Building information modeling & value to the AEC industry Part 1 v1
- 1. Building Information Modeling & Value to the AEC Industry Part 1Part 1 Stephen AUp Sept 26, 2013 Lecture Class BRE398: Building Information Modeling BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 2. TopicsTopics Building Construction Challenges Building Information Modelingg g 3D BIM Architectural / Structural / MEP DesignArchitectural / Structural / MEP Design Realistic Simulation 4D BIM4D BIM 5D BIM V l f BIM t th i d tValue of BIM to the industry BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 3. Lecture Objectives and ResultsLecture Objectives and Results Objectives The challenges of Building Construction Industry To understand how BIM technology improve the building construction industry The value of using BIM for the industry QuestionQuestion What are the benefits and limitation in applying BIM technology to the industry?technology to the industry? BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 4. TopicsTopics Building Construction Challenges Building Information Modelingg g 3D BIM Architectural / Structural / MEP DesignArchitectural / Structural / MEP Design Realistic Simulation 4D BIM4D BIM 5D BIM V l f BIM t th i d tValue of BIM to the industry BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 5. 5 What doe the building look like? H h d it t?How much does it cost? When will it be finish? BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 6. Construction Mega-Trendsg Gl b l i b % f $ 2 Construction Industry Growth drives Global Economy Global construction to grow by 67% from $7.2 trillion today to $12 trillion in 2020. Growth in China, India and the US will generate 54% of the $4 8 trillionIndia and the US will generate 54% of the $4.8 trillion increase in global construction output. A total of $97 7 trillion will be spent on constructionA total of $97.7 trillion will be spent on construction globally during the next decade and by 2020 construction will account for 13.2% of world GDP. By 2020 emerging markets will account for 55% of global construction, up from 46% today. Construction will make up 16.5% of GDP in emerging markets by 2020, up from 14.7% in 2010. R f Gl b l C i 2020 Gl b l C i P i d O f d E i BRE398: Building Information Modeling Ref: Global Construction 2020, Global Construction Perspectives and Oxford Economics
- 7. The AEC Industrial TrendThe AEC Industrial Trend Project Innovation – Technology, Environmental Complexity Design 全 球p y g Time to Delivery C t C t l 球 最 環 Cost Control Global Collaboration 環 保 大廈 Pre-fabricate Construction Early and Off Shore Procurement 廈 垃 圾發 Early and Off Shore Procurement Rapid ROI 發 電 BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 8. Challenges along a Building Project B ildi M difi ti Lifecycle Asset Development – EPC , Suppliers Building Modifications & Retrofits Data Handover 0.5 – 8 years Lifecycle 20 – 30 – 60 years Test &Test & Operations &Operations & PlanningPlanning DevelopmentDevelopment Test &Test & ValidationValidation ConstructionConstruction Operations &Operations & MaintenanceMaintenance DeDecommissioncommission Asset Maintenance- O/O BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 9. Building Project Management 9 Building Project Management What to Design? PProductroduct -Needs, Idea, Regulation,… How to Build? PPProcessProcess -Task, Role & Skill With What to Build? RRResourcesResources -Knowledge, Finance, Machinery People &Machinery, People & Technology
- 10. Current Situation in the AEC IndustryCurrent Situation in the AEC Industry Product Life Cycle Feasibility Select Define Execute Operate Owner Owner Owner Contractor OwnerOwner Architect Architect Contractor Owner Front End Design (1) Front End Design (2) Engineering D i Maintain Design Procurement Construction & Procurement Unclear Weak Weak Resources Problem information Problems are pushed to next phase communication collaboration wastageProblem BRE398: Building Information Modeling 10
- 11. Time FactorsTime Factors Project clarity Communication is mainly by email, telephone ory y , p business meeting Time consuming in discussion & reinventTime consuming in discussion & reinvent Design data translation Design data re-define Too many design changes in construction stagesy g g g BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 12. Quality Factors – Multi-disciplines Conflict
