Internet of things
- 1. Internet of Things Magesh Parthasarathy
- 2. Standards bodies working on IoT • ITU standards IoT Global Standards Initiative, IoT overview Y.2060, Y.2061 (Requirements for support of machine-oriented communication applications in the NGN environment) • Within IoT-GSI [numerous Recommendations completed] SG11 - APIs and protocols for IoT (activity started 07/2014), IoT Testing SG13 - Focus on Network Aspects of IoT SG16 - Focus on IoT applications, including e-health SG17 - Security and privacy protection aspects of IoT (already published some specs related to USN and services using tag-based identification) Other activities SG15 -Smart Grids, Home Networks Focus Group on Smart Sustainable Cities (FG SSC) (since 02/2013) Focus Group on Smart Water Management (FG SWM) (since 06/2013) Focus Group on M2M Service Layer (FG M2M) (closed 03/2014) Collaboration on ITS Communication Standards (also some past FGs on Cars)
- 3. Standards bodies working on IoT • IEEE P2413 – Standard for an Architectural Framework for the Internet of Things • Industrial Internet Consortium • OneM2M • LoRA alliance • IPSO alliance (IP for Smart Objects) • IETF – 6LoWPAN working group, CoRE(Constrained Restful Environment) working group, ROLL (Routing over Low Power and Low Noisy networks) working group • NIST – Smart grid forum • ETSI • 3GPP standards – IMS • 5G americas • CENELEC – European Committee for ElectroTechnical standardization • IoT-A • ATIS • TIA • Open Mobile Alliance • Broadband Forum • OASIS • OGC • GS1
- 4. M2M communications • Telematics – connected cars used for safety and security; services and infotainment • Metering – meters to report consumption mainly electricity • Remote monitoring – sensors connected to assets are tracked and monitored in real-time • Fleet management – Vehicles can be managed and tracked through the path they go • Security – connectivity used for home and small business security alarms • ATM/Point of Sales – ATM and POS devices are connected to a centralized secure environment
- 5. IoT –Internet of Things Applications Application Enablement Internet connectivity Automo tive Transpo rt Utility Smart City Agricult ure Health People Vehicle Building Assets Industri al Resourc es Spaces Devices
- 7. Functional layers and capabilities of an IoT solution Asset Layer Resource Layer Communication Layer Service Support Layer Data and Information layer Application layer Business Layer SECURITY Management IoTDataandServices
- 8. Functional layers and capabilities of an IoT solution Assets Layer- The assets of interest are the realworld objects and entities that are subject to being monitored and controlled,as well as having digital representations and identities. The typical examples include vehicles and machinery, fixed infrastructures such as buildings and utility systems, homes, and people themselves. Identification of assets using RFID or optical bar codes Resource Layer - provides the main functional capabilities of sensing, actuation, and embedded identities. Sensors and actuators in various devices that may be smartphones or Wireless Sensor Actuator Networks (WSANs), M2M devices like smart meters, or other sensor/actuator nodes,deliver these functions. Communication Layer – LAN and WAN networks using wired and wireless networking technologies. Wireless LAN technologies like ieee 802.11, ieee802.15.4 (Low rate WPAN), Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low energy, Zigbee networks Service Support Layer – done from data centers for tasks like remote device management that can do remote software upgrades, remote diagnostics or recovery, and dynamically reconfigure application processing such as setting event filters. Data and Information Layer - main purposes are to capture knowledge and provide advanced control logic support Application Layer - provides the specific IoT applications Business Layer - This is where any integration of the IoT applications into business processes and enterprise systems takes place. The enterprise systems can, for example, be Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), or other Business Support Systems (BSS). Management - management of various parts of the system solution related to its operation, maintenance, administration, and provisioning. This includes management of devices, communications networks, and the general Information Technology (IT) infrastructure as well as configuration and provisioning data, performance of services delivered, etc. Security – Information and Communication Security. Trust, Identity management, authentication and authorization are key capabilites. Data and Services – Data mining and data analytics done here and transfer of data into knowledge is done here
- 9. IoT devices and gateways • A device can be characterized as having several properties, including: • Microcontroller: 8-, 16-, or 32-bit working memory and storage. • Power Source: Fixed, battery, energy harvesting, or hybrid. • Sensors and Actuators: Onboard sensors and actuators, or circuitry that allows them to be connected, sampled, conditioned, and controlled. • Communication: Cellular, wireless, or wired for LAN and WAN communication. • Operating System (OS): Main-loop, event-based, real-time, or fullfeatured OS with low foot print TCP/IP stack Contiki, TinyOS, FreeRTOS, uIP stack open source • Applications: Simple sensor sampling or more advanced applications. • User Interface: Display, buttons, or other functions for user interaction. • Device Management (DM): Provisioning, firmware, bootstrapping, and monitoring. • Execution Environment (EE): Application lifecycle management and Application Programming Interface (API).
- 10. Device management Device management (DM) is an essential part of the IoT and provides efficient means to perform many of the management tasks for devices: • Provisioning: Initialization (or activation) of devices in regards to configuration and features to be enabled. • Device Configuration: Management of device settings and parameters. • Software Upgrades: Installation of firmware, system software, and applications on the device. • Fault Management: Enables error reporting and access to device status. Examples of device management standards include TR-069 and OMA- DM.
