Diffusion report
- 1. Powerpoint Templates Page 1 Diffusion Material Science Presentation by Group 5
- 2. Powerpoint Templates Page 2 Topics Covered What is Diffusion? •Interdiffusion •Self-diffusion Diffusion Mechanisms Vacancy Diffusion Interstitial Diffusion Mathematics of Diffusion (Fick’s Laws) • Steady-State Diffusion • Non Steady-State Diffusion Factors affecting Diffusion • Diffusing Species • Host Solid • Temperature • Microstructure
- 3. Powerpoint Templates Page 3 What is Diffusion? o It is the motion of atoms, ions, or vacancies through a material. o Inhomogeneous materials can become homogeneous by diffusion.
- 4. Interdiffusion and Self-diffusion Interdiffusion (Impurity Diffusion) occurs in response to a concentration gradient. Concentration Gradient - concentration that exists between a two different materials. Powerpoint Templates Page 4
- 5. Interdiffusion and Self-diffusion Self-diffusion is the diffusion of an atom to a new site in a crystal when all atoms are of the same type. Powerpoint Templates Page 5
- 6. Powerpoint Templates Page 6 Diffusion Mechanisms 1) Vacancy Diffusion An atom from its normal lattice position changes position with an adjacent vacancy lattice site, so the atoms and vacancies travel in opposite directions.
- 7. Powerpoint Templates Page 7 Diffusion Mechanisms 1) Vacancy Diffusion
- 8. Powerpoint Templates Page 8 Diffusion Mechanisms 2) Interstitial Diffusion Atoms move from one interstitial site to another vacant interstitial site. Interstitial diffusion is generally faster than vacancy diffusion because bonding of interstitials to the surrounding atoms is normally weaker and there are many more interstitial sites than vacancy sites to jump to. Requires small impurity atoms (e.g. C, H, O) to fit into interstices in host.
- 9. Powerpoint Templates Page 9 Diffusion Mechanisms 2) Interstitial Diffusion
- 10. Powerpoint Templates Page 10 Other mechanisms which are quite rare but nonetheless important in semiconductors are: 1)Indirect interstitial mechanism for self-interstitials > The simulation shows the elementary step: A self-interstitial (shown in light blue for easier identification) pushes a lattice atom into the interstitial lattice. The net effect is the migration of an self-interstitial from one interstitial site to an different one. 2)The "kick-out" mechanism for impurity atoms > Interstitial impurity atoms move rather fast by a direct interstitial mechanism, until they eventually displace a lattice atom. This is shown in the simulation. We now have a self-interstitial (that may or may not be very mobile) and a rather immobile substitutional impurity atom, which may now diffuse with one of the other (slow) mechanisms.
- 11. 3) Frank-Turnbull mechanisms (or dissociative mechanism). 5) “Extended interstitial" mechanism Powerpoint Templates Page 11 > This is the pendant to the kick-out mechanism. Except that the diffusing impurity atom does not dislodge a lattice atom, but gets trapped in a vacancy, whereupon it is almost immobile. The total effect may be quite similar to the kick-out mechanism. 4) Various direct diffusion mechanisms > Shown is a direct exchange of places between two atoms. Variants are exchanges involving more that 2 atoms (a whole "ring" that "rotates"). Direct mechanisms are every now and then suggested in the literature to account for some new diffusion phenomena, but so far do not seem to occur in crystals. > This is a possibility not yet discussed or observed. It is mentioned just to show that there might be more atomic mechanisms than have been discovered so far.
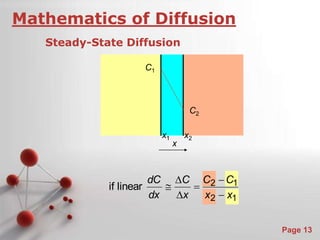
- 12. dC Powerpoint Templates Fick’s First Law of Diffusion dC Page 12 Mathematics of Diffusion Steady-State Diffusion - Rate of diffusion independent of time. Flux proportional to concentration gradient = dx dx J D Where: D = diffusion coefficient
- 13. C C C dC if linear 2 1 Powerpoint Templates Page 13 Mathematics of Diffusion Steady-State Diffusion C1 C2 x C1 C2 x1 x2 x x 2 1 x dx
- 14. C1 = 0.44 g/cm3 Powerpoint Templates Page 14 Mathematics of Diffusion Steady-State Diffusion Example: Chemical Protective Clothing (CPC) Methylene chloride is a common ingredient of paint removers. Besides being an irritant, it also may be absorbed through skin. When using this paint remover, protective gloves should be worn. If butyl rubber gloves (0.04 cm thick) are used, what is the diffusive flux of methylene chloride through the glove? Data: diffusion coefficient in butyl rubber: D = 110 x10-8 cm2/s surface concentrations: C2 = 0.02 g/cm3
- 15. 2 C C D dC - 2 1 C1 = 0.44 g/cm3 Data: (0.02 g/cm 0.44 g/cm ) C1 skin paint remover (110 x 10 cm /s) 2 Powerpoint Templates x x g Page 15 Mathematics of Diffusion Steady-State Diffusion Example: Chemical Protective Clothing (CPC) Solution – Assuming linear conc. Gradient D tb 6 2 1 dx J D cm s 1.16 x 10 (0.04 cm) -5 3 3 -8 2 J C2 x1 x2 D = 110x10-8 cm2/s C2 = 0.02 g/cm3 x2 – x1 = 0.04 cm
- 16. Powerpoint Templates Page 16 Mathematics of Diffusion Non Steady-State Diffusion - Concentration profile and the concentration gradient are changing with time. The solution of this equation is concentration profile as function of time, C(x,t) Fick’s Second Law of Diffusion Where: D = diffusion coefficient t = temperature x = position C = concentration profile
- 17. Non Steady-State Diffusion Powerpoint Templates Page 17 Mathematics of Diffusion 퐶푥 − 퐶표 퐶푠 − 퐶표 = 1 − erf 푥 2 퐷푡 Where: x – is the distance into the solid Cx – is the concentration of diffusing species at distance x Co – is the initial bulk concentration of the diffusing species in the solid. Cs- is the surface concentration (constant) D- is the Diffusivity t – is time erf – is the Gaussian Error Function.
- 18. Powerpoint Templates Page 18 Mathematics of Diffusion Non Steady-State Diffusion Fick’s second law relates the rate of change of composition with time to the curvature of the concentration profile: Concentration increases with time in those parts of the system where concentration profile has a positive curvature. And decreases where curvature is negative.
- 19. Powerpoint Templates Page 19 Mathematics of Diffusion Non Steady-State Diffusion Example:
- 20. Powerpoint Templates Page 20 Mathematics of Diffusion Non Steady-State Diffusion Solution:
- 21. Powerpoint Templates Page 21 Factors Affecting Diffusion Diffusion of interstitials is typically faster as compared to the vacancy diffusion mechanism. Smaller atoms cause less distortion of the lattice during migration and diffuse more readily than big atoms. Diffusion is faster in open lattices or in open directions.
- 22. Powerpoint Templates Page 22 Factors Affecting Diffusion Temperature - diffusion rate increases very rapidly with increasing temperature Diffusion mechanism – diffusion by interstitial mechanism is usually faster than by vacancy mechanism Diffusing and host species - Do, Qd are different for every solute, solvent pair Microstructure - diffusion is faster in polycrystalline materials compared to single crystals because of the accelerated diffusion along grain boundaries.
- 23. Powerpoint Templates Page 23 Factors Affecting Diffusion Formula (Arrhenius dependence): Where: