16. bytics engineering ag. All Rights Reserved. / 09.01.2013 A.Schukin 24 User Requirements Business Requirements Successful Product Technical Requirements SCENEWhat is “well designed” product? Every commercially successful products is a result of finding a “golden middle” of the business requirements, user needs, and technology available.