20 - 11 - 13
- 1. TAVI 2013 Dr. Claudio Cigalini
- 4. INDICACIONES
- 6. ESTENOSIS AORTICA INDICACIONES DE REEMPLAZO VALVULAR • I - Est.Ao severa sintomática; • • • • I - Est.Ao severa sintomática o no, en contexto de CRM, CRV ò cirugía de Aorta; I - Est.Ao severa y Fey < 50% IIa - Est.Ao moderada en contexto de CRM, CRV, o cirugía de Aorta; IIa - Est.Ao severa asintomática y Fey < 50% o respuesta anormal al ejercicio (hipotensión); IIb - Est.Ao severa asintomática con TV, o con excesiva HVI (>15mm), ò con estenosis valvular crítica; IIb - Est.Ao severa y alta probabilidad de progresión rápida (edad, calcificación, enf.coronaria); III - Prevención de muerte súbita en pacientes asintomáticos. • • • Task Force Valvulopatìas, AHA/ACC, 2006
- 7. ESTENOSIS AORTICA INDICACIONES DE TVAR • I - Est.Ao severa sintomática; • • • • I - Est.Ao severa sintomática o no, en contexto de CRM, CRV ò cirugía de Aorta; I - Est.Ao severa y Fey < 50% IIa - Est.Ao moderada en contexto de CRM, CRV, o cirugía de Aorta; IIa - Est.Ao severa asintomática y Fey < 50% o respuesta anormal al ejercicio (hipotensión); IIb - Est.Ao severa asintomática con TV, o con excesiva HVI (>15mm), ò con estenosis valvular crítica; IIb - Est.Ao severa y alta probabilidad de progresión rápida (edad, calcificación, enf.coronaria); III - Prevención de muerte súbita en pacientes asintomáticos. • • • Task Force Valvulopatìas, AHA/ACC, 2006
- 10. “El elemento clave para establecer si los pacientes son de alto riesgo para la cirugía es el juicio clínico, que debe ser utilizado en asociación con uno evaluación cuantitativa, basado en la combinación de varios validados scores " (EACTS/ESC/EAPCI Position Statement, Eur Heart J, 2008; 29: 1463-1470, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 34 (2008) 1-8, Eurointerv. 2008; 4:193-199)
- 16. Dos tipos de accesos
- 17. CoreValve Válvula de Pericardio Porcino Stent autoexpandible de nitinol Parcialmente reposicionable 18Fr 1° Generación 25F 2° Generación 21F 3° Generación 18F
- 18. Biocompatibilidad e Integración Noble S. Bonan R. et al Eurointervention 2009;1:5, 78-86
- 24. Anatomical Considerations Access site – peripheral anatomy Abdominal and thoracic aorta Ascending aorta and aortic arch Aortic root and valve anatomy Left ventricle and coronary arteries
- 26. Abdominal Aorta & Runoffs CT SCAN Minimal Tortuosity ANGIOGRAM ≥ 6mm Diameter
- 27. Acceso femoral o subclavio
- 33. Parámetros Anatómicos C=33 mm D=19 mm B=30 mm A=22 mm CoreValve 26 mm CoreValve 29 mm A = Diámetro Anillo 20-23 mm 24-27 mm B = Diámetro SV ≥27 mm ≥ 29 mm C = Diámetro Ao Ascendente ≤ 40 mm ≤ 43 mm D = Altura SV ≥ 15 mm ≥ 15 mm
- 37. Exact Location and Severity of Aortic Valve Calcification Midly calcified AoV. small isolated spots Moderate calcified AoV, > at base of the leaflets. Heavily calcified AoV, > at the tips of the leaflets. •incomplete or nonuniform expansion .
- 46. Left Ventricle • No moderate to severe LV hypertrophy (≥ 1.4 cm wall thickness), • No evidence of subaortic stenosis, including Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HOCM) or Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis (IHSS) • No significant coronary artery disease, • No Horizontal Ventricle.
- 48. No Horizontal Ventricle this angle should be < 30°.