- 13. • Cost FactorsCost Factors Change orders cost 5 times the value of the change approvedChange orders cost 5 times the value of the change approved 90% of large construction projects have cost overruns averaging 28% Low Cost Estimates Due To : Inadequate preliminary engineeringInadequate preliminary engineering Insufficient contingencies for unexpected incidents Incentives to Underestimate Material Waste : Poor site supervision Poor planning Improper storage B i k t bi t tBricks, concrete are biggest waste 1-10% of weight of material leaves site as waste 9% in one study, 10-20% in another Example: 17% of plasterboard delivered to construction sites leaves as waste Cost Overruns: 30% of cost overruns are avoidable Average cost overrun is 5-8% Ref: Stanford University Center For Integrated Facility Engineering (CIFE) Statistics For Current U.S. Construction Industry Inefficiencies BRE398: Building Information Modeling y
- 14. Cost Factor - Increasing cost of correction Concept Specification Engineering Development Tendering Process Planning Construction 1000 10 100 * Fred Y Phillips Market Oriented Technology Management 1 0 BRE398: Building Information Modeling www.iconasolutions.com Fred Y Phillips, Market Oriented Technology Management
- 15. Limitation of 2D Drawing (1/2)Limitation of 2D Drawing (1/2) The reader must interpret 2D Drawings and recreate design intend b their knowledge and experience. These drawings can run into hundreds of separate documents, which make it very difficult to gain an overview of operations resulting in inconsistencies (Stebbins, 2007). CAD documents exclude information required for evaluating a design and monitoring construction activities (Oskouie et al., 2010). . BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 16. Limitation of 2D Drawing (2/2)Limitation of 2D Drawing (2/2) Bids and contract documents, bill of materials (BOM), time frame specifications, costs, labelling as well as installing and maintaining guides are also not included. According to Knight (2008), the growing complexities of design models threaten to makecomplexities of design models threaten to make CAD drawings insufficient and redundant. BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 17. Business ChallengesBusiness Challenges Missed schedule d dli Too many outstanding i d RFI Poor decision-making deadlines due to resource under estimation issues and RFI insufficient phase/gate reviews due to use of outdated and/or wrong information Optimize the deployment and Ensure delivery of projects within Ensure streamline consumption of enterprise resources within performance and timing guidelines project handshake and correct outcome BRE398: Building Information Modeling guidelines
- 18. Business ChallengesBusiness Challenges Difficulty finding project information Unpredictable results due to inconsistent Poor management visibility because it is stored in multiple databases or persons’ desktops due to inconsistent processes and lack of deliverable templates visibility of troubled projects that require corrective actionaction Improve traceability of Ensure projects are running based on Improve visibility through project project information and data based on company standards and processes through project dashboards and reporting BRE398: Building Information Modeling processes
- 19. Key Drivers of Construction Productivity Shifting construction activity to the factory affords better quality control, optimized production, lower cost labor and greater safety Field work shifts to coordinationsafety. Field work shifts to coordination, assembly, and unique conditions. Improving productivity in construction : prefabrication/modularization is seeing a renaissance as technologies, such as BIM, have enabled better integration ofhave enabled better integration of components. Out of over 800 architecture, engineering and contracting (AEC) professionals surveyed: • 66% report that project schedules are decreased - 35% by four weeks or more • 77% report that construction site waste is decreased - 44% by 5% or more BRE398: Building Information Modeling is decreased - 44% by 5% or more
- 20. Key Drivers of Construction Productivity I f ti T h lInformation Technology: Construction simulation for better planning Technology in the field for fast and accurate problem-solving Smart Supplies, Smart Materials,Smart Supplies, Smart Materials, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities… Virtually-building allows problem-solving, optimizing projects in advance of actualoptimizing projects in advance of actual construction so that fewer issues arise in the field. C BIM l i lCurrent BIM solutions struggle to support this change BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 21. SHoP ConstructionSHoP Construction B i Ch llBusiness Challenge Deliver 12,000 pre-weathered façade panels, with no two alikealike