S01.W01 - Introduction to to computer (how comps work, types of comps)
- 1. What is a Computer?
- 2. What is a Computer? • A computer is an electronic machine that makes mathematical calculations and logical comparisons quickly and without any mistakes. Computers take data, process them according to a list of instructions, and show or store the results of the processing. They can store the results forever.
- 3. What is a Computer? • Computers consist of two parts, hardware and software. Hardware is the physical parts of the computer. • Software is the programs in the computer. Software tells the hardware what to do. The relation between hardware and software is like the relation between our body and our mind.
- 4. How do computers work? Booting Up Your Computer When you switch on your computer, a small initiating program BIOS (Basic Input/Output System or Built In Operating System) is loaded into memory (RAM). The BIOS software is written in a ROM on the mainboard. The primary function of the BIOS is to identify and initialize system hardware devices and to copy (load) the operating system software from permanent storage to RAM (Random Access Memory). This process is known as booting, or booting up, which is short for bootstrapping.
- 5. How do computers work? Booting Up Your Computer • Computers can store information in two different ways: in permanent storage (for example, on a disk or a CD) and in temporary storage, also called the computer’s memory or RAM. Data in temporary storage only last as long as the computer is switched on.
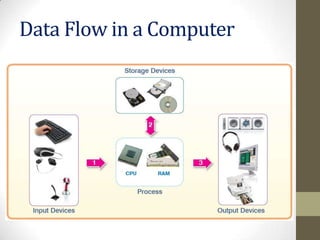
- 6. How do computers work? Data Flow in a Computer • When you switch on a computer, first, a special software called the operating system is copied (loaded) from permanent storage to the RAM. The computer gets data from an input device, such as a keyboard, mouse, hard disk, or scanner, and makes all the calculations and the comparisons in the central processing unit (CPU).
- 7. How do computers work? Data Flow in a Computer • The CPU is like the computer’s brain. It uses the RAM to maintain the data. When the CPU has processed the data, it sends the results to an output device, such as a monitor or printer, or saves them in a permanent storage device, such as a hard disk.
- 8. Data Flow in a Computer
- 10. TYPES OF COMPUTERS • Mainframe Computers A mainframe computer is a big, powerful, and expensive computer. Many people can use the power of a mainframe computer at the same time, using either a Personal Computer (PC) or a Dumb Terminal. A PC performs a lot of processing itself. A dumb terminal uses the mainframe computer to do all the processing and just shows the results on a screen. Large organizations, for example, banks and insurance companies, use mainframe computers.
- 11. TYPES OF COMPUTERS • Minicomputers Like mainframe computers, minicomputers are multi-user computers. They are very powerful and expensive. Mainframes and minicomputers are used for very similar purposes. Middle-sized companies use minicomputers. As microcomputers developed in 1970s and 1980s, minicomputers filled the mid- range area between low powered single- user microcomputers and high capacity multi-user mainframes. Since microcomputers have become more powerful and the PC networks emerged in 1980s and 1990s, the minicomputers role has been filled by microcomputers.
- 12. TYPES OF COMPUTERS • Supercomputers A supercomputer is a mainframe computer that is incredibly powerful and has a very large capacity for processing data. Supercomputers are often used by the military services. They are also used for such research as weather forecasting, in which a huge amount of data must be processed rapidly.
- 13. TYPES OF COMPUTERS • Microcomputers Microcomputers are usually used only by one person at a time. An IBM PC and Apple Macintosh are two kinds of microcomputers. There are desktop, laptop, palmtop, tabletop, pocket, tablet, and netbook models of microcomputers.
- 14. Questions