TYPES OF JOINTS
- 1. TYPES OF JOINTS By 14-ARID-2022 PMAS 1 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 2. Joints “An articulation or joints is formed by the union of two or more bones or cartilages by other tissue.” There are three subdivision of joints Synarthroses Diarthroses Amphiarthrosis 2 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 3. SYNARTHROSES In this group the segments are united by fibrous tissue or cartilage,or amixture of the two in such a manner as practically to perclude movement;hence they are often termed fixed or immovable joints. The cheif classes in this group of joints are as follows: 1)Suture “ These are the joints of skull in which the adjacent bones are colsely united by fibrous tissues_the suture ligaments.” suture is further divided into followings a) Suture serrata b) Suture squamosa c) Suture harmonia 3 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 4. a) Suture serrata “In this suture egdes of the bones have irregular interlocking margins”e.g the frontal suture.e.g the frontal suture. b) Suture squamosa “In this suture edges are beveled and overlap to for suture squamosa.”e.g the parieto_temporal suture. c) Suture harmonia “In this suture edges are plane or slightly roughened,the term suture harmonia.”e.g the nasal suture. 4 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 5. 2)Syndesmosis “ In these the uniting medium is white fibrous or elastic tissues or mixture.”e.g the union of shafts of the metacarpal bones and the attachments to each other of costal cartilages. 3)Synchondrosis “In these the two bones are united by cartilage”.e.g the joint b/w the basilar part of the occipital bone and the sphenoid bone. 4)Symphysis “This term is usually limited to a few median joints which connect the symmetrical parts of the skeleton.”e.g syphysis pelvis,symphysis mandibulae. 5 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 6. 5)Gomphosis “This term is some time applied to the implantation of the teeth in the alveoli.The gomphosis is not, properly considered a joint at all since the teeth are not parts of the skeleton. 6 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 7. DIARTHROSES “ These joints are characterized by the presence of a joint cavity with a synovial membrane in the joint capsule and by their mobility.They are often called moveable or true joints.” The following structures enter into their formation: a) The articular surfaces b) The articular cartilages c) The articular or joint capsule d) Ligaments e) Articular discs or menisci f) A marginal cartilage 7 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 8. a)The articular surfaces “These surfaces in most cases are smooth and vary much in form. They are formed of specially dense bone,which differs histologicaly from ordinary compact substance.The surface is intrupted by non-articular cavities known as synovial fossa. b)The articular cartilages “These are usually hyaline in type ,form a covering over the articular surfaces of the bones.They vary in thickness in different joints;they are thickest on those which are subjected to most pressure and friction. 8 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 9. c)The articular or joint capsule(capsula articularis) In its simplest form a,tube ,the ends of which are attached around the articulating surfaces.It consist of two layers1)fibrous layer,2)Synovial layer 1)Fibrous layer “It is some times term the capsular ligament,is attached either close to the margins of the articular surfaces at a variable distancefrom them.” 2)Synovial layer “this layer lines the joint cavity except where this is bounded by the articular cartilages;it stops at the margin of the latter” 9 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 10. 4)Ligaments “These are strong bands or membranes usually composed of white fibrous tissue ,which bind the bones together.”There are two types of ligaments 1)Collateral ligaments(ligamenta collateralia) “Those which are situated on the sides of a joint is termed as collateral ligaments” 2)Interosseous ligament “Those which connect directly opposed surfaces of bones are termed as Interosseous ligaments. 10 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 11. 5)Articular Disc or menisci “The plates of fibro-cartilage are dense fibrous tissue placed b/w the articular cartilage and divide the joint cavity partially or completely into two compartments. They render certain surfaces congurent, allow greater range or variety of movement. 6)Marginal cartilage(labrun glenoidale) “It is a ring of fibro-cartilage which encircles the rim of an articular cavity.It enlarges the cavity and tends to prevent fracture of the margin. 11 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 12. MOVEMENTS The movements of a joint are determined chiefly by the form extent of the joint surfaces and the arrangement of ligaments.They are classified as follows: a) Gliding b) Angular movement c) Circumduction d) Rotation e) Adduction and abduction 12 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 13. Classification o This is based on the form of the join surfaces and the movements which occur.The following chief classes may be recognized: 1) Arthrodia or gliding joint 2) Ginglymus or hing joint 3) Trochoid joint or pivot joint 4) Enarthrosis or ball and socket joint 1)Arthrodia or gliding joint • In these the surfaces are pertically flat,admitting of gliding movement.e.g carpo-metacarpal joints. 2)Ginglymus or hing joint • In this class joint surface consist usually of two condyles,or of a segment of a cylinder or cone,which are received by coresponding cavities.e.g atlanto-occipital and elbow joint. 13 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
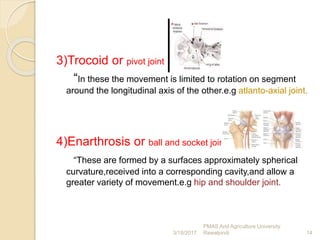
- 14. 3)Trocoid or pivot joint “In these the movement is limited to rotation on segment around the longitudinal axis of the other.e.g atlanto-axial joint. 4)Enarthrosis or ball and socket joint “These are formed by a surfaces approximately spherical curvature,received into a corresponding cavity,and allow a greater variety of movement.e.g hip and shoulder joint. 14 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 15. Amphiarthroses • These joints,as the name indicate share some characters with both preceding group. • In them segments are directly unite by ligaments also. • The amount and kind of movement is determined by the shape of joint surfaces and the amount and pliability uniting medium. • These joints are nearly all medial in position and are illustrated by the joints b/w the bodies of the vertebrae. • There is type no joint cavity, but 15 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017
- 16. Thank You 16 PMAS Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi3/18/2017