Solution Using the BIM application linkUsing the BIM application, link construction planning directly to CNC fabrication. Develop a workflow toDevelop a workflow to automate panel unfolding and fabrication tickets with bending schedules. Develop a unitized system with color-coded installation instructions. BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 22. Industry Equity | What Does The AEC d l hIndustry Value The Most? V l f O V l f AECValue for Owner Value for AEC Capital Lower operating costs On time p efficiency On budget Sustainability Safety Quality of Experience Less risk BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 23. TopicsTopics Building Construction Challenges Building Information Modeling 3D BIM Architectural / Structural / MEP Design/ / g Realistic Simulation 4D BIM4D BIM 5D BIM Value of BIM to the industryValue of BIM to the industry BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 24. 3D BIM BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 25. The Power of Information TechnologyThe Power of Information Technology C t Digitization Cost Vi li i R h InternetVisualization Reach TimeQuality BRE398: Building Information Modeling Timey
- 26. Building Information ModelingBuilding Information Modeling B ildi I f ti M d li (BIM) hi h h b d fi dBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) which has been defined as “a digital representation or visualisation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. In addition BIM serves as a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life- cycle from inception onward” (Eastman and Tiecholz, 2008).y p ( , ) From this definition it is evident that BIM is a multipurpose tool facilitating design and development, data management and planning functions.and planning functions. The drivers for BIM are the exigencies of a fast expanding, increasingly complex construction industry, the need for more d i i d di i ll k h ld dproductivity and co-ordination amongst all stakeholders and reducing variance between customer expectation and final product (Tolman, 2008). BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 27. Purposes of the BIM Model (1/2)Purposes of the BIM Model (1/2) fEstablish a single primary repository for critical architectural geometry and information Facilitate rapid design changes that are automatically reflected in the ancillary documents Provide automatically coordinated drawings to the architects Facilitate full 3D modeling of structure by the structural engineers Eliminate conflicts that typically arise with the integration of MEP BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 28. Purposes of the BIM Model (2/2)Purposes of the BIM Model (2/2) Allow automated reporting of certain quantities for the QS Provide an easily accessible source of accurate information for tenderingg Provide a constructionally accurate rendering model All t t t i li t tiAllow contractors to visualize construction sequencing and anticipate possible delays Become the basis for facilities management work after construction BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 29. Design + Documentation + CommunicationDesign Documentation Communication Ref: Paul Seletsky,2005 ‘Digital Design and the Age of Building Simulation’ ACEbytes Viewpoint #19 www.aecbytes.com/viewpoint/issue_19_pr.ht
- 30. BIM Model for Building DesignBIM Model for Building Design Ref: Paul Seletsky,2005 ‘Digital Design and the Age of Building Simulation’ ACEbytes Viewpoint #19 www.aecbytes.com/viewpoint/issue_19_pr.ht
- 31. Maturity Level of BIMMaturity Level of BIM A maturity model was developed by the UK Department of Business Innovations and Skills (BIS). BIS defined the levels from 0 through 3. A majority of the market is still working with Level 1 processes, and the best in class are experiencing significant benefits in Level 2.
- 32. Economic Functional Working Tender & Construction + O Building Information Modeling Lifecycle Study Design g Drawing Tender & Award Construction + Commission Operate Procurement Pre-lease Sales & Marketing 2D Design Drawing from Consultants Marketing Interactive 3D Rendering Simulation model Extraction of Building Quantities from the As- Design BIM Model Linked facility management information to As- As- As-Built Design BIM Model Linked construction schedule with As-Design BIM model As-Built BIM model Design BIM Model As- Constructed BIM Model As-Built BIM Model 3D collision checking report
- 33. Quebec Hydro Power Plant 33 BRE398: Building Information ModelingMercier_Demo_AnimatedwithText.avi