- 11. Data Management • Data generation • Data acquisition – continuous monitoring, interval-poll, event based • Data validation – Failure to validate data leads to security breaches, database corruption, Denial of service • Data storage – massive parallel processing DB’s, distributed file systems, cloud computing platforms needed • Data processing – working with data at rest (already stored) or in motion( stream data), F to C conversion of data in temp reading • Data remanance – even if data is erased or removed/deleted, it can be retrieved/data recovery • Data analysis – data mining, machine learning, statistics
- 12. Data Analytics • Hadoop’s MapReduce • HBase: A column-oriented data store that provides real-time read/write access to very large tables distributed over HDFS. • Mahout: A distributed and scalable library of machine learning algorithms that can make use of MapReduce. • Pig: A tool for converting relational algebra scripts into MapReduce jobs that can read data from HDFS and HBase. • Hive: Similar to Pig, but offers an SQL-like scripting language called HiveQL instead. • Impala: Offers low-latency queries using HiveQL for interactive exploratory analytics, as compared to Hive, which is better suited for long running batch-oriented tasks.
- 13. ETSI M2M Functional Architecture M2M Applications M2M service capabilities Core Network Access Network M2M Applications M2M service capabilities M2M device M2M Applications M2M Service Capabilities M2M Management function Network Management Function M2M Gateway M2M Area Network M2M device Network Domain Device and Gateway Domain
- 14. ETSI M2M Architecture • M2M Device: This is the device of interest for an M2M scenario, for example, a device with a temperature sensor. An M2M Device contains M2M Applications and M2M Service Capabilities. An M2M device connects to the Network Domain either directly or through an M2M Gateway: • Direct connection: The M2M Device is capable of performing registration, authentication, authorization, management, and provisioning to the Network Domain. Direct connection also means that the M2M device contains the appropriate physical layer to be able to communicate with the Access Network. • Through one or more M2M Gateway: This is the case when the M2M device does not have the appropriate physical layer, compatible with the Access Network technology, and therefore it needs a network domain proxy. Moreover, a number of M2M devices may form their own local M2M Area Network that typically employs a different networking technology from the Access Network. The M2M Gateway acts as a proxy for the Network Domain and performs the procedures of authentication, authorization, management, and provisioning. An M2M Device could connect through multiple M2M Gateways. • M2M Area Network: This is typically a local area network (LAN) or a Personal Area Network (PAN) and provides connectivity between M2M Devices and M2M Gateways. Typical networking technologies are IEEE 802.15.1 (Bluetooth), IEEE 802.15.4 (ZigBee, IETF 6LoWPAN/ROLL/CoRE), MBUS, KNX (wired or wireless) PLC, etc. • M2M Gateway: The device that provides connectivity for M2M Devices in an M2M Area Network towards the Network Domain. The M2M Gateway contains M2M Applications and M2M Service Capabilities. The M2M Gateway may also provide services to other legacy devices that are not visible to the Network Domain. The Network Domain contains the following functional/topological entities: • Access Network: this is the network that allows the devices in the Device and Gateway Domain to communicate with the Core Network.Example Access Network Technologies are fixed (xDSL, HFC) and wireless (Satellite, GERAN, UTRAN, E-UTRAN W- LAN, WiMAX).
- 15. ETSI M2M Architecture • Core Network: Examples of Core Networks are 3GPP Core Network and ETSI TISPAN Core Network. It provides the following functions: • IP connectivity. • Service and Network control. • Interconnection with other networks. • Roaming. • M2M Service Capabilities: These are functions exposed to different M2M Applications through a set of open interfaces. These functions use underlying Core Network functions, and their objective is to abstract the network functions for the sake of simpler applications. • M2M Applications: These are the specific M2M applications (e.g. smart metering) that utilize the M2M Service Capabilities through the open interfaces. • Network Management Functions: These are all the necessary functions to manage the Access and Core Network (e.g. Provisioning, Fault Management, etc.). • M2M Management Functions: These are the necessary functions required to manage the M2M Service Capabilities on the Network Domain while the management of an M2M Device or Gateway is performed by specific M2M Service Capabilities. There are two M2M Management functions: • M2M Service Bootstrap Function (MSBF): The MSBF facilitates the bootstrapping of permanent M2M service layer security credentials in the M2M Device or Gateway and the M2M Service Capabilities in the Network Domain. In the Network Service Capabilities Layer, the Bootstrap procedures perform, among other procedures, provisioning of an M2M Root Key (secret key) to the M2M Device or Gateway and the M2M Authentication Server (MAS). • M2M Authentication Server (MAS): This is the safe execution environment where permanent security credentials such as the M2M Root Key are stored. Any security credentials established on the M2M Device or Gateway are stored in a secure environment such as a trusted platform module.
