Session 09 - OOP with Java - Part 3
- 1. Java & JEE Training Day 9 – OOP with Java Contd.
- 2. Page 1Classification: Restricted Day 9 Agenda • Review of last class concepts • Types of Inheritance and a look at Aggregation • Polymorphism • Method overloading • Method overriding
- 3. Java & JEE Training Inheritance in Java, and Aggregation
- 4. Page 3Classification: Restricted Inheritance in Java • A mechanism in which one object acquires all the properties and behaviours of parent object. • Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship, also known as parent- child relationship. • Why use inheritance in java oFor Method Overriding (so runtime polymorphism can be achieved). oFor Code Reusability.
- 5. Page 4Classification: Restricted Inheritance in Java
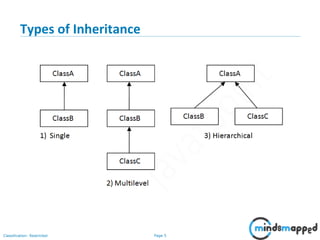
- 6. Page 5Classification: Restricted Types of Inheritance
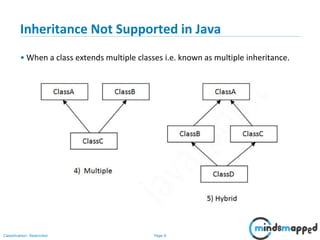
- 7. Page 6Classification: Restricted Inheritance Not Supported in Java • When a class extends multiple classes i.e. known as multiple inheritance.
- 8. Page 7Classification: Restricted Why multiple inheritance not supported in Java? class A{ void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");} } class B{ void msg(){System.out.println("Welcome");} } class C extends A,B{//suppose if it were public static void main(String args[]){ C obj=new C(); obj.msg();//Now which msg() method would be invoked? Compile-time error } }
- 9. Page 8Classification: Restricted Aggregation in Java • If a class have an entity reference, it is known as Aggregation. • Aggregation represents HAS-A relationship. • Why use Aggregation? oFor Code Reusability.
- 10. Page 9Classification: Restricted Aggregation in Java class Operation{ int square(int n){ return n*n; } } class Circle{ Operation op;//aggregation double pi=3.14; double area(int radius){ op=new Operation(); int rsquare=op.square(radius);//code reusability (i.e. delegates the method call). return pi*rsquare; } public static void main(String args[]){ Circle c=new Circle(); double result=c.area(5); System.out.println(result); } }
- 11. Page 10Classification: Restricted Example: Employee HAS-A Address • Demo
- 12. Java & JEE Training Method Overriding in Java, and a re-look into Method Overloading
- 13. Page 12Classification: Restricted Method Overriding in Java • If subclass (child class) has the same method as declared in the parent class, it is known as method overriding in java. • If subclass provides the specific implementation of the method that has been provided by one of its parent class, it is known as method overriding. • Method overriding is used to provide specific implementation of a method that is already provided by its super class. • Method overriding is used for runtime polymorphism • Rules: • method must have same name as in the parent class • method must have same parameter as in the parent class. • must be IS-A relationship (inheritance).
- 14. Page 13Classification: Restricted Example of Method Overriding class Vehicle{ void run(){System.out.println("Vehicle is running");} } class Bike2 extends Vehicle{ void run(){System.out.println("Bike is running safely");} public static void main(String args[]){ Bike2 obj = new Bike2(); obj.run(); }
- 15. Page 14Classification: Restricted Point to ponder.. Can we override static methods in Java? Why? Think… (This is one of the exercises for today)
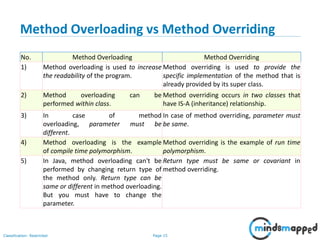
- 16. Page 15Classification: Restricted Method Overloading vs Method Overriding No. Method Overloading Method Overriding 1) Method overloading is used to increase the readability of the program. Method overriding is used to provide the specific implementation of the method that is already provided by its super class. 2) Method overloading can be performed within class. Method overriding occurs in two classes that have IS-A (inheritance) relationship. 3) In case of method overloading, parameter must be different. In case of method overriding, parameter must be same. 4) Method overloading is the example of compile time polymorphism. Method overriding is the example of run time polymorphism. 5) In Java, method overloading can't be performed by changing return type of the method only. Return type can be same or different in method overloading. But you must have to change the parameter. Return type must be same or covariant in method overriding.
- 17. Page 16Classification: Restricted super keyword in Java • The super keyword in Java is a reference variable that is used to refer immediate parent class object. • Usage of super Keyword osuper is used to refer immediate parent class instance variable. osuper() is used to invoke immediate parent class constructor. osuper is used to invoke immediate parent class method.
- 18. Page 17Classification: Restricted super used to refer immediate parent class instance variable class Vehicle{ int speed=50; } class Bike3 extends Vehicle{ int speed=100; void display(){ System.out.println(speed);//will print speed of Bike System.out.println(super.speed);//will print speed of Vehicle } public static void main(String args[]){ Bike3 b=new Bike3(); b.display(); } }