- 35. BIM Solutions Bridging the gap between concept design & construction BIM Solutions Common understanding Bridging the gap between concept, design & construction Common understanding Informed decision makingInsight Conflict/issues brought openly to tableCollaboration Reduced risk/improved build quality Integration Confidence in achieving right first time Integration BRE398: Building Information Modeling www.iconasolutions.com g
- 36. Exceeding Perceived Quality targets Innovation Exceeding Perceived Quality targets Innovation Early insight into the effects of design / construction variation Wh t if t di t fi d i ti l tiWhat-if studies to find innovative solutions Collaboration Informed decisions/unambiguous communication Complex issues visualised and shared between teamsp Reducing time/cost/risk C l d f d d l d lCritical engineering issues identified and resolved early Late discovery of costly production issues avoided BRE398: Building Information Modeling www.iconasolutions.com
- 38. A hit t l / St t l / MEPArchitectural / Structural / MEP Design 3D Complex surface design Architectural and structural design Design Architectural and structural design MEP design Knowledge driven designg g BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 39. BIM Data StructuringBIM Data Structuring 39 Assembled by a collection of files representing the physicalAssembled by a collection of files, representing the physical differentiation of building components Each consultant designs on respective component individually and concurrently ArchitectArchitect B. S. Engineer Structural Engineer BRE398: Building Information Modeling
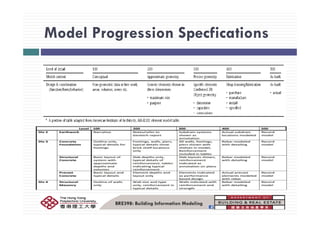
- 40. Model Progression SpecficationsModel Progression Specfications BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 41. 3D Complex Surface Design 41 3D Complex Surface Design All type of surface elements: from stylist to final surfaces ready for manufacturingready for manufacturing Memphis Canopy structure -p py Freeform metal finishes to manufacturing Building envelope and associated structural design
- 42. Complex Surface Design 42 Complex Surface Design Project: London 2012 Olympic Games Aquatic Centre Architect: Zaha Hadid MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page
- 43. 43 Complex Surface DesignComplex Surface Design Aquacenter1.aviAquacenter1.avi
- 44. Parametric design 44 a a e c des g Architectural and structural design from2Dto3D-short.avi MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page
- 45. Life-Build DesignLife Build Design BRE398: Building Information Management
- 46. Values of BIM on DesignValues of BIM on Design BIM i t i t 2D d 3D d iBIM is a great improvement over 2D and 3D drawings since it enables designers to view the building from all angles (Bentley, 2009). This enables identification ofg ( y, ) any errors at an early stage which can then be corrected avoiding costly rework. O f h f i li i f BIM i i i fOne of the functionalities of BIM is incorporation of parametric design elements. Changes, additions or editions in any one parameter results in simultaneouseditions in any one parameter results in simultaneous reconfiguration of all other elements involved in the design including sectional and elevation dimensions, raw material requirements cost of production andmaterial requirements, cost of production and construction schedules and timelines (Emery, 2008) BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 47. MEP Design BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 48. Process & Systems Design 48 Process & Systems Design 0) P li i L t 4) Process Planning Reaction planning0) Preliminary Layout Import Terrain data Building and Main equipment General Arrangement Preliminary weight estimates Cost Estimates Reaction planning Assembly hierarchy Association of resources Extract manufacturing document 1) Basic Design Define major system allocation Equipment Lists Preliminary BOM estimates Preliminary Weight estimates Pressure lose calculations 2) Detail Design Add secondary hangers & support Finish the detailing Define reaction spool 3) Manufacturing Deliverables Extract Mfg. Documents Assembly drawings Bill of Materials
- 49. Equipment & Systems Design Ventilation systems HVAC Equipment & Systems Design Electrical Cabling Conceptual Layout System Routing Raceway & Conduit Drainage & Firing systems Piping y Hangers
- 50. MEP System Assembly and Design Collaboration D fi d b di i li f M&E tDefined by disciplines of M&E systems Enable collaborate design among Engineers Lighting Fixture Fire Services System Electricity System Plumbing Systemg y Drainage System