- 16. ITU-T IoT Reference Model Application Layer IoT Applications Service & Application support Layer Generic Support Capabilities Specific Support Capabilities Network Layer Networking Capabilities Transport Capabilities Device Layer Device Capabilities Gateway Capabilities Security Capabilities Management Capabilities GenericManagementCapabilities GenericManagementCapabilities SpecificManagementCapabilities SpecificManagementCapabilities Remote patient monitoring Data storage and Data processing Mobility Mgmt and AAA FCAPS, device mgmt, traffic mgmt, network topology mgmt
- 17. IETF CoRE HTTP Proxy HTTP-CoAP Proxy CoAP-HTTP Proxy HTTP Client HTTP Server CoAP Server CoAP Client HTTP Proxy
- 18. Request from HTTP client to CoAP server through HTTP proxy 802802.15.4 8026LoWPAN 802IPv6 UDP ROLL CoAP CoAP Server App 802802.15.4 8026LoWPAN 802IPv6 UDP ROLL CoAP 8802.11.3 8IP v4 8TCP 8HTTP 8802.11.3 8IP v4 8TCP 8HTTP Cross Proxy Device Sensor Area Network SAN Internet SAN Gateway Internet Cloud Application
- 19. Application level protocols in IoT • COAP (Constrained Application Protocol)/UDP • RESTful HTTP/HTTP • IBM’s MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport)/TCP • XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence protocol)/TCP • AMQP ( Advanced message queing protocol)/TCP • Websockets/TCP • JMS – Java message service API • DDS – Data Distribution Service open source middleware
- 20. IoT Security • DOS/DDOS attacks • Protection from Hacking • Cybersecurity attacks • Access control mechanisms • Authentication and authorization • Protection of Automation using machine learning • Privacy of data • Identity management – digital identity with biometrics • Network Security – Nessus Scan • Internet Security – browser vulnerabilities, operating system vulnerabilities, data base vulnerabilities, Eavesdropping/wiretap, Forge, Replay, Delay and Rush, Reorder, Delete transit packets Defense : Key generate, Encryption and Decryption • Botnet/Keylogger/Hypervisors/rootkits – Identity theft, Denial of service attacks, spam, click fraud Defense : Signature based detection using antivirus • Intranet Security – Access control and NAC, Risk Audit, physical securiity, Application level firewall to connet outside vendors to intranet called XML firewall • LAN Security – NDS attacks like ip address spoofing, mac address spoofing, arp cache poisoning,dns name corruption, Firewall, IDS/IPS, signature analysis using pattern matching of the content in the data packets, network scanner nmap, port scanning tools Superscan, network sniffer ethereal, Ethersnoop light • Network Intrusion and Detection SNORT • Intrusion Prevention Systems • Wireless networks security – WEP( Wireless Equivalent Privacy), WPA and WPA2 (Wi-fi protected access), SPINS ( Security Protocol for sensor networks) • Cellular network security • RFID security • Storage networks security • Physical security – smart card reader, biometric card readers • Disaster recovery from natural disasters • Firewalls • Forensics
- 21. Emerging IoT applications Consumer Electronics • Connected gadgets • Wearables • Robotics • Participatory sensing • Social Web of Things Automotive transport • Autonomous Vehicles • Multimodal transport Retail Banking • Micro Payments • Retail logistics • Product life-cycle info • Shopping assistance Environmental • Pollution • Air,Water,Soil • Weather, climate • Noise Infrastructures • Buildings and Homes • Roads and rails Utilities • Smart grid • Water management • Gas,oil and renewables • Waste management • Heating and cooling Health well-being • Remote monitoring • Assisted living • Behavioral change • Treatment compliance • Sports and Fitness
- 22. Emerging IoT Applications Smart Cities • Integrated environments • Optimized Operations • Convenience • Socioeconomics • Sustainability • Inclusive living Process Industries • Robotics • Manufacturing • Natural resources • Remote operations • Automation • Heavy machinery Agriculture • Forestry • Crops and Farming • Urban Agriculture • Livestock and fisheries
- 23. Smart Solutions
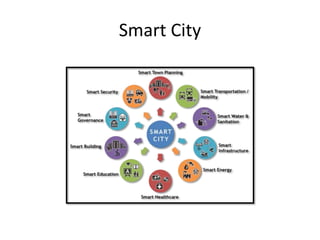
- 24. Smart City
- 25. Smart Home
- 26. NIST Smart Grid

![Standards bodies working on IoT
• ITU standards IoT Global Standards Initiative, IoT overview Y.2060, Y.2061
(Requirements for support of machine-oriented communication applications in the
NGN environment)
• Within IoT-GSI [numerous Recommendations completed]
SG11 - APIs and protocols for IoT (activity started 07/2014), IoT Testing
SG13 - Focus on Network Aspects of IoT
SG16 - Focus on IoT applications, including e-health
SG17 - Security and privacy protection aspects of IoT (already published
some specs related to USN and services using tag-based identification)
Other activities
SG15 -Smart Grids, Home Networks
Focus Group on Smart Sustainable Cities (FG SSC) (since 02/2013)
Focus Group on Smart Water Management (FG SWM) (since 06/2013)
Focus Group on M2M Service Layer (FG M2M) (closed 03/2014)
Collaboration on ITS Communication Standards (also some past FGs on Cars)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internetofthings-170216160642/85/Internet-of-things-2-320.jpg)