- 49. PARTNER Study Design Symptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis ASSESSMENT: High Risk AVR Candidate 3105 Total Patients Screened Total = 1058 patients n= 700 2 Parallel Trials: Individually Powered High Risk n=358 Inoperable ASSESSMENT: Transfemoral Access ASSESSMENT: Transfemoral Access High Risk TF High Risk TA 1:1 Randomization 1:1 Randomization TAVI Trans femoral Surgical AVR VS TAVI Trans Apical Surgical AVR VS Primary Endpoint: All Cause Mortality (1 yr) (Non-inferiority) 1:1 Randomization TAVI Trans femoral VS Not In Study Standard Therapy (usually BAV) Primary Endpoint: All Cause Mortality over length of trial (Superiority)
- 50. Patient Characteristics - 1 TAVI Standard Rx n=179 n=179 83.1 ± 8.6 83.2 ± 8.3 0.95 45.8 46.9 0.92 11.2 ± 5.8 12.1 ± 6.1 0.14 26.4 ± 17.2 30.4 ± 19.1 0.04 NYHA I or II (%) III or IV (%) 7.8 92.2 6.1 93.9 0.68 0.68 CAD (%) 67.6 74.3 0.20 Prior MI (%) 18.6 26.4 0.10 Prior CABG (%) 37.4 45.6 0.17 Prior PCI (%) 30.5 24.8 0.31 Prior BAV (%) 16.2 24.4 0.09 CVD (%) 27.4 27.5 1.00 Characteristic Age - yr Male sex (%) STS Score Logistic EuroSCORE P value
- 51. Patient Characteristics - 2 TAVI n=179 Standard Rx PVD (%) 30.3 25.1 0.29 COPD Any (%) O2 dependent (%) 41.3 21.2 52.5 25.7 0.04 0.38 Creatinine >2mg/dL (%) 5.6 9.6 0.23 Atrial fibrillation (%) 32.9 48.8 0.04 Perm pacemaker (%) 22.9 19.5 0.49 Pulmonary HTN (%) 42.4 43.8 0.90 Frailty (%) 18.1 28.0 0.09 Porcelain aorta (%) 19.0 11.2 0.05 Chest wall radiation (%) 8.9 8.4 1.00 Chest wall deformity (%) 8.4 5.0 0.29 Liver disease (%) 3.4 3.4 1.00 Characteristic n=179 P value
- 52. All Cause Mortality Standard Rx All-cause mortality (%) TAVI ∆ at 1 yr = 20.0% NNT = 5.0 pts 50.7% 30.7% Months Numbers at Risk TAVI Standard Rx 179 179 138 121 122 83 67 41 26 12
- 53. Cardiovascular Mortality 100 Cardiovascualr mortality (%) Standard Rx TAVI 80 ∆ at 1 yr = 24.1% NNT = 4.1 pts 60 44.6% 40 20 20.5% 0 0 6 12 18 24 Months Numbers at Risk TAVI Standard Rx 179 179 138 121 122 83 67 41 26 12
- 54. Mortality or Repeat Hosp 100 Standard Rx All-cause mortality or Repeat Hospitalization (%) TAVI HR [95% CI] = 0.46 [0.35, 0.59] P (log rank) < 0.0001 80 60 40 20 0 0 6 12 18 24 Months Numbers at Risk TAVI Standard Rx 179 179 117 121 102 49 56 23 22 4
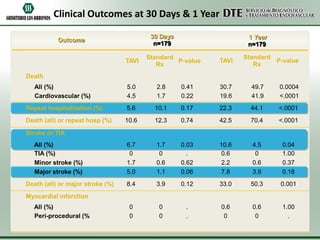
- 55. Clinical Outcomes at 30 Days & 1 Year 30 Days n=179 Outcome TAVI 1 Year n=179 Standard P-value Rx TAVI Standard P-value Rx Death All (%) Cardiovascular (%) 5.0 4.5 2.8 1.7 0.41 0.22 30.7 19.6 49.7 41.9 0.0004 <.0001 Repeat hospitalization (%) 5.6 10.1 0.17 22.3 44.1 <.0001 Death (all) or repeat hosp (%) 10.6 12.3 0.74 42.5 70.4 <.0001 6.7 0 1.7 5.0 1.7 0 0.6 1.1 0.03 . 0.62 0.06 10.6 0.6 2.2 7.8 4.5 0 0.6 3.9 0.04 1.00 0.37 0.18 8.4 3.9 0.12 33.0 50.3 0.001 0 0 0 0 . . 0.6 0 0.6 0 1.00 . Stroke or TIA All (%) TIA (%) Minor stroke (%) Major stroke (%) Death (all) or major stroke (%) Myocardial infarction All (%) Peri-procedural (%
