Final Class Presentation on Direct Problem-solving Intervention Projects.pptx
- 1. IRL6050-A: PROJECT MANAGEMENT IN INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS Direct Problem-solving Intervention Projects
- 2. What is a proposal? Your proposal is an important document Development Partners will decide to finance your project or not from what they read. Any proposal should show thoughtful planning
- 3. Identify the project idea Do your Pre-Planning and Stakeholders Analysis Look at possible funding and local resources What you learn from this will point you in the direction of the best way to help - the ‘project approach’ and ‘project logic’
- 4. Identify the project idea Your pre-planning should have pointed to an approach that fits into this model: Available resources Needs identified by experts Project Community Interests
- 5. Good ideas 1. Make sure there is a genuine problem and that you can face it. 2. Two-step approach: First define your project thoroughly using a participatory approach, Then adapt your project proposal according to the targeted donor. 3. Use the logical framework - a tool to design a project in a systematic and logical way.
- 6. Package your project into an attractive proposal Follow a logical thread: Background Problem Solution Sustainability Ensure match-up between: Problem – Outcomes – Means (this is called internal coherence) Many donors want the Logical Framework Approach
- 7. Package your project into an attractive proposal cont. Logic checklist Don’t leave a problem unsolved Don’t identify outcomes that do not correspond to a problem Don’t identify outcomes for which you don’t have a solution Don’t propose activities that are not related to problems and outcomes Don’t list human resources that don’t match the outcomes you aim to achieve
- 8. Proposal structure 1. Executive Summary 2. Organisation description 3. Project background 4. Problem statement 5. Goal and objectives 6. Beneficiaries 7. Theory of Change 8. Proposed methodology: 8. Budget 9. Monitoring and Evaluation 10. Sustainability 11. Exit Strategy 12. Annexes Partners Project implementation Activities Risks and assumptions Means
- 9. Executive Summary It is the first part that is read Sometimes the only part that is read… It can be used by the donor to communicate to others about your project Why is it important: 9
- 10. Executive Summary What do you propose to do? Where? Why? For whom? With whom? For how long? Summary
- 11. Executive Summary DO : Write it last Do it carefully Keep it short DON’T : Cut and paste
- 12. 2. Presentation of the organisation Purpose: to establish credibility and image of a well-managed organization that meets critical needs in its area of work Tips Should not be too long If you are approaching a new donor, attach in appendix an organisation brochure and the last annual report Why is it important?
- 13. 2. Presentation of the organisation Who are you? Philosophy / mandate? History and significant interventions / track record Expertise in addressing the problem or need Organisational structure Major sources of support Affiliations / accreditations / linkages Contents
- 14. 3. Project Background Who took the initiative? Does the project fit into an existing development plan or programme? Is this the first phase of the project, or continues an activity already started? If continuing, what have been the main results of the previous phase? What studies have been done to prepare the project? Who else operates in this field? Contents
- 15. 3. Project Background The project arises from the beneficiaries and/or the local partners You know the local context very well You have the experience needed to run the project successfully You have been successful before Tips: You need to demonstrate that :
- 16. 4. Problem Statement Unless donors are convinced that there is a real problem, they will not agree to pay for our project! Tips A “good” problem should: concern people be concrete and demonstrated be solvable come from a demand be an emergency or priority Why is it important?
- 17. 4. Problem Statement Describe the scope and size of the problem What are the immediate causes? What are the underlying causes? What are the effects? How does it affect people? Why does it have to be addressed? Why now and not later? Contents
- 18. 5. Goal and Objectives Goals (or overall objectives): Describes the long-term goals your project will contribute to. Project Purpose or Specific Objective: Describes the objective of your project in response to the core problem. Expected Results: Describes the outputs (or outcomes) - the concrete results of your project. 23
- 19. 5. Goal and Objectives Objectives should be SMART: Specific = they must meet the needs (problems) identified Measurable = they should be measured by concrete indicators which should reflect the extent to which they have been attained Acceptable = by all involved partners Relevant = they must be adequate to the project socio-cultural environment Timely = must be reached by the end of the project
- 20. Theory of Change (ToC) • Definition Theory of change is an on-going process of reflection to explore change and how it happens – and what that means in a particular context, sector, and/or group of people. ToC thinking • Structured way of thinking about change and impact organizations would like to achieve • Integrated approach to programme design, implementation, M+E, and communication
- 21. Theory of Change: Main Questions What is the programme? What outcomes does the programme aim to achieve? What intermediate steps lead to those outcomes? What assumptions are associated with each link in the causal chain? How can we measure outcomes?