- 51. MEP design – Routing of Electrical TrunkingMEP design Routing of Electrical Trunking 51 Route_Elect_800.aviRoute_Elect_800.avi BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 52. MEP design – Modify Electrical TrunkingMEP design Modify Electrical Trunking Route_Modify_800.aviRoute_Modify_800.avi
- 53. Space reservation and Design for 53 MEP systems & equipment XSteel CATIA HVAC D i iHVAC_Design.avi
- 54. MEP Design - Design CollaborationMEP Design Design Collaboration HVAC system Fully co-ordinated Electrical system MEP design Plumbing system Drainage system
- 55. MEP Design - Design Collaboration 55 MEP Design Design Collaboration MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 机电系统同步設計 & 干涉检查
- 57. 57 BRE398: Building Information ModelingMTECH Confidential– 2005 Page The order of magnitude of information to achieve true 3D coordination of all elements of the project prior to tender
- 58. MEP Design - Clash & Collision CheckingMEP Design Clash & Collision Checking Clash_final2.aviClash_final2.avi
- 59. 3D CSD Combine Service Drawing 59 MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page
- 60. 2D-CSD Combined Service Drawing 60 MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page
- 61. Benefits for Collaborated DesignBenefits for Collaborated Design Perform digital design collaboration Increase information accuracy in early stagey y g UNCERTAINTY of information COST OF CHANGE BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 62. Maximize Variation to Minimize Deviation M cost Max. rangeofc Actual Cost Most stimatedr Most likely Es Feasibility Study Design Bid Construction Settlement Min. BRE398: Building Information Modeling Time
- 63. 3D Visualization MIT.aviMIT.avi BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 64. Paradigm Transformation (1)Paradigm Transformation (1) Traditional 2D drawing New 3D Visualization Depending on imagination, skill and experience Viewing the same information without Independent works Accumulated errors imagination Collaborative workAccumulated errors Huge communication cost Many iterations Low communication cost Right at the First TimeMany iterations Right at the First Time BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 65. Challenges of Design ChangesChallenges of Design Changes The design for a hotel lobby shown here evolves into increasing levels of detail through the continuous iteration with schedule, goals andof detail through the continuous iteration with schedule, goals and project organization Main Body E Review work plan, team plan and goal plan Entrance Registration Seating Area Review work plan, team plan and goal plan Landing Doorway Foyer Desk Work space Office Coffee Bar Seating Toilet Review work plan, team plan and goal plan p Ref: George Elvin, Integrated Practice in Architecture, p.112, John Wiley & Sons, 2007
- 66. Design Changes & Automatic UpdateDesign Changes & Automatic Update 66 Design & modeling with its geometrical definition linked contextually to other geometryDesign & modeling with its geometrical definition linked contextually to other geometry Changing context -> propagating change to linked geometry Process recorded in tree -> capture and reuse Advantages Automatic update parametric controlAdvantages : Automatic update, parametric control Process of modeling is recorded in tree BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 67. Design Change of Public Toilet 67 Design Change of Public Toilet WC_Update3_1024.avi
- 68. Design Change of Str ct ral Core 68 Design Change of Structural Core Corewall-Auto Update2 aviCorewall-Auto Update2.avi
- 69. 69 Design intend capture and Reuse M llion sho t a iMullion-short.avi
- 70. Design Reuse - Catalogs 70 Design Reuse Catalogs Arch, structural, MEP catalogs Quick reuse and build-up of standardized designQuick reuse and build up of standardized design by Catalogs User defined & Customization
- 71. Reuse of Sanitary Fitments and 71 Design Update Toilet_Auto Update_1280.avi
- 72. Design Intent Capture & Reuse 72 Design Intent Capture & Reuse Flexible to customize building entities. E.g. columns, beams doors escalatorsbeams, doors, escalators, curtain walls. Embedding geometricEmbedding geometric elements, formulas, constraints, etc., for full Escalator Powercopy parametric control Capturing design intent and re-specify for reuse Modeling standard well controlled Curtain wall Powercopy
- 73. 73 Knowledge Base Engineering DesignKnowledge Base Engineering Design StairStair--short.avishort.avi
- 74. Dynamic SectioningDynamic Sectioning 74 18WLR Sectioning.avi
