Zener diode
- 1. ZENER DIODE
- 2. INTRODUCTION A Zener diodeallows current to flow from its anode to its cathode like a normal semiconductor diode, but it also permits current to flow in the reverse direction when its "Zener voltage" is reached.
- 3. The device was named after Clarence Melvin Zener, who discovered the Zener effect. Zener reverse breakdown is due to electron quantum tunnelling caused by a high strength electric field. However, many diodes described as "Zener" diodes rely instead on avalanche breakdown.
- 4. OPERATION Current-voltage characteristic of a Zener diode with a breakdown voltage of 17 volts. Notice the change of voltage scale between the forward biased (positive) direction and the reverse biased (negative) direction.
- 5. conventional solid-state diode allows significant current if it is reverse-biased above its reverse breakdown voltage. When the reverse bias breakdown voltage is exceeded, a conventional diode is subject to high current due to avalanche breakdown. Unless this current is limited by circuitry, the diode may be permanently damaged due to overheating.
- 6. Another mechanism that produces a similar effect is the avalanche effect as in the avalanche diode. The two types of diode are in fact constructed the same way and both effects are present in diodes of this type. In silicon diodes up to about 5.6 volts, the Zener effect is the predominant effect and shows a marked negative temperature coefficient. Above 5.6 volts, the avalanche effect becomes predominant and exhibits a positive temperature coefficient.
- 7. Modern manufacturing techniques have produced devices with voltages lower than 5.6 V with negligible temperature coefficients, but as higher-voltage devices are encountered, the temperature coefficient rises dramatically. A 75 V diode has 10 times the coefficient of a 12 V diode. Zener and avalanche diodes, regardless of breakdown voltage, are usually marketed under the umbrella term of "Zener diode".
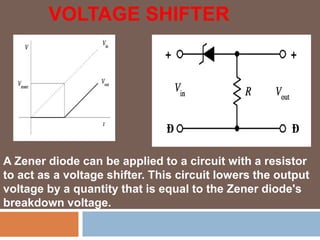
- 9. VOLTAGE SHIFTER A Zener diode can be applied to a circuit with a resistor to act as a voltage shifter. This circuit lowers the output voltage by a quantity that is equal to the Zener diode's breakdown voltage.
- 10. REGULATOR A Zener diode can be applied in a voltage regulator circuit to regulate the voltage applied to a load, such as in a linear regulator.
- 11. CONSTRUCTION The Zener diode's operation depends on the heavy doping of its p-n junction. The depletion region formed in the diode is very thin (<1 µm) and the electric field is consequently very high (about 500 kV/m) even for a small reverse bias voltage of about 5 V, allowing electrons to tunnel from the valence band of the p-type material to the conduction band of the n-type material.
- 12. SURFACE ZENERS The emitter-base junction of a bipolar NPN transistor behaves as a Zener diode, with breakdown voltage at about 6.8 V for common bipolar processes and about 10 V for lightly doped base regions in BiCMOS processes. Older processes with poor control of doping characteristics had the variation of Zener voltage up to ±1 V, newer processes using ion implantation can achieve no more than ±0.25 V. The NPN transistor structure can be employed as a surface Zener diode, with collector and emitter connected together as its cathode and base region as anode.
- 13. A subsurface Zener diode, also called 'buried Zener', is a device similar to the Surface Zener, but with the avalanche region located deeper in the structure, typically several micrometers below the oxide. The hot carriers then lose energy by collisions with the semiconductor lattice before reaching the oxide layer and cannot be trapped there. The Zener walkout phenomenon therefore does not occur here, and the buried Zeners have voltage constant over their entire lifetime. Most buried ZeneA subsurface Zener diode, also called 'buried Zener', is a device similar to the Surface Zener, but with the avalanche region located deeper in the structure, typically several micrometers below the oxide. The hot carriers then lose energy by collisions with the semiconductor lattice before reaching the oxide layer and cannot be trapped there. The Zener walkout phenomenon therefore does not occur here, and the buried Zeners have voltage constant over their entire lifetime. Most buried Zeners have breakdown voltage of 5–7 volts. Several different junction structures are used.rs have breakdown voltage of 5–7 volts.
- 14. USES Zener diodes are widely used as voltage references and as shunt regulators to regulate the voltage across small circuits. When connected in parallel with a variable voltage source so that it is reverse biased, a Zener diode conducts when the voltage reaches the diode's reverse breakdown voltage.
- 17. THANK YOU