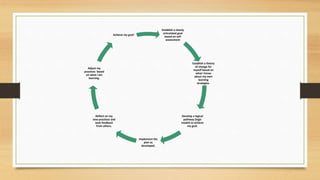
- 24. Establish a clearly articulated goal based on self assessment Establish a theory of change for myself based on what I know about my own learning strategies. Develop a logical pathway (logic model) to achieve my goal. Implement the plan as developed, Reflect on my new practices and seek feedback from others. Adjust my practices based on what I am learning. Achieve my goal!
- 26. Differences between the Theory of Change and the Logic Model
- 27. 6. Beneficiaries Clearly identify direct and indirect beneficiaries: Direct support to target group Indirect benefits to others How many? Where? Characteristics? Specify how and at what stage they will be involved in the project Contents
- 28. 7. Proposed Methodology Partners Project implementation Activities Risks and assumptions Means Why is it important? Shows how objectives will be achieved Contents
- 29. 7. Proposed Methodology Partners: Clearly divide main partners and other partners Provide background information: Goals/philosophy? Area of intervention? Relationship with beneficiaries? Cooperation track- record? Type of partnership you set up Specify each partner’s role
- 30. 7. Proposed Methodology Project implementation: Rationale for selecting this methodology Project implementation structure: roles and responsibilities of all the project stakeholders Tip Use a chart to show the project implementation structure
- 31. 7. Proposed Methodology Activities: What will be done? How? By whom? Where? By when? Tips Be as precise as possible Cluster activities by expected result Use a work plan to summarise
- 32. 7. Proposed Methodology - Training How many persons? For how long? Starting when? Which methodology will be used (seminars, in- house training, ad hoc courses, etc.) Why is the training necessary? Which new skills will the trainees acquire? Year Year 1 Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Activity 1 Activity 2 Activity 3 Activity 4
- 33. 7. Proposed Methodology -Risks/Assumptions Risks are external factors that could potentially jeopardise your project and are beyond your control Assumptions are things you are expecting to be a certain way Why is it important? It helps assess the factors which could jeopardise your project It helps examining the project for completeness and consistency
- 34. 7. Proposed methodology -Means Human resources: Explain the responsibilities and tasks of each key person in the project. Justify the need for expatriate personnel Material resources: Give an explanation of the most important budget lines Justify vehicles
- 35. 8. Budget Contents Budget spreadsheet Budget explanations and justifications Tips Prepare it using your action plan Don’t inflate the budget Carefully follow donor’s requirements Divide your budget into years
- 36. 9. Monitoring & Evaluation Why is it important? Monitoring: to assess whether your project activities are on track Evaluation: to assess whether your project is effective, efficient, has an impact, is relevant and sustainable Contents What will be monitored and why? By whom? How often? Using which tools and methods?
- 37. 10. Sustainability Contents Institutional sustainability Technical sustainability Socio-cultural sustainability Financial sustainability Why is it important? Because donors want to be sure that their investment will not be lost at the end of the project and that you are already planning the phasing out of the project.
- 38. 11. Annexes / Appendices Glossary Maps Statistics/ policy documents Proof of registration and tax benefits for donors Financial statement Composition of Board of Directors List of major donors Annual report, brochures & publications Specific studies or evaluation reports Memorandum of agreement with partners Letters of support Pictures, case studies Other... Contents
- 39. 11. Appendices / Annexes - Tips Refer to the appendices in the proposal (see appendix a), but.... If something is crucially important, write it in the proposal! Add a table of contents for the appendices Put the appendix number on the top of each page “appendix no xy” Separate each appendix by a coloured page