- 56. Clinical Outcomes at 30 Days & 1 Year 30 Days n=179 Outcome TAVI 1 Year n=179 Standard P-value Rx TAVI Standard P-value Rx Vascular complications All (%) 30.7 5.0 <.0001 32.4 7.3 <.0001 Major (%) 16.2 1.1 <.0001 16.8 2.2 <.0001 Acute kidney injury Creatinine >3 mg/dL (%) RRT (%) 0 1.1 1 1.7 1.00 1.00 1.1 1.7 2.8 3.4 0.45 0.50 Bleeding - major (%) 16.8 3.9 <.0001 22.3 11.2 0.007 BAV (%) 0.6 1.1 1.0 0.6 36.9 <.0001 Re-TAVI (%) 1.7 na 1.7 na 0 1.7 0.25 1.1 9.5 <.0001 0 0 . 1.1 0.6 0.31 New atrial fibrillation (%) 0.6 1.1 1.00 0.6 1.7 0.62 New pacemaker (%) 3.4 5.0 0.60 4.5 7.8 0.27 Cardiac re-intervention AVR (%) Endocarditis (%) Arrhythmias
- 57. Mortality vs. Major Vasc Complics TAVI patients Major Vascular Complication (n=31) No Major Vascular Complication (n=148) Mortality (%) P (log rank) = 0.069 47.2% 27.7% Months
- 58. Mortality vs. Major Bleeding TAVI patients Major Bleed (n=46) Mortality (%) No Major Bleed (n=133) P (log rank) = 0.0046 43.5% 26.3% Months
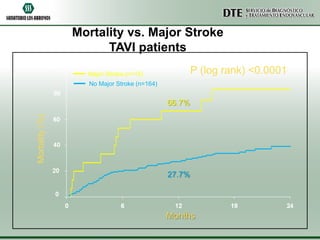
- 59. Mortality vs. Major Stroke TAVI patients P (log rank) <0.0001 Major Stroke (n=15) No Major Stroke (n=164) Mortality (%) 66.7% 27.7% Months
- 80. Predictores de requerimiento de marcapaso definitivo • 34 ptes. con RVP; Edad media 84 años • Entre Enero 2007 y Marzo 2008 en UK, unicéntrico • 33% requirió MCP definitivo durante la internación. eléctricos PREDICTORES Sensibilidad 75% Especificidad 100% Eje a la izquierda c/s BCRI p=.004 p=.002 Septum >17mm (ETT) p=.045 Grosor de la valva no coronariana >8mm (ETE) p=.002 anatómicos American Heart Journal, Mayo 2009
- 88. CONCLUSIONES PROCEMIMIENTO: Inicialmente complejo / Cada vez más simple. HEMODINAMIA: gradiente abolido / buen incremento en el área/ aceptable I. Ao. COMPLICACIONES INTRAPROCEDIMIENTO: todavía un problema / vasculares / neurológicas / marcapasos / RESULTADOS ALEJADOS: comparable o mejor a cirugia hasta 2 años INDICACIONES: solamente indicada en paciente inoperables o con alto riesgo quirúrgico DURAVILIDAD DE LA VALVULA: falta tiempo
- 93. All Cause Mortality Standard Rx All-cause mortality (%) TAVI PARTNER INOPERABLES ∆ at 1 yr = 20.0% NNT = 5.0 pts 50.7% 30.7% Months Numbers at Risk TAVI Standard Rx 179 179 138 121 122 83 67 41 26 12




















































![Mortality or Repeat Hosp
100
Standard Rx
All-cause mortality or
Repeat Hospitalization (%)
TAVI
HR [95% CI] =
0.46 [0.35, 0.59]
P (log rank) < 0.0001
80
60
40
20
0
0
6
12
18
24
Months
Numbers at Risk
TAVI
Standard Rx
179
179
117
121
102
49
56
23
22
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-11-13actualizaciontavi-140306133151-phpapp01/85/20-11-13-54-320.jpg)