- 75. Drawing ProductionDrawing Production 2D Dressup & Symbols2D Dressup & Symbols BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 76. Paradigm Transformation (2)Paradigm Transformation (2) Traditional No alternative New Multiple ideas Unknown impact analysis Time consuming Clear impact analysis by all stakeholders forg Huge amount of cost Limited performance right decision QuickLimited performance Almost at no cost Optimize performanceOptimize performance BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 77. 3D Realistic Simulation Structural Analysis Di i l M kDigital Mockup Photo Realistic Rendering BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 78. Structural Analysis – Data Interoperability78 St li C ll b tiStreamlines Collaboration between Architects and Engineersg Live integration with Market leading Structural Analysis tools R b tRobot ETABS SAP2000 IFC Export Interoperate between IGES, STEP, 3D Dxf and Dwg (Autocad), SDNFSDNF CIS/2 (design data) export BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 79. Structural Analysis – Data Integration 79 Structural Analysis Data Integration Drawings Specification Bidding Des autocad® 3D Master E i i Bidding sign&Co Model Engineering onstruction STEP CIS/2 Fluent Fabrication nProcess Fluent … Construction
- 80. Structural Analysis in Civil Engineering
- 81. Rendering & VisualizationRendering & Visualization BRE398: Building Information Modeling MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 81
- 82. Rendering & VisualizationRendering & Visualization BRE398: Building Information Modeling MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 82
- 83. Rendering & VisualizationRendering & Visualization BRE398: Building Information Modeling MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 83
- 84. Rendering & VisualizationRendering & Visualization BRE398: Building Information Modeling MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 84
- 85. Virtual Prototyping by Digital MockUp (DMU)85 Typical AEC projects are 2D basedTypical AEC projects are 2D based 2D does not represent the reality and is subject to mis- understandingunderstanding Owner facing •Critical decision information •Marketing BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 86. Virtual Prototyping by DigitalVirtual Prototyping by Digital MockUpMockUp (DMU)(DMU)Virtual Prototyping by DigitalVirtual Prototyping by Digital MockUpMockUp (DMU)(DMU) accommo aviaccommo aviaccommo.aviaccommo.avi
- 87. Design for Operations and Maintenance87 T i l AEC j t t f ll ti i d fTypical AEC projects not fully optimized for maintenance and operations BIM supports design optimization for operations andBIM supports design optimization for operations and maintenance The Virtual Prototype serves as the basis for operations and maintenance simulation during the design phase BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 88. Design for Operations and MaintenanceDesign for Operations and Maintenance mainte.avimainte.avi BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 89. Values of BIMValues of BIM According to Middlebrooks (2008), BIM promotes facility management. Facility personnel use BIM to access data stored in a single repository to prepare schedules, implement daily operations and make predictive and futuristic plans with regard to purchases and construction activities. BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 90. Lighting Realization, Analysis & Measurement Analyze and virtually validate innovative lighting systems Ph t t i l i t i i t lPhotometric, colorimetric virtual measurement and analysis Taking into account real measured opticalTaking into account real measured optical properties of materials, surfaces Y h 01 / 02 BRE398: Building Information Modeling Yacht01 / 02. wmv
- 91. Visual Ergonomics for HK MTRVisual Ergonomics for HK MTR Geometry and artificial light sources Catalog of light sources Intensity distribution of source Measure optical property from material BRE398: Building Information Modeling Illuminance result for concourse
- 92. Visual Ergonomics for HK MTRVisual Ergonomics for HK MTR BRE398: Building Information Modeling Luminance Analysis
- 93. HVAC Engineering Fluid Dynamic /Simulation (1/2) W ll T Di ib i T C lWall Temperature Distribution Temperature Cut-planes Old Design Wall Temperature Distribution New Design BRE398: Building Information Modeling 93 .
- 94. HVAC Engineering Fluid Dynamic /Simulation (2/2) Temperature Distribution (10 cm from floor) Flow patterns Summary: New design shows superior temperature uniformity; shown in these animations (t = 0 to 80 seconds). Temperature Distribution (10 cm from floor) Flow patterns Sanyo-floorcontours.avi Sanyo-streamlines.avi BRE398: Building Information Modeling .
