Lec 08 - DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 1. DESIGN PROCEDURE D.R.V.L.B Thambawita October 29, 2017 D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE https://sites.google.com/view/vajira-thambawita/leaning-materials/slides
- 2. DESIGN PROCEDURE Design procedures or methodologies specify hardware that will implement a desired behavior. The design effort for small circuits may be manual, but industry relies on automated synthesis tools for designing massive integrated circuits. The design of a clocked sequential circuit starts from a set of specifications and culminates in a logic diagram or a list of Boolean functions from which the logic diagram can be obtained. In contrast to a combinational circuit, which is fully specified by a truth table, a sequential circuit requires a state table for its specification. The first step in the design of sequential circuits is to obtain a state table or an equivalent representation, such as a state diagram. D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 3. DESIGN PROCEDURE 1 From the word description and specifications of the desired operation, derive a state diagram for the circuit. 2 Reduce the number of states if necessary. 3 Assign binary values to the states. 4 Obtain the binary-coded state table. 5 Choose the type of flip-flops to be used. 6 Derive the simplified flip-flop input equations and output equations. 7 Draw the logic diagram. D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 4. DESIGN PROCEDURE: Example Suppose we wish to design a circuit that detects a sequence of three or more consecutive 1’s in a string of bits coming through an input line (the input is a serial bit stream). D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 5. DESIGN PROCEDURE: Example We need to assign binary codes to the states and list the state table. We choose two D flip-flops to represent the four states, and we label their outputs A and B . There is one input x and one output y. D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 6. DESIGN PROCEDURE: Example The characteristic equation of the D flip-flop is Q(t +1) = DQ Which means that the next-state values in the state table specify the D input condition for the flip-flop. The flip-flop input equations can be obtained directly from the next-state columns of A and B and expressed in sum-of-minterms form as A(t + 1) = DA(A, B, x) = (3, 5, 7) B(t + 1) = DB(A, B, x) = (1, 5, 7) y(A, B, x) = (6, 7) D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 7. DESIGN PROCEDURE: Example The Boolean equations are simplified by means of the maps plotted in the following figure. DA = Ax + Bx DB = Ax + B x y = AB The advantage of designing withD flip-flops is that the Boolean equations describing the inputs to the flip-flops can be obtained directly from the state table. D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 8. DESIGN PROCEDURE: Example Figure: Moore type circuit D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 9. Excitation Tables When D -type flip-flops are employed, the input equations are obtained directly from the next state. This is not the case for the JK and T types of flip-flops. It is necessary to derive a functional relationship between the state table and the input equations. The flip-flop characteristic tables are useful for analyzing sequential circuits and for defining the operation of the flip-flops. During the design process, we usually know the transition from the present state to the next state. Wish to find the flip-flop input conditions that will cause the required transition. we need a table that lists the required inputs for a given change of state. Such a table is called an excitation table . D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 10. Excitation Tables Do you remember? Figure: Characteristic Tables D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 11. Excitation Tables Figure: Flip-Flop Excitation Tables D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 12. Synthesis Using JK Flip-Flops Example: Figure: State Table and JK Flip-Flop Inputs D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 13. Example:JK flip-flop Figure: Maps for J and K input equations D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 14. Example:JK flip-flop Figure: Logic diagram for sequential circuit with JK flip-flops D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
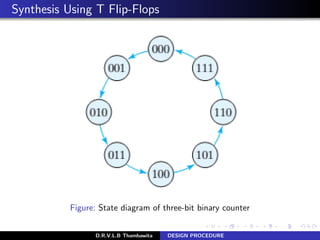
- 15. Synthesis Using T Flip-Flops Figure: State diagram of three-bit binary counter D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 16. Synthesis Using T Flip-Flops Figure: State Table for Three-Bit Counter D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
- 17. Synthesis Using T Flip-Flops Figure: Maps for three-bit binary counter D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE
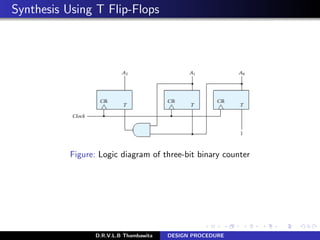
- 18. Synthesis Using T Flip-Flops Figure: Logic diagram of three-bit binary counter D.R.V.L.B Thambawita DESIGN PROCEDURE