Image Restoration (Digital Image Processing)
- 1. Image Restoration Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 1 / 13
- 2. Outlines 1 Image restoration technique 2 Difference between image enhancement and restoration 3 Image formation process and degradation model 4 Degradation model in continuous and discrete formulation 5 Frequency domain technique 6 References Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 2 / 13
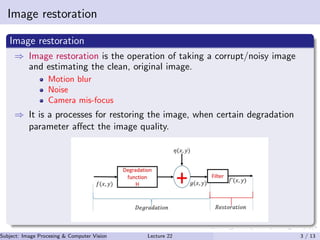
- 3. Image restoration Image restoration ⇒ Image restoration is the operation of taking a corrupt/noisy image and estimating the clean, original image. Motion blur Noise Camera mis-focus ⇒ It is a processes for restoring the image, when certain degradation parameter affect the image quality. Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 3 / 13
- 4. Continued– Space domain representation g(x, y) = f (x, y) ∗ h(x, y) + η(x, y) (1) Frequency domain representation G(u, v) = F(u, v)H(u, v) + N(u, v) (2) Definition: g(x, y) = H[f (x, y)] + η(x, y) (3) → For simplicity, let η(x, y) = 0. → H is the degradation operator. Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 4 / 13
- 5. Properties of H 1. Linearity property Let f1(x, y) and f2(x, y) are the two 2D signals and k1 and k2 are two arbitrary constant then H k1f1(x, y) + k2f2(x, y) = k1H f1(x, y) + k2H f2(x, y) (4) It shows the linear operation and also follow the superposition theorem → k1 = k2 = 1 then H f1(x, y) + f2(x, y) = H f1(x, y) + H f2(x, y) (5) From (4), let f2(x, y) = 0 then H k1f1(x, y) = k1H f1(x, y) (6) From (6), this is called as homogeneity property. Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 5 / 13
- 6. 2 Position invariant property H f (x − α, y − β) = g(x − α, y − β) (7) Since, g(x, y) = H f (x, y) . Definition of Dirac delta function in 2D δ(x, y) = 1 x = 0, y = 0 = 0 Otherwise or δ(x − x0, y − y0) = 1 x = x0, y = y0 = 0 Otherwise or ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (x, y)δ(x − x0, y − y0)dxdy = f (x0, y0) (8) or f (x, y) = ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (α, β)δ(α − x, β − y)dαdβ (9) Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 6 / 13
- 7. Continued– From the expression of degradation function g(x, y) = H f (x, y) + η(x, y) From (9), when η(x, y) = 0 g(x, y) = H ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (α, β)δ(α − x, β − y)dαdβ (10) or g(x, y) = ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ H f (α, β)δ(α − x, β − y)dαdβ (11) or g(x, y) = ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (α, β)H δ(α − x, β − y) dαdβ (12) Here, H δ(α − x, β − y) = h(x, α, y, β) → Impulse response of h. Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 7 / 13
- 8. Continued– g(x, y) = ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (α, β)h(x, α, y, β)dαdβ (13) → Superposition integral of first kind. → If H is a position invariant then H δ(x − α, y − β) = h(x − α, y − β). Hence, g(x, y) = ∞ −∞ ∞ −∞ f (α, β)h(x − α, y − β)dαdβ Convolution operation (14) Discrete formulation Analysis of 1D signal: Let f (x) is the input function and h(x) is the degradation function. → f (x) : x = 0, 1, 2, .....A − 1 → h(x) : x = 0, 1, 2, .....B − 1 Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 8 / 13
- 9. Continued– ge(x) = M−1 m=0 fe(x)he(x − m) ⇒ x : 0, 1, 2, ...M − 1 Matrix form g = Hf or f = fe(0) fe(1) ... fe(M − 1) g = ge(0) ge(1) ... ge(M − 1) Here, H → M × M matrix H = he(0), he(−1), ....he(−M + 1) he(1), he(0), ....he(−M + 2) ... he(M − 1), he(M − 2), ....he(0) Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 9 / 13
- 10. Continued– Let he(x) is a periodic signal with period M then he(x) = he(x + M) or H = he(0), he(M − 1), he(M − 2)....he(1) he(1), he(0), he(M − 1), ....he(2) ... he(M − 1), he(M − 2), he(M − 3)....he(0) Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 10 / 13
- 11. 2D signal analysis Let f (x, y) and h(x, y) be the 2D input and degradation function. ⇒ f (x, y) : A × B ⇒ h(x, y) : C × D ⇒ {fe(x, y), he(x, y)} : M × N ge(x, y) = M−1 m=0 N−1 n=0 fe(m, n)he(x − m, y − n) (15) or g = Hf + n (16) where, the size of g is MN × MN. H = H0, HM−1, ....H1 H1, H0, ....H2 ... HM−1, HM−2, ....H0 Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 11 / 13
- 12. Continued– where Hj → N × N Hj = he(j, 0), he(j, M − 1), he(j, M − 2)....he(j, 1) he(j, 1), he(j, 0), he(j, M − 1), ....he(j, 2) ... he(j, M − 1), he(j, M − 2), he(j, M − 3)....he(j, 0) Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 12 / 13
- 13. References M. Sonka, V. Hlavac, and R. Boyle, Image processing, analysis, and machine vision. Cengage Learning, 2014. D. A. Forsyth and J. Ponce, “A modern approach,” Computer vision: a modern approach, vol. 17, pp. 21–48, 2003. L. Shapiro and G. Stockman, “Computer vision prentice hall,” Inc., New Jersey, 2001. R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, and S. L. Eddins, Digital image processing using MATLAB. Pearson Education India, 2004. Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 13 / 13


![Continued–
Space domain representation
g(x, y) = f (x, y) ∗ h(x, y) + η(x, y) (1)
Frequency domain representation
G(u, v) = F(u, v)H(u, v) + N(u, v) (2)
Definition:
g(x, y) = H[f (x, y)] + η(x, y) (3)
→ For simplicity, let η(x, y) = 0.
→ H is the degradation operator.
Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 22 4 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturer22-201202143810/85/Image-Restoration-Digital-Image-Processing-4-320.jpg)