- 95. Life-Like ExperienceLife Like Experience Value proposition : improve design/styling by submitting it to « experience » trial increase sales by providing customers with experience and vivid 3d graphics While realistic rendering used to be the only focus, « life-like » experience becomes a growing complement of the design/planning phase Virtools format is ideal for large deployement, high realism, entertaining experience BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 96. Application of Life-Like ExperienceApplication of Life Like Experience City / Urban Planning Realistic experience / simulation Interior / Exterior Design Realistic experience / simulationp / Large model visualization Realistic experience / simulation 3D option simulation Virtual Showroom Entertaining experience T i i M i t & M it iEntertaining experience Wide range of deployment Training, Maintenance & Monitoring Interactive 3D application Various input device support
- 97. As-Built BIM ModelAs Built BIM Model Properties selling & rental Interior design Virtual show room Properties management Virtool_ferdinand.aviVirtool_ferdinand.avi
- 98. Shopping Mall ConfiguratorShopping Mall Configurator BRE398: Building Information Modeling 98
- 99. http://www.expo.cn/#c=homehttp://www.expo.cn/#c home BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 100. Values of BIMValues of BIM BIM allows visualization of form with some resemblance to realities (Manning and Messner, 2008). This allows evaluation of both aesthetic and functional features. Thus even non – technical stakeholders can easily understand these models. BIM reduces safety barriers which in turn reduceBIM reduces safety barriers which in turn reduce insurance costs, legal fees and professional liabilities.liabilities. BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 101. 4D BIM = 3D + Schedule (Time) The construction of the 4D models enables the various participants (from architects, designers, contractors to owners) of a construction project, to visualize the entire duration of a series of events and display the progress of construction activities through the life time of the project. This BIM-centric approach towardsp j pp project management technique has a very high potential to improve the project management and delivery of construction project, of any size or complexity.project, of any size or complexity. BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 102. Construction Sequencing – Scheduling & Simulation Linking to Microsoft Project and PrimaveraPrimavera Link tasks to sets of geometry “Play” construction schedule in time
- 103. Construction SequencingConstruction Sequencing ––q gq g Scheduling & SimulationScheduling & Simulation Construction 1024 x 768.aviConstruction 1024 x 768.avi BRE398: Building Information Modeling MTECH Confidential– 2005 Page Construction 1024 x 768.aviConstruction 1024 x 768.avi
- 104. 5D BIM = 3D + schedule (time) + cost which refers to the intelligent linking of individual 3D CAD components or assemblies with schedule (time) constraint and cost-related information. Th f h 5D i i d d f h ddi i f f hThe use of the term 5D is intended to refer to the addition of fourth dimension: time and fifth dimension: cost to the 3D model, i.e. 5D is 3D + schedule (time) + cost. The construction of the 5D models enables the various participants ( from architects, designers, contractors to owners) of any construction project, to visualize the progress of construction activities and its related costs Mover time. This BIM-centric project management technique has a potential to vastly improves the project management and delivery of construction project of any size and complexity. BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 105. Data Extraction and Reporting E l i h d l k i l i ibEvery element in the model knows its name, location, attribute set By-attribute and by-feature model search Taking Measurements: Dimensions Distance Coordinates Area Volume Batch Dimensional Data ExtractionBatch Dimensional Data Extraction HKIS Standard
- 106. MaterialsMaterials 106 SimpleMaterial Family Multiply Material Family BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 107. Simple MaterialsSimple Materials BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 108. Multiply MaterialsMultiply Materials BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 109. Ply-by-Ply Top and Bottom ControlPly by Ply Top and Bottom Control 109 BRE398: Building Information Management
- 110. Cost itemsCost items BRE398: Building Information Modeling 110
- 111. Door 1024 x 768.avi
- 112. FILE STATUS e mation rence scription Product rceeded PROJECT ISSUEDIGITAL PROJECT FILE NAME 112 AssemblyCode ElementInform MasterorRefer Date Revision ComponentDes Description CATIAPartorP Current/Super IssueDate IssueName 00_General 00R _ ALL _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 00000 _ Project Grid Part Current 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 03_Concrete 03S _ ALL _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 03300 _ Concrete Substruture Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 03S ALL MST 040706 D18 03300 C t S b t t P t S d d 07/06/04 I 18 90% CD03S _ ALL _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 03300 _ Concrete Substruture Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 03S _ ALL _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 03300 _ Concrete Superstructure Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 03S _ ALL _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 03300 _ Concrete