- 19. Page 18Classification: Restricted super is used to invoke parent class constructor class Vehicle{ Vehicle(){System.out.println("Vehicle is created");} } class Bike5 extends Vehicle{ Bike5(){ super();//will invoke parent class constructor System.out.println("Bike is created"); } public static void main(String args[]){ Bike5 b=new Bike5(); } }
- 20. Page 19Classification: Restricted super can be used to invoke parent class method class Person{ void message(){System.out.println("welcome");} } class Student16 extends Person{ void message(){System.out.println("welcome to java");} void display(){ message();//will invoke current class message() method super.message();//will invoke parent class message() method } public static void main(String args[]){ Student16 s=new Student16(); s.display(); } }
- 21. Page 20Classification: Restricted super not required here class Person{ void message(){System.out.println("welcome");} } class Student17 extends Person{ void display(){ message();//will invoke parent class message() method } public static void main(String args[]){ Student17 s=new Student17(); s.display(); } }
- 22. Java & JEE Training final keyword
- 23. Page 22Classification: Restricted final keyword in Java • final keyword applied to • Variable: stops value change • Methods: stops overriding • Class: stops inheritance
- 24. Page 23Classification: Restricted final variable final variable once assigned a value can never be changed. class Bike9{ final int speedlimit=90;//final variable void run(){ speedlimit=400; //compile-time error } public static void main(String args[]){ Bike9 obj=new Bike9(); obj.run(); } }//end of class
- 25. Page 24Classification: Restricted final method – cannot override class Bike{ final void run(){System.out.println("running");} } class Honda extends Bike{ void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");} //compile-time error public static void main(String args[]){ Honda honda = new Honda(); honda.run(); } }
- 26. Page 25Classification: Restricted final class – cannot extend final class Bike{} class Honda1 extends Bike{ //compile-time error void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");} public static void main(String args[]){ Honda1 honda= new Honda(); honda.run(); } }
- 27. Page 26Classification: Restricted Blank final variables must be initialized only in constructor class Bike10{ final int speedlimit; // blank final variable Bike10(){ speedlimit=70; // initialized in constructor System.out.println(speedlimit); } public static void main(String args[]){ new Bike10(); } }
- 28. Page 27Classification: Restricted final parameter example class Bike11{ int cube(final int n){ n=n+2; //can't be changed as n is final n*n*n; } public static void main(String args[]){ Bike11 b=new Bike11(); b.cube(5); } }
- 29. Page 28Classification: Restricted Point to ponder…Can constructors be declared final? Think… (Exercise for today)
- 30. Page 29Classification: Restricted Java Runtime Polymorphism – Example of Upcasting class Animal{ void eat(){System.out.println("eating");} } class Dog extends Animal{ void eat(){System.out.println("eating fruits");} } class BabyDog extends Dog{ void eat(){System.out.println("drinking milk");} public static void main(String args[]){ Animal a1,a2,a3; a1=new Animal(); a2=new Dog(); a3=new BabyDog(); a1.eat(); a2.eat(); a3.eat(); } }
- 31. Page 30Classification: Restricted Static and dynamic binding Static Binding: Type of object determined at Compile time. class Dog{ private void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");} public static void main(String args[]){ Dog d1=new Dog(); d1.eat(); } } Dynamic Binding: Type of object determined at run time class Animal{ void eat(){System.out.println("animal is eating...");} } class Dog extends Animal{ void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");} public static void main(String args[]){ Animal a=new Dog(); a.eat(); } }
- 32. Page 31Classification: Restricted instanceof operator • used to test whether the object is an instance of the specified type (class or subclass or interface). class Simple1{ public static void main(String args[]){ Simple1 s=new Simple1(); System.out.println(s instanceof Simple1);//true } } class Animal{} class Dog1 extends Animal{//Dog inherits Animal public static void main(String args[]){ Dog1 d=new Dog1(); System.out.println(d instanceof Animal);//true } }
- 33. Page 32Classification: Restricted class Dog2{ public static void main(String args[]){ Dog2 d=null; System.out.println(d instanceof Dog2);//false } } instanceof operator
- 34. Page 33Classification: Restricted Downcasting Dog d=new Animal();//Compilation error Dog d=(Dog)new Animal(); //Compiles successfully but ClassCastException could be thrown at runtime
- 35. Page 34Classification: Restricted Topics to be covered in next session • Overview of OOP continued… • Abstraction – using Abstract Classes and Interfaces.





