Algorithm defination, design & Implementation
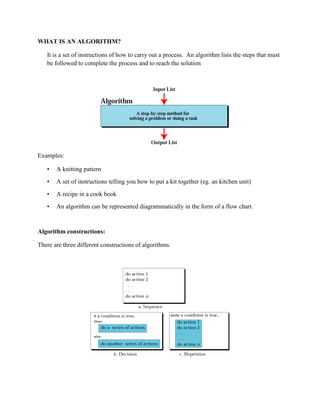
- 1. WHAT IS AN ALGORITHM? It is a set of instructions of how to carry out a process. An algorithm lists the steps that must be followed to complete the process and to reach the solution Examples: • A knitting pattern • A set of instructions telling you how to put a kit together (eg. an kitchen unit) • A recipe in a cook book • An algorithm can be represented diagrammatically in the form of a flow chart. Algorithm constructions: There are three different constructions of algorithms.
- 2. Properties of Algorithms: • An algorithm is an exact specification of how to solve a computational problem • An algorithm must specify every step completely, so a computer can implement it without any further “understanding” • An algorithm must work for all possible inputs of the problem. • Algorithms must be: Correct: For each input produce an appropriate output Efficient: run as quickly as possible, and use as little memory as possible – more about this later • There can be many different algorithms for each computational problem. Algorithms Phases: A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: 1. Problem solving phase (Designing) • produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution of problem • this sequence of steps is called an algorithm 2. Implementation phase • implement the program in some programming language Problem solving phase (Designing) : Steps in Problem Solving • First produce a general algorithm (one can use pseudocode) • Refine the algorithm successively to get step by step detailed algorithm that is very close to a computer language.
- 3. • Pseudocode is an artificial and informal language that helps programmers develop algorithms. Pseudocode is very similar to everyday English. Pseudocode Example: Example 1: Write an algorithm to determine a student’s final grade and indicate whether it is passing or failing. The final grade is calculated as the average of four marks. Pseudocode: Input a set of 4 marks Calculate their average by summing and dividing by 4 if average is below 50 Print “FAIL” else Print “PASS” The Flowchart: • (Dictionary) A schematic representation of a sequence of operations, as in a manufacturing process or computer program. • (Technical) A graphical representation of the sequence of operations in an information system or program. Information system flowcharts show how data flows from source documents through the computer to final distribution to users. Program flowcharts show the sequence of instructions in a single program or subroutine. Different symbols are used to draw each type of flowchart. • shows logic of an algorithm • emphasizes individual steps and their interconnections • e.g. control flow from one action to the next
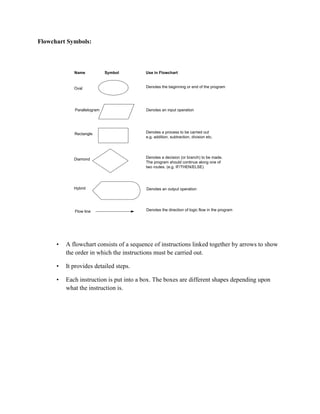
- 4. Flowchart Symbols: • A flowchart consists of a sequence of instructions linked together by arrows to show the order in which the instructions must be carried out. • It provides detailed steps. • Each instruction is put into a box. The boxes are different shapes depending upon what the instruction is. Oval Parallelogram Rectangle Diamond Hybrid Name Symbol Use in Flowchart Denotes the beginning or end of the program Denotes an input operation Denotes an output operation Denotes a decision (or branch) to be made. The program should continue along one of two routes. (e.g. IF/THEN/ELSE) Denotes a process to be carried out e.g. addition, subtraction, division etc. Flow line Denotes the direction of logic flow in the program
- 5. Example 1: MAKING A CUP OF TEA! Pseudocode: 1. Take tea bag out of cup 2. Boil the water 3. Put tea bag in cup 4. Add milk? 5. Pour boiling water in cup 6. Fill kettle 7. Stir 8. Ready 9. Add sugar ? 10. Fetch cup Algorithm: 1. Fill kettle 2. Boil the water 3. Fetch cup 4. Put tea bag in cup 5. Pour boiling water in cup 6. Take tea bag out of cup 7. Add sugar ? 8. Stir 9. Add milk? 10. Stir 11. Ready
- 6. Example 2: Grade students to identify pass & fail. Algorithm: Step 1: Input M1,M2,M3,M4 Step 2: GRADE (M1+M2+M3+M4)/4 Step 3: if (GRADE <50) then Print “FAIL” else Print “PASS” endif Example 3 Write an algorithm and draw a flowchart that will read the two sides of a rectangle and calculate its area. Pseudocode 1. Input the width (W) and Length (L) of a rectangle 2. Calculate the area (A) by multiplying L with W 3. Print A Algorithm Step 1: Input W,L Step 2: A L x W Step 3: Print A
- 7. Pseudocode for three constructs: Flowcharts for three constructs