Superstructure Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04_Masonry 04G _ EST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 04G _ EST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04G _ TOW _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 04G _ TOW _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04G _ WST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 04G _ WST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04210 _ Brick Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04S EST MST 040816 B02 04220 Concrete Masonry Units Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01_ _ _ _ _ _ y 04S _ EST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04220 _ Concrete Masonry Units Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04S _ TOW _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 04220 _ Concrete Masonry Units Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 04S _ TOW _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04220 _ Concrete Masonry Units Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 04S _ WST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 04220 _ Concrete Masonry Units Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 04S _ WST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 04220 _ Concrete Masonry Units Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 05_Metals 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05100 _ Primary Steel Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 05100 _ Primary Steel Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05100 _ Secondary Steel Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 05100 _ Secondary Steel Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 05S EST MST 040816 B02 05100 Wireframe Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 BRE398: Building Information ModelingMTECH Confidential– 2005 Page 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05100 _ Wireframe Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05300 _ Composite and Metal Deck Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S _ EST _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 05300 _ Composite and Metal Deck Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 05S _ TOW _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05100 _ Primary Steel Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S _ TOW _ MST _ 040706 _ D18 _ 05100 _ Primary Steel Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD 05S _ TOW _ MST _ 040816 _ B02 _ 05100 _ Secondary Steel Part Current 08/16/04 Issue 19: BID2/ADD01 05S TOW MST 040706 D18 05100 Secondary Steel Part Superceded 07/06/04 Issue 18: 90% CD
- 113. TopicsTopics Building Construction Challenges Building Information Modeling 3D BIM 3D Design / MEP Designg / g Realistic Simulation 4D BIM4D BIM 5D BIM Value of BIM to the industryValue of BIM to the industry BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 114. Values of BIMValues of BIM BIM i t it f h i d i f tiBIM is a one stop repository for such varied information as supplier data, manufacturer information, costing, dimensional data and component specifications.p p Consolidation of data allows the project managers to provide clients with value added services. These include information on lighting heat power usage furnitureinformation on lighting, heat, power usage, furniture and post occupancy requirements (Howard, 2008). Liston and Fischer (2010) believe that data attached toListon and Fischer (2010) believe that data attached to individual components increases accuracy of pricing and bidding. Construction schedules can be optimized in the face of constant changes in availability andthe face of constant changes in availability and delivery of raw materials and design changes. BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 115. Value PropositionValue Proposition Developers • Improved project insight • Higher Quality • Procurement improvements• Procurement improvements •Reduce development cost • Increased Design Control Architects and Engineers • Increased Design Control • Improved Coordination • Design Freedom Contractors and Fabricators • Reliable data • Reduced errors in construction L Ri k• Less Risk BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 116. ROI for BIM R f 15 t di b St f d U i itRef: 15 case studies by Stanford University: http://www.stanford.edu/~gaoju/3D4DFramework/cases.htm 40% elimination of unbudgeted change. Industry average 10- 20% on a project. Thus 4-8% of overall cost I i i hi / 3%Improve cost estimate accuracy within +/-3% Less than 1% cost growth Bids within +/- 2.5% 60% less RFI’s 80% reduction in time to generate cost estimate ROI of 3D model: 5X-10X, saved 10% of contract sum through clash detection (based on 2D ->3D project) 7% schedule reduction BRE398: Building Information Modeling
- 117. The PLM Value (Build/Upgrade the Asset, and Manage the Asset Increased profitability $ $ $ $ Lower maintenance cost Faster time to market or T t ti Larger scale construction & market share $ $ $ $ To construction $Profit Loss TimeFaster Time to Market With the right product/asset Cost reduction Less downtime to more money • Decrease changeover time 10%-50% Faster time to more money Time to construction: 5%-30% faster P j t t 2 6% A t NPV • Increased asset utilization rate: 10-20% • Increase life duration: 3 – 6% BRE398: Building Information Modeling Project cost : - 2-6% Asset NPV
- 118. 118 BRE398: Building Information Management
- 119. Questions & Answers stephenau@mtech.com.hk BRE398: Building Information Modelling
- 120. ReferencesReferences BRE398: Building Information Modeling