![Page 7Classification: Restricted
Why multiple inheritance not supported in Java?
class A{
void msg(){System.out.println("Hello");}
}
class B{
void msg(){System.out.println("Welcome");}
}
class C extends A,B{//suppose if it were
public static void main(String args[]){
C obj=new C();
obj.msg();//Now which msg() method would be invoked? Compile-time error
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-8-320.jpg)

![Page 9Classification: Restricted
Aggregation in Java
class Operation{
int square(int n){
return n*n;
}
}
class Circle{
Operation op;//aggregation
double pi=3.14;
double area(int radius){
op=new Operation();
int rsquare=op.square(radius);//code reusability (i.e. delegates the method call).
return pi*rsquare;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Circle c=new Circle();
double result=c.area(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-10-320.jpg)



![Page 13Classification: Restricted
Example of Method Overriding
class Vehicle{
void run(){System.out.println("Vehicle is running");}
}
class Bike2 extends Vehicle{
void run(){System.out.println("Bike is running safely");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike2 obj = new Bike2();
obj.run();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-14-320.jpg)


![Page 17Classification: Restricted
super used to refer immediate parent class instance variable
class Vehicle{
int speed=50;
}
class Bike3 extends Vehicle{
int speed=100;
void display(){
System.out.println(speed);//will print speed of Bike
System.out.println(super.speed);//will print speed of Vehicle
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike3 b=new Bike3();
b.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-18-320.jpg)
![Page 18Classification: Restricted
super is used to invoke parent class constructor
class Vehicle{
Vehicle(){System.out.println("Vehicle is created");}
}
class Bike5 extends Vehicle{
Bike5(){
super();//will invoke parent class constructor
System.out.println("Bike is created");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike5 b=new Bike5();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-19-320.jpg)
![Page 19Classification: Restricted
super can be used to invoke parent class method
class Person{
void message(){System.out.println("welcome");}
}
class Student16 extends Person{
void message(){System.out.println("welcome to java");}
void display(){
message();//will invoke current class message() method
super.message();//will invoke parent class message() method
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student16 s=new Student16();
s.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-20-320.jpg)
![Page 20Classification: Restricted
super not required here
class Person{
void message(){System.out.println("welcome");}
}
class Student17 extends Person{
void display(){
message();//will invoke parent class message() method
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student17 s=new Student17();
s.display();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-21-320.jpg)


![Page 23Classification: Restricted
final variable
final variable once assigned a value can never be changed.
class Bike9{
final int speedlimit=90;//final variable
void run(){
speedlimit=400; //compile-time error
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike9 obj=new Bike9();
obj.run();
}
}//end of class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-24-320.jpg)
![Page 24Classification: Restricted
final method – cannot override
class Bike{
final void run(){System.out.println("running");}
}
class Honda extends Bike{
void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");}
//compile-time error
public static void main(String args[]){
Honda honda = new Honda();
honda.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-25-320.jpg)
![Page 25Classification: Restricted
final class – cannot extend
final class Bike{}
class Honda1 extends Bike{ //compile-time error
void run(){System.out.println("running safely with 100kmph");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Honda1 honda= new Honda();
honda.run();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-26-320.jpg)
![Page 26Classification: Restricted
Blank final variables must be initialized only in constructor
class Bike10{
final int speedlimit; // blank final variable
Bike10(){
speedlimit=70; // initialized in constructor
System.out.println(speedlimit);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
new Bike10();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-27-320.jpg)
![Page 27Classification: Restricted
final parameter example
class Bike11{
int cube(final int n){
n=n+2; //can't be changed as n is final
n*n*n;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Bike11 b=new Bike11();
b.cube(5);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-28-320.jpg)

![Page 29Classification: Restricted
Java Runtime Polymorphism – Example of Upcasting
class Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("eating");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("eating fruits");}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog{
void eat(){System.out.println("drinking milk");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a1,a2,a3;
a1=new Animal();
a2=new Dog();
a3=new BabyDog();
a1.eat();
a2.eat();
a3.eat();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-30-320.jpg)
![Page 30Classification: Restricted
Static and dynamic binding
Static Binding: Type of object determined at Compile time.
class Dog{
private void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog d1=new Dog();
d1.eat();
}
}
Dynamic Binding: Type of object determined at run time
class Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("animal is eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void eat(){System.out.println("dog is eating...");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Animal a=new Dog();
a.eat();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-31-320.jpg)
![Page 31Classification: Restricted
instanceof operator
• used to test whether the object is an instance of the specified type (class or subclass or interface).
class Simple1{
public static void main(String args[]){
Simple1 s=new Simple1();
System.out.println(s instanceof Simple1);//true
}
}
class Animal{}
class Dog1 extends Animal{//Dog inherits Animal
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog1 d=new Dog1();
System.out.println(d instanceof Animal);//true
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-32-320.jpg)
![Page 32Classification: Restricted
class Dog2{
public static void main(String args[]){
Dog2 d=null;
System.out.println(d instanceof Dog2);//false
}
}
instanceof operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session09-oopwithjava-part3-slides-180607171629/85/Session-09-OOP-with-Java-Part-3-33